Cell cycle entry triggers a switch between two modes of Cdc42 activation during yeast polarization
Figures
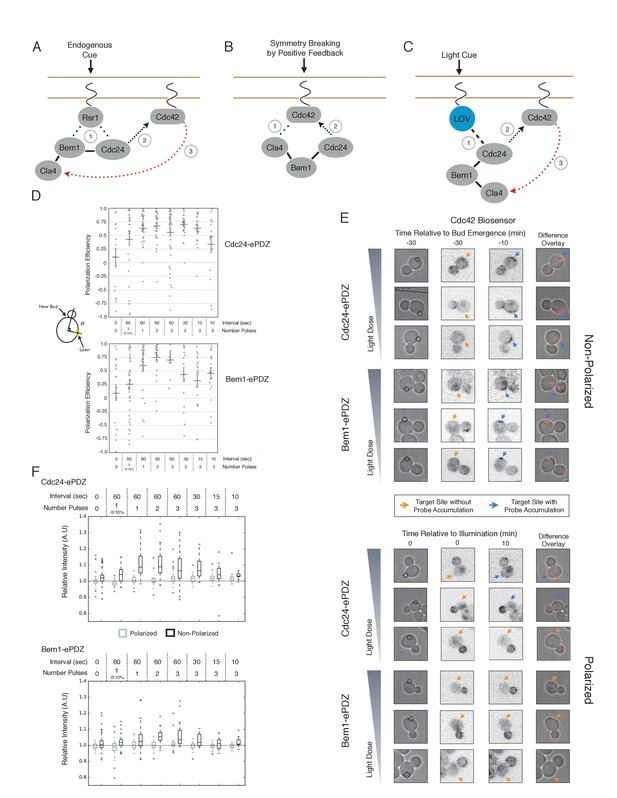
Cdc24 recruitment can induce Cdc42 activation in polarized and unpolarized cells.
(A) The endogenous cue is mediated by a system involving Rsr1 to yield patterned budding. Rsr1 directly interacts with Bem1 and Cdc24 to recruit and activate Cdc42 at an adjacent bud position. Rsr1 recruits Bem1 and/or Cdc24 (1) to activate Cdc42 (2) adjacent to the previous bud neck. Cdc42 undergoes positive feedback (3) by interacting with Cla4 to promote its own accumulation. (B) In the absence of Rsr1, cells undergo a symmetry breaking event mediated by positive feedback. The symmetry breaking event may involve a stochastic accumulation of Cdc42-GTP at a unique location that then recruits the Cla4-Bem1-Cdc24 complex (1). Cdc24 activates additional molecules of Cdc42 (2) to promote positive feedback (3). (C) Light-induced symmetry breaking by recruiting the GEF Cdc24 to activate Cdc42 at a prescribed position and induce positive feedback. Localized photo-activation of LOVpep recruits Cdc24-ePDZb (1) to activate Cdc42 (2). Activated Cdc42 interacts with Cla4 to induce positive feedback. (D) Polarization efficiency of a population of cells where each point represents an individual cell. The angle Θ is defined by the angle between the site of bud emergence and the laser position. Data are averages of all cells across multiple experiments (n experiments >= 2, N total cells > 15 for each group). Average and ± SEM is indicated. Statistical analysis in Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Strains used: WYK8440 and WYK8301. (E) Representative phase and inverted fluorescent images depicting the activation of Cdc42 in response to either Cdc24 or Bem1 recruitment in polarized or non-polarized cells. Difference overlay images place the subtraction of the two fluorescent images overlaid onto the phase contrast image. An increase in fluorescent signal is depicted by red pseudo-coloring on the overlay. Cells were treated to increasing doses of light. Shown from bottom to top, representative images for each group:1 pulse/60 s, 3 pulses/30 s, and 3 pulses/15 s. Each image is 16.2 µm x 16.2 µm. Strains used: WYK8440 and WYK8301. (F) Box-and-Whisker plots depicting the relative change in mean fluorescence intensity of the Cdc42 biosensor at targeted regions. The relative intensity of polarized cells is the mean of the intensity at 10 min post initial illumination normalized to a control site (typically 180° from target) on the same time. The relative intensity for non-polarized cells compares accumulation of the biosensor 10 min before bud emergence normalized to a control site at the same time. Data is combined across multiple experiments (n experiments >= 2, N total cells > 15 for each group). Statistical analysis in Figure 1—figure supplement 5. Strains used: WYK8440 and WYK8301.
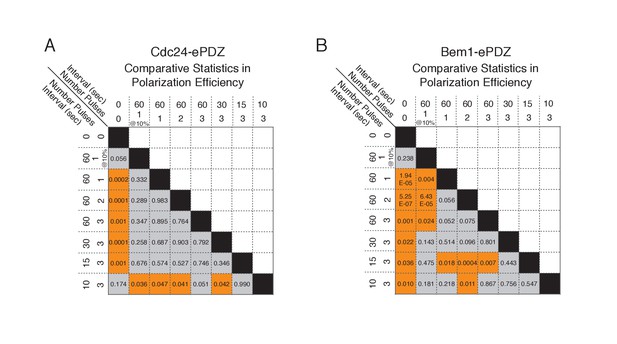
Statistical analysis of polarization efficiency as a function of light dose.
(A) Comparative statistical analysis of polarization efficiency in response to Cdc24-ePDZ recruitment at various light doses (Data shown in Figure 1D). Gray box indicates populations not statistically different at p=0.05, orange box denotes statistically significant at p<0.05, Mann-Whitney U test. (B) Comparative statistics for Polarization efficiency in response to Bem1 recruitment at various light doses as in (A).
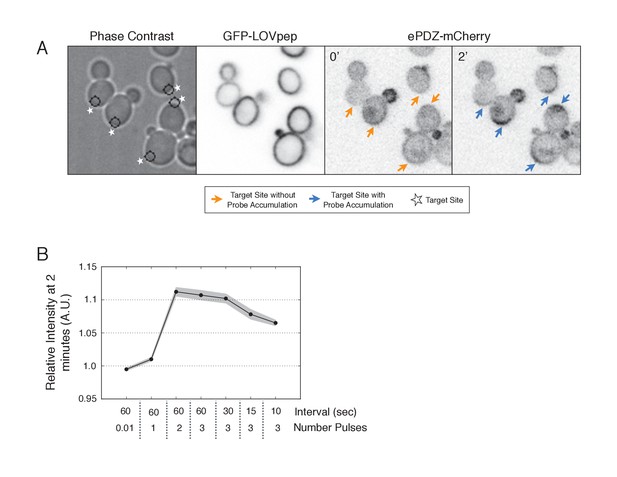
Recruitment of ePDZ-mCherry as a function of light dose.
(A) Phase contrast and fluorescence images of GFP-LOVpep and ePDZ-mCherry in response to two light pulses per 60 s. Panels on the right indicate ePDZ-mCherry distribution prior to photo-illumination (0’) and after 2 min of photo-illumination to the indicated positions (2’). Each image is 32.4 µm x 34.2 µm. Strain used: WYK8476. (B) The relative change in mean intensity of ePDZ-mCherry at the targeted region after 2 min of illumination relative to the intensity at time 0. Light gray indicates +/-SEM. Data is combined across multiple experiments (n experiments >= 5, N total cells > 75 for each group).
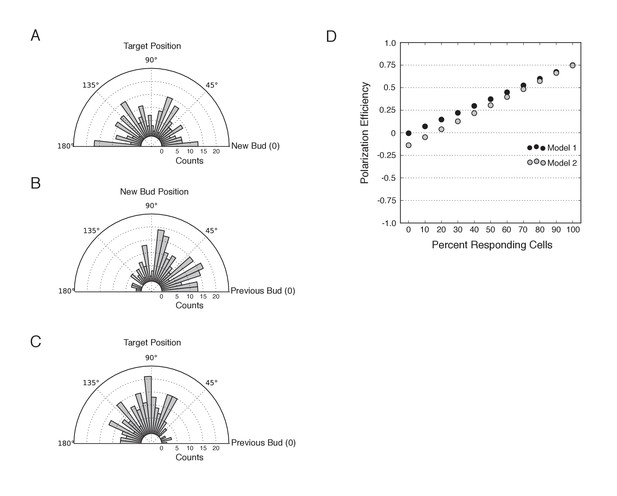
Bias in target position and new bud position relative to the previous bud.
(A) Distribution of targeting position relative to new bud formation in mock-illuminated cells (N cells > 120; aggregated from all mock illumination conditions). (B) Distribution of new bud site relative to the previous bud site in mock-illuminated cells (N cells > 120). (C) Distribution of target position relative to the previous bud site in mock-illuminated cells (N cells > 120). (D) Comparative polarization efficiency in two simulations. Model 1 assumes that there is no bias in target or new bud position. Model 2 approximates the biases the new bud and target positions as in B and C, respectively. Specifically, responding cells were simulated to respond with polarization efficiency = 0.75. In model 1, cells that do not respond were assumed to bud randomly in the range 46°−180°, with an average angle of 90°, corresponding to the angle expected if both targets and the new bud were random relative to the previous bud. In Model 2, cells that do not respond were assumed to bud randomly in the range 46°−180°, with an average angle of 102°, as an average difference of 102° approximates the aggregate bias resulting from the experimental bias in target position and the bias in bud site selection.
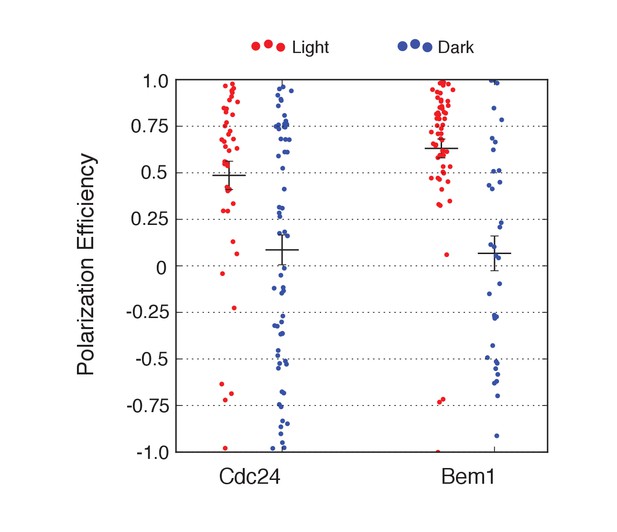
Local accumulation of either Cdc24 or Bem1 is sufficient to override the landmark-directed pathway.
Polarization efficiency of a population of cells heterozygous for Rsr1 in response to recruitment of Cdc24-ePDZ or Bem1-ePDZ. Each point represents an individual cell. Average and +/- SEM is indicated. Polarization in response to both Cdc24 and Bem1 recruitment are statistically significant to their dark state controls. Strains used: WYK8598 and WYK8599.
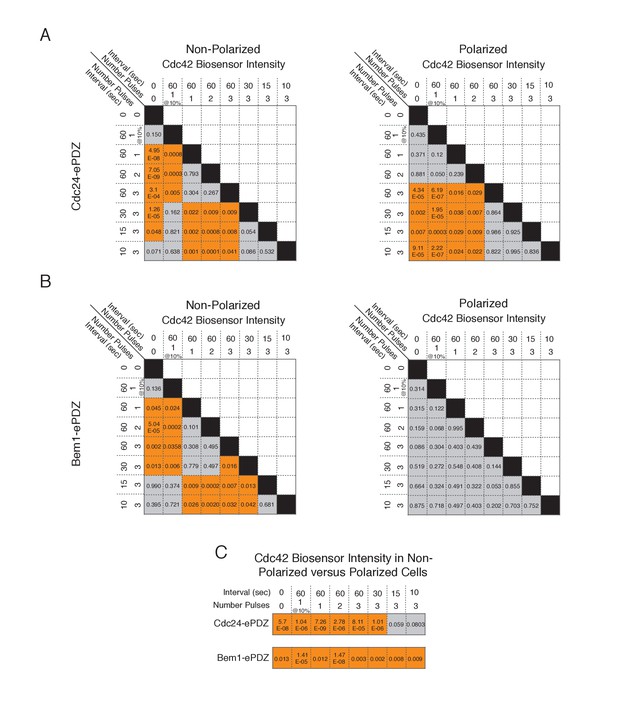
Statistical analysis of Cdc42 biosensor accumulation in polarized and non-polarized cells as a function of light dose.
(A) Statistical analysis for Cdc42 biosensor accumulation in response to Cdc24-ePDZ recruitment in polarized and non-polarized cells (data from Figure 1F). Gray box indicates populations not statistically different at p=0.05, orange box denotes statistically significant at p<0.05, Mann-Whitney U test. (B) Statistics for Cdc42 biosensor accumulation in response to Bem1 recruitment as in A. (C) Statistical comparison of Cdc42 biosensor accumulation in polarized vs. non-polarized cells at each light dose. Statistical analysis as in A and B.
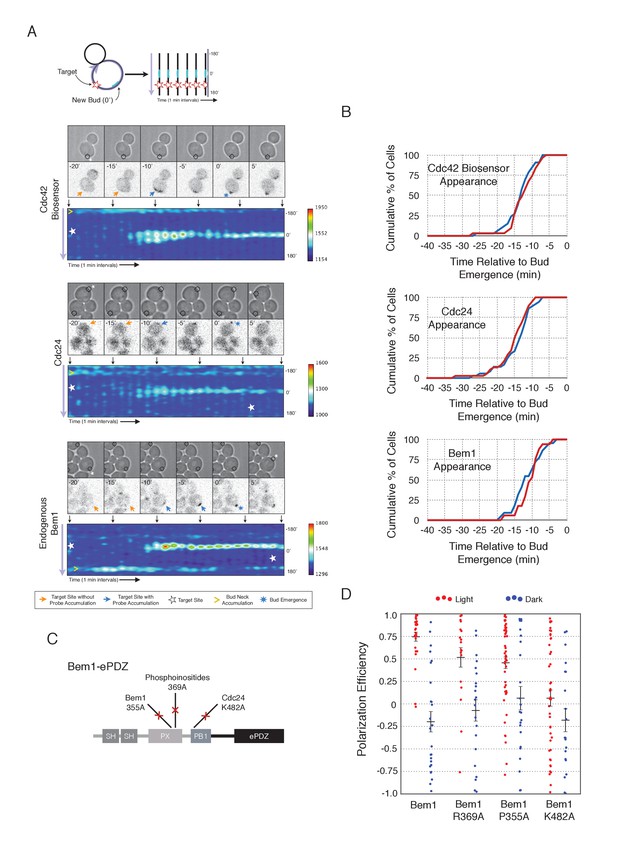
Local accumulation of Bem1 directs bud site positioning via positive feedback.
(A) Representative phase and fluorescence images and kymographs showing the position of the laser target and accumulation of the Cdc42 biosensor, Cdc24, and endogenous Bem1 (respectively). Each image is 16.2 µm x 16.2 µm. Kymographs are generated by iteratively linearizing the membrane at each time point (schematic). Bud emergence occurs at Y = 0° and at time = 0 min. Arrows between the kymograph and fluorescent images indicate equivalent time points. Strains used: WYK8308, WYK8318, and WYK8576. (B) Accumulation kinetics for each component in response to Bem1 recruitment. Red line is photo-activated cells, blue line is mock-illuminated cells. Bud emergence is time = 0. Data combined across multiple experiments (n experiments >= 2, N total cells > 20 for each condition). (C) Domain schematic of Bem1-ePDZ, annotated with mutation sites and interactions. (D) Polarization efficiency of a population of cells as in 1F. Red dots are single photo-activated cells. Blue dots are single mock-illuminated cells. Data is combined across multiple experiments (n experiments > 2, N total cells > 20 for each group). Error bars indicate S.E.M. Polarization efficiency of Bem1, Bem1 R369A, and Bem1 P355A in the light is statistically significant relative to Bem1 K482A light and dark, and their respective dark-state controls. Bem1 K482A was not statistically significant relative to its dark state control. p<0.05, Mann-Whitney U test. Strains used: WYK8308, WYK8434, WYK8435, and WYK8436.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26722.010
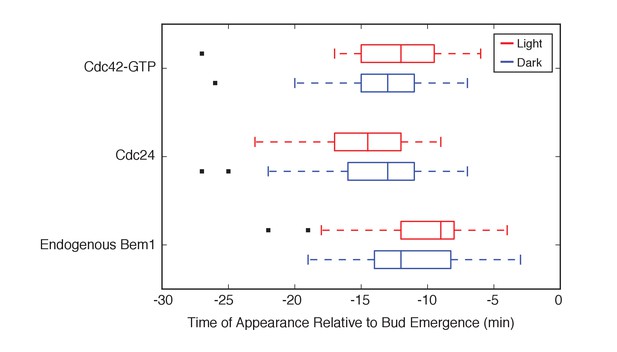
Photo-recruited Bem1 does not alter timing of accumulation of Cdc42-GTP, Cdc24 and Bem1.
Box-and-whisker plot of Cdc42-GTP and Cdc24 appearance time in response to Bem1 recruitment in photo-activated (red) or mock-illuminated (blue) cells. Outliers are depicted by black squares. Data are as in Figure 2B.
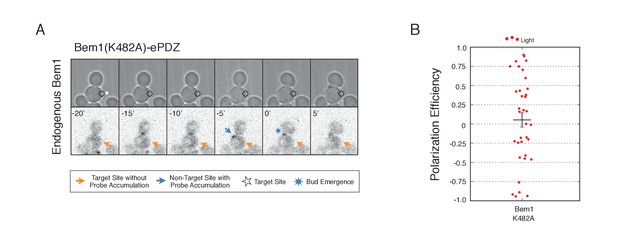
Recruitment of Cdc24-binding deficient Bem1 cannot induce accumulation of endogenous Bem1.
(A) Phase contrast and fluorescence images of Bem1-tdTomato accumulation in response to photo-recruitment of Bem1(K482A). Each image is 16.2 µm x 16.2 µm. Strain used: WYK8505. (B) Polarization efficiency of population of cells where each point represents an individual cell from the condition depicted in A. Data are averages of all cells across multiple experiments (n experiments >= 2, N total cells > 20 for each group). Average and ± SEM is indicated.
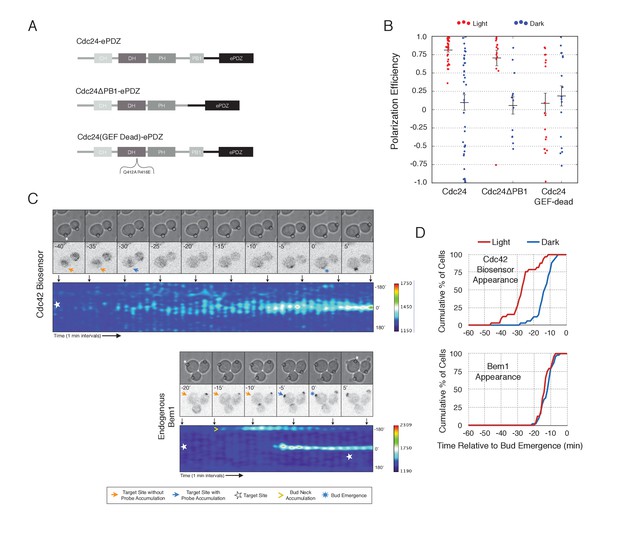
Light-mediated recruitment of Cdc24 directs bud site positioning.
(A) Domain schematic of Cdc24-ePDZ and variants thereof. (B) Polarization efficiency of photo-illuminated (red) or mock-illuminated (blue) cells. Data are averaged across multiple experiments (n experiments > = 2, N total cells > 15, for each group). Average and ± S.E.M. indicated. Polarization efficiency of Cdc24 and Cdc24ΔPB1 were statistically significant relative to Cdc24-GEF-dead light/dark, and statistically significant compared to their respective dark state controls. The difference between Cdc24 and Cdc24ΔPB1 were not statistically significant. The response to Cdc24-GEF dead was not statistically significant relative to its dark state control. p<0.05, Mann-Whitney U test. Strains used: WYK8440, WYK8437, and WYK8439. (C) Panels of representative phase and fluorescence images and kymographs showing the position of the laser target and accumulation of a Cdc42 biosensor or endogenous Bem1 in response to Cdc24 recruitment. Each image is 16.2 µm x 16.2 µm. Strains used: WYK8440 and WYK8301. (D) Accumulation kinetics for the Cdc42 biosensor or endogenous Bem1 in response to Cdc24 recruitment. Data are combined across multiple experiments (n experiments >= 2, N total cells > 15 for each condition).
-
Figure 3—source data 1
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26722.014
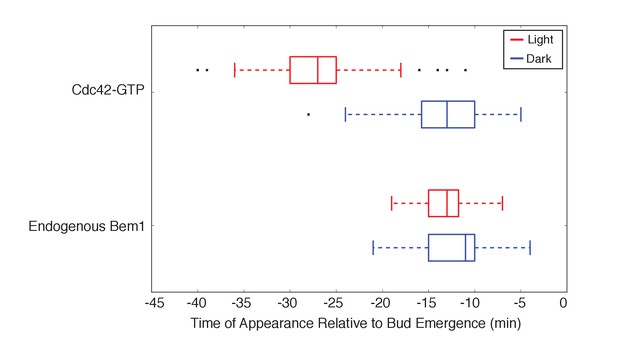
Light-induced recruitment of Cdc24 induce precocious Cdc42 activation, but does not alter Bem1 kinetics.
Box-and-whisker plot of Cdc42-GTP and Bem1 appearance in response to Cdc24-ePDZ in photo-activated (red) and mock-illuminated (blue) cells. Outliers are depicted by black squares. Bud emergence occurs at time = 0. Data are as in Figure 3D.
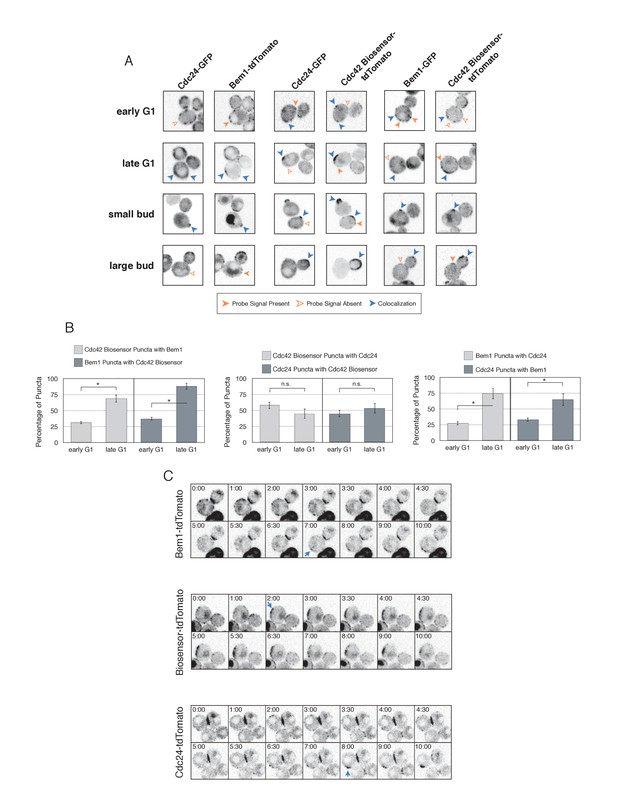
Cdc42-GTP, Cdc24, and Bem1 do not constitutively colocalize prior to polarity establishment.
(A) Inverted fluorescent images depicting the three pairwise combinations of Cdc42-GTP, Bem1, and Cdc24. All images are Z projections of 0.25 µm slices for the center 3 µm. Each image is 13.5 µm x 13.5 µm. Strains used: WYK8550, WYK8551, and WYK8552. (B) Percentage of colocalization amongst puncta in early G1 or late G1 cells. Plots are separated by pairs as in A. Data are averages of all cells across multiple experiments (n experiments = 2; N cells > 15 for each condition; N total cells > 100). Error bars S.E.M. n.s indicates populations not statistically different at p>=0.05, *p<0.05, Mann-Whitney U test. (C) Time-lapse images capturing polarization in non-perturbed cells expressing either the Cdc42 Biosensor-tdTomato, endogenous Bem1-tdTomato, or Cdc24-tdTomato. Images are single planes of the center of the cell. Blue arrows denote the time and position of polarity establishment. Time = 0 is the onset of imaging, and images were captured for ten minutes at either 60 s or 30 s intervals as denoted. Strains used: WYK8301, WYK8440, and WYK8575.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26722.018
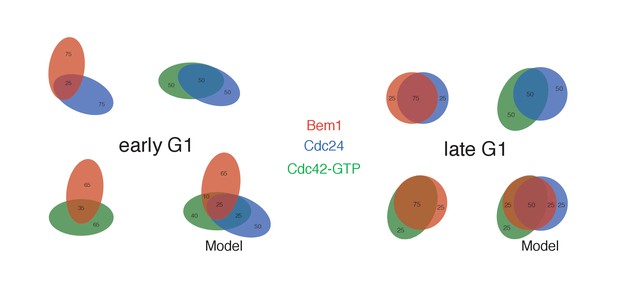
Pairwise analysis depicting the percent colocalization.
Venn diagrams for early G1 and late G1 depicting the extent of colocalization between each pair. The numbers within each shape refer to the number of puncta, with the total number of puncta within each shape equaling 100. The colocalization of all three components is presented in a model that is consistent with the pair-wise results. Related to results shown in Figure 4B.
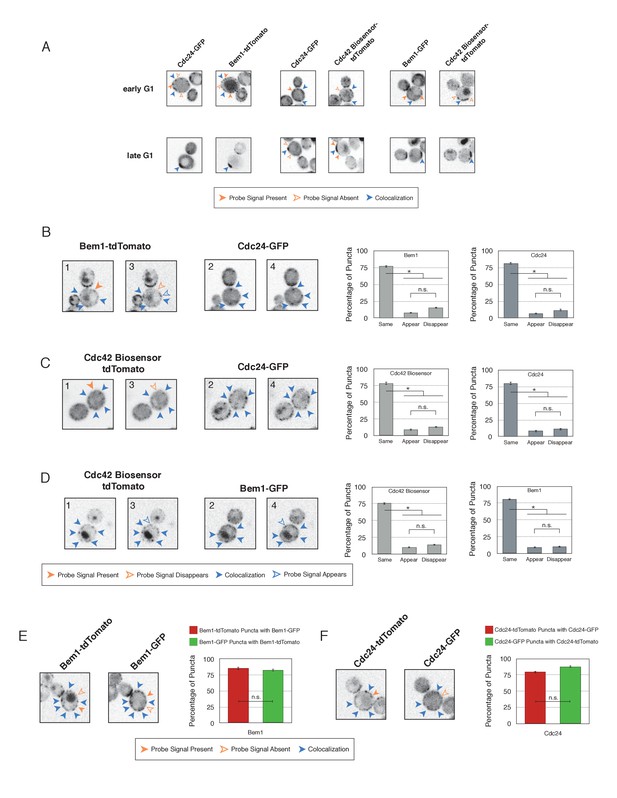
Validation of distinct pools of polarity proteins in early G1.
(A) Single plane snapshots feature similar distributions of Cdc24, Bem1, and Cdc42-GTP as in the Z-projections. Each image is 13.5 µm x 13.5 µm. Strains used: WYK8550, WYK8551, and WYK8552. (B) Inverted fluorescent images depicting the pairwise combination of Bem1 and Cdc24 in early G1. All images are single planes and the number in the upper left corresponds to the order in which the images were acquired. Each image is 13.5 µm x 13.5 µm. Quantification corresponds to the percentage of puncta that remain the same, appear, or disappear between 1 and 3 or 2 and 4. Data are averages of all cells across multiple experiments (n experiments = 2; N cells > 50). Error bars S.E.M. n.s indicates populations not statistically different at p>=0.05, *p<0.05, Mann-Whitney U test. Strains used: WYK8551. (C) Representative images corresponding to the pairwise combination of the Cdc42 biosensor and Cdc24 in early G1. All images and quantification as in A. Data are averages of all cells across multiple experiments (n experiments = 2; N cells > 50). Error bars S.E.M. n.s indicates populations not statistically different at p>=0.05, *p<0.05, Mann-Whitney U test. Strains used: WYK8552. (D) Representative images depicting the pairwise combination of the Cdc42 biosensor and Bem1 in early G1. All images and quantification as in A. Data are averages of all cells across multiple experiments (n experiments = 2; N cells > 50). Error bars S.E.M. n.s indicates populations not statistically different at p>=0.05, *p<0.05, Mann-Whitney U test. Strains used: WYK8550. (E) Representative fluorescent images of early G1 cells co-expressing Bem1-tdTomato and Bem1-GFP. All images are Z projections of 0.25 µm slices for the center 3 µm. Each image is 13.5 µm x 13.5 µm. Quantification is the percentage of colocalization amongst puncta in early G1. Data are averages of all cells across multiple experiments (n experiments = 2; N cells > 75). Error bars S.E.M. n.s indicates populations not statistically different at p>=0.05, *p<0.05, Mann-Whitney U test. Strain used: WYK8554. (F) Representative fluorescent images of early G1 cells co-expressing Cdc24-tdTomato and Cdc24-GFP. All images and quantification as in D. Data are averages of all cells across multiple experiments (n experiments = 2; N cells > 75). Error bars S.E.M. n.s indicates populations not statistically different at p>=0.05, *p<0.05, Mann-Whitney U test. Strain used: WYK8553.
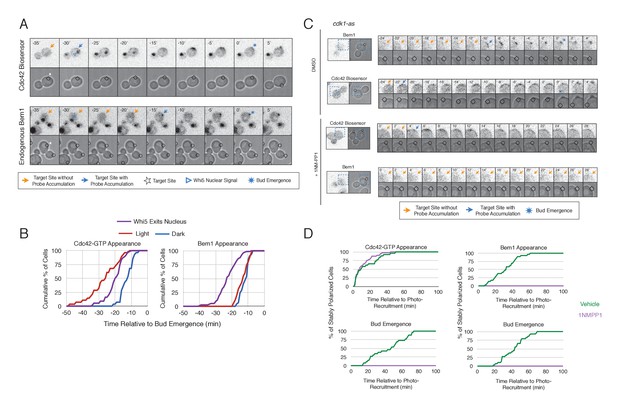
Cdk1 Activation is required for Bem1 accumulation, but dispensable for Cdc42 activation.
(A) Representative panel of time-course images from Cdc24-ePDZ recruitment in cells co-expressing Whi5-tdTomato with either the Cdc42 biosensor or Bem1-tdTomato. Each image is 16.2 µm x 16.2 µm. Strains used: WYK8500 and WYK8502. (B) Whi5 nuclear exit kinetics and accumulation kinetics for either Cdc42 activation or Bem1 at Cdc24-ePDZ recruitment sites. Purple line represents Whi5 exit, with data combined for both light- and dark-state conditions as they are not significantly different (Figure 5—figure supplement 1). Bud emergence occurs at time = 0. Data are combined across multiple experiments (n experiments > 2; N total cells > 25 for each condition). (C) Representative panels and sub-images of cells depicting the response to Cdc24 recruitment +/- Cdk1 activity. Each inset is 6.5 µm x 6.5 µm. Strains used: WYK8441 and WYK8442. (D) Accumulation plots indicating the response of Cdc42 biosensor or Bem1 in response to Cdc24 recruitment +/- Cdk1 activity. Purple lines represent cells treated with 75 µM 1NM-PP1. Green lines represent Vehicle-treated cells. Data are combined across multiple experiments (n experiments = 2; N total cells > 25 for each condition).
-
Figure 5—source data 1
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26722.022
-
Figure 5—source data 1
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26722.023
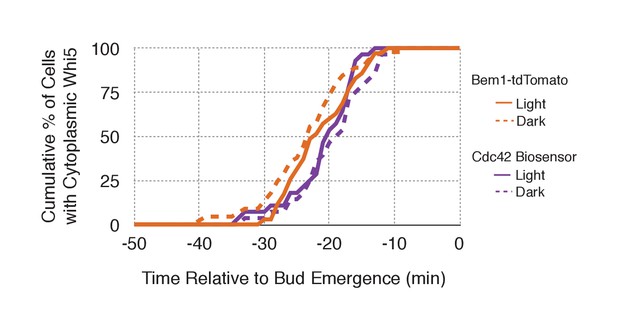
Neither probe expression nor illumination affects the timing of Whi5 nuclear exit.
Timing for nuclear exit of Whi5 for each condition in Figure 5B plotted on a single plot.
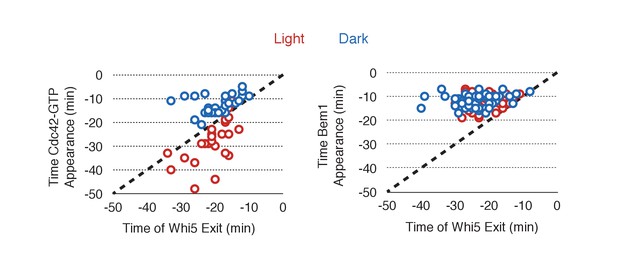
Photo-recruited Cdc24 activates Cdc42 prior to Whi5 nuclear exit.
Correlation between Whi5 nuclear exit and either Cdc42 activation or Bem1 accumulation at Cdc24 recruitment sites. Dashed line represents simulataneous occurrence of the event and Whi5 nuclear exit; points below the dashed line indicate the event occurs before Whi5 nuclear exit and points above the line indicate the event occurs after Whi5 nuclear exit. Data are as in Figure 5B.
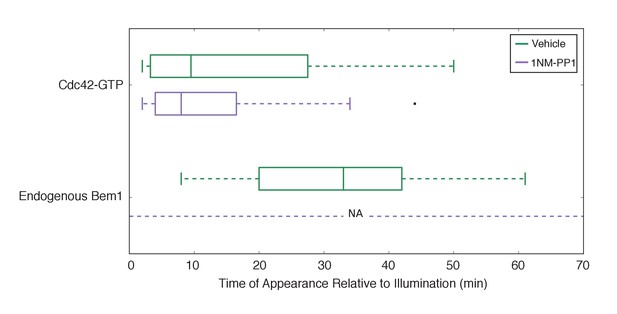
Bem1 accumulation requires Cdk1 activity in response to light-induced recruitment of Cdc24.
Box-and-whisker plot of Cdc42-GTP and Bem1 appearance in cdk1-as cells. Green boxes are vehicle-treated cells, while purple boxes are 1NM-PP1-treated cells. Outliers are depicted by black squares. Vehicle or 1NM-PP1 is added at time = −20 min; time = 0 is the start of live-cell imaging and photo-activation. Data are as in Figure 5D.
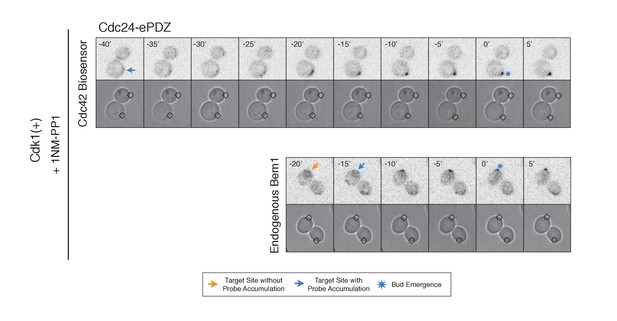
Addition of 1NM-PP1 to Cdk1(+) does not adversely affect Cdc42 Biosensor, Bem1 accumulation, or bud emergence.
Fluorescent and phase images depicting representative Cdk1(+) treated with 1NM-PP1. Each image is 16.2 µm x 16.2 µm. Strains used: WYK8440 and WYK8301.
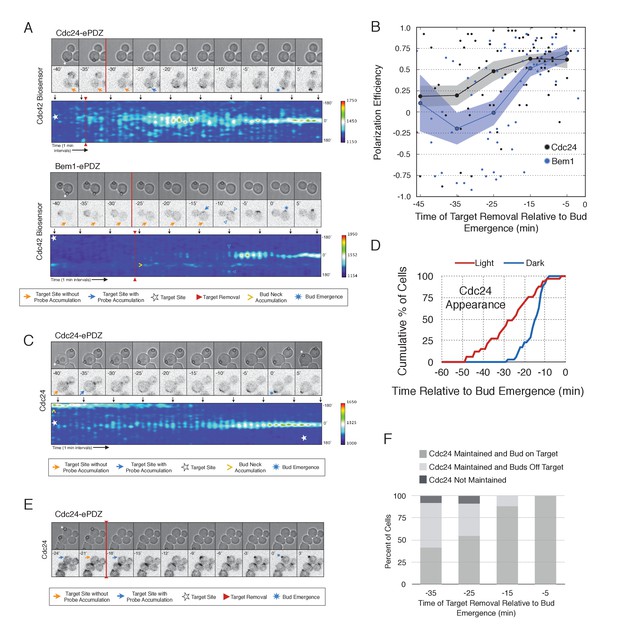
Cdc24 recruitment induces precocious Cdc42 activation and self sustaining Cdc24-tdTomato accumulation.
(A) Phase and fluorescence images and kymographs of representative cells depicting the response to the transient recruitment of Cdc24-ePDZ or Bem1-ePDZ. Initial target site denoted by white stars; note time of target removal. Each image is 16.2 µm x 16.2 µm. Strains used: WYK8440 and WYK8308. (B) Polarization efficiency following transient recruitment of Cdc24 and Bem1. Time indicates when the target was removed relative to bud emergence (bud emergence occurs at time = 0). Black dots represent polarization of individual cells in response to transient Cdc24 recruitment. Blue dots represent polarization of individual cells in response to transient Bem1 recruitment. Lines represent averages (+/- SEM) of data binned in 10 min intervals, with the middle time point represented on the plot. Results are pooled across multiple experiments (n experiments >= 2; N cells > 10 for each time interval; N total cells > 75). Polarization Efficiencies of Cdc24 at −5,–15, and −25 min and Bem1 at −5 and −15 min were statistically significant relative to the corresponding earlier time points. Polarization Efficiencies of Cdc24 and Bem1 are statistically significant at −25 min. p<0.05, Mann-Whitney U test. (C) Representative phase and fluorescence images and kymographs showing the position of the laser target and accumulation of Cdc24-tdTomato in response to Cdc24-ePDZ recruitment. Strain used: WYK8575. (D) Accumulation kinetics for Cdc24-tdTomato. Data are combined across multiple experiments (n experiments > 2, N total cells > 30 for each condition). (E) Panels of representative phase and fluorescence images indicating the response of Cdc24-tdTomato to transient Cdc24-ePDZ recruitment. Target removal occurred at −20 min. Orange arrows denote sites of illumination without Cdc24-tdTomato accumulation. Strain used: WYK8575. (F) Stacked bar chart indicating the percentage of cells that maintain Cdc24-tdTomato accumulation in response to Cdc24 recruitment and whether they polarize to the prescribed site. Buds that formed within 45° of the target were defined as budding on target. Data is binned by 10 min time intervals, with the middle time point represented on the plot. Data combined across multiple experiments (n experiments > 3, N total cells > 25).
-
Figure 6—source data 1
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26722.029
-
Figure 6—source data 2
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26722.030
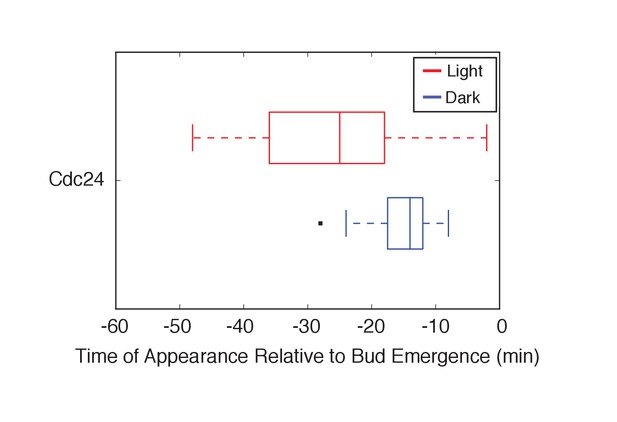
Optogenetic Cdc24 recruitment induces precocious accumulation of Cdc24-tdTomato.
Box-and-whisker plot of Cdc24-tdTomato appearance in photo-activated (red) and mock-illuminated (blue) cells. Outliers are depicted by black squares. Bud emergence occurs at time = 0. Data as in Figure 6D..
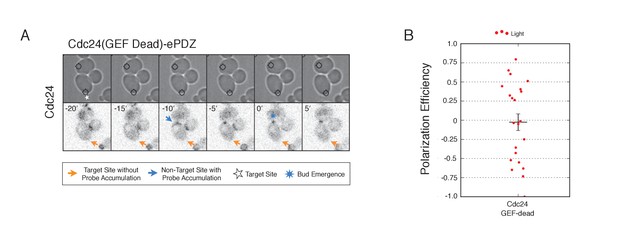
Recruitment of catalytically inactive Cdc24 does not induce Cdc24-tdTomato accumulation.
(A) Phase contrast and fluorescence images of Cdc24-tdTomato accumulation in response to photo-recruitment of Cdc24(GEF-dead). Each image is 16.2 µm x 16.2 µm. Strain used: WYK8504. (B) Polarization efficiency of population of cells where each point represents an individual cell from the condition depicted in A. Data are averages of all cells across multiple experiments (n experiments >= 2, N total cells > 20 for each group). Average and +/- SEM is indicated.
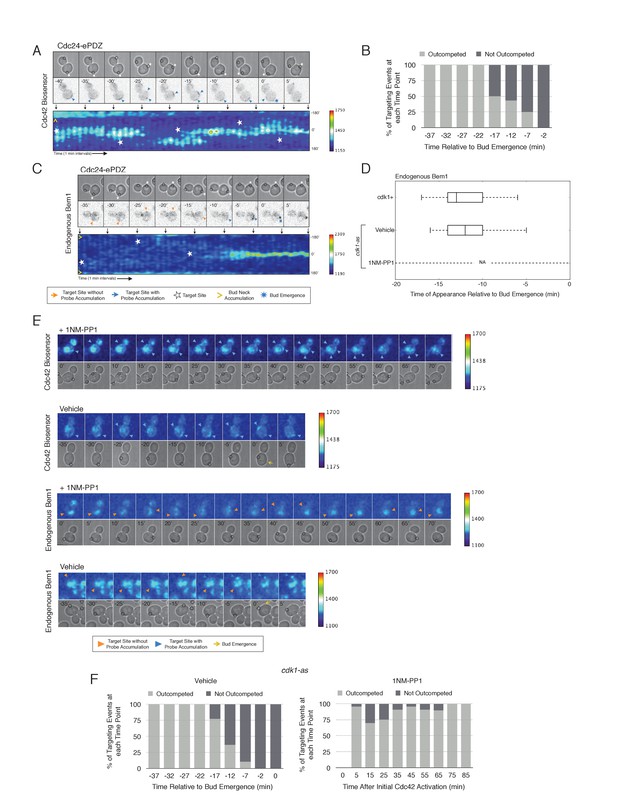
Local Cdc24 recruitment induces precocious activation of Cdc42 that is dynamically maintained in the apparent absence of Bem1.
(A) Panels of representative cells depicting the response to dynamically re-positioned Cdc24 recruitment. Upper panels consist of phase contrast and fluorescent images and the lower panel is a kymograph. The laser was moved every 10 ± 2 min throughout the cell cycle, as denoted by the white stars. Each image is 16.2 µm x 16.2 µm. Strain used: WYK8440. (B) Percentage of targeting events ‘Outcompeted’ or ‘Not Outcompeted’ relative to bud emergence (Time = 0). Time indicates when the target was moved to a new position relative to bud emergence. Data is binned by 5 min time intervals, with the middle time point represented on the plot. The event was scored as ‘outcompeted’ if Cdc42 activity dissipated from the original position and accumulated at the new position. Conversely, the event was scored as ‘not outcompeted’ if Cdc42 activity remained at the initial position upon target repositioning. Data are combined across multiple experiments (n total experiments > 2; n targeting events per time interval >10; N total targeting events > 100; N total cells > 20). (C) Panels and a kymograph of a representative cell depicting the accumulation of Bem1 in response to dynamically re-positioned Cdc24 recruitment. Strain used: WYK8301. (D) Box-and-whisker plot denoting Bem1 accumulation in CDK1, cdk1-as + DMSO, and cdk1-as + 1 NM-PP1 cells. (E) Time-course images of cdk1-as cells challenged with Cdc24 dynamic reorientation. Panels consist of phase contrast and either Cdc42-GTP or Bem1 accumulation pseudo-colored as a heat map. Cells were treated with either DMSO or 1NM-PP1 as indicated. Strains used: WYK8441 and WYK8442. (F) Quantification of dynamic reorientation in vehicle-treated or 1NM-PP1-treated cdk1-as cells. (n total experiments > 2; n targeting events per time interval >10; N total targeting events > 100; N total cells > 20) Described in B.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26722.034
-
Figure 7—source data 2
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26722.035
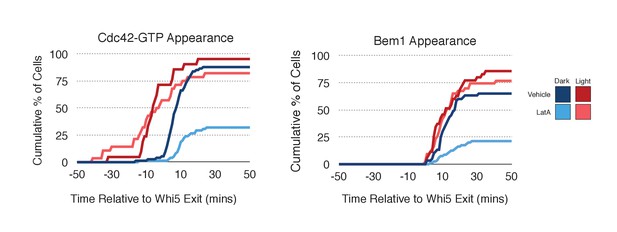
Localized recruitment of Cdc24 can overcome the polarity defect caused by actin depolymerization.
Accumulation kinetics for Cdc42-GTP or Bem1 in response to Cdc24 recruitment in the presence or absence of polymerized actin. Cells were scored as ‘polarized’ if they retained accumulation of active Cdc42 or Bem1 for >15 min during the course of the experiment (>100 min). Red lines represent cells exposed to light-induced Cdc24 recruitment. Blue lines represent mock-illuminated cells. Dark lines represent vehicle-treated cells, while lighter-colored lines represent latrunculin A-treated cells (see schematic). Whi5 nuclear exit was used as a cell cycle marker and accumulation of Cdc42-GTP or Bem1 was scored relative to Whi5 exit. Data was binned by 5 min intervals and combined across multiple experiments (n experiments = 2; N total cells > 20). Stains used: WYK8500 and WYK8502.
-
Figure 8—source data 1
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26722.038
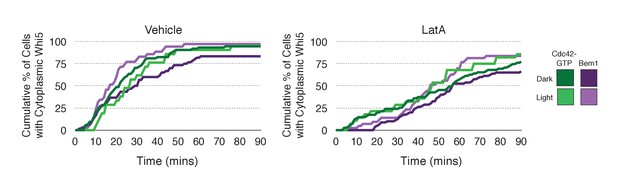
Loss of f-actin slows cell cycle entry.
Whi5 nuclear exit kinetics in Vehicle-treated (left) or Latrunculin A-treated (right) cells. Green lines refer to cells expressing the Cdc42 biosensor, while purple lines refer to cells expressing endogenous Bem1-tdTomato. Darker-colored lines represent mock-illuminated cells, while lighter-colored lines represent photo-activated cells (see schematic). Whi5 nuclear exit was slowed in LatA-treated cells. Data were binned by 5 min intervals and combined across multiple experiments (n experiments = 2; N total cells > 20).
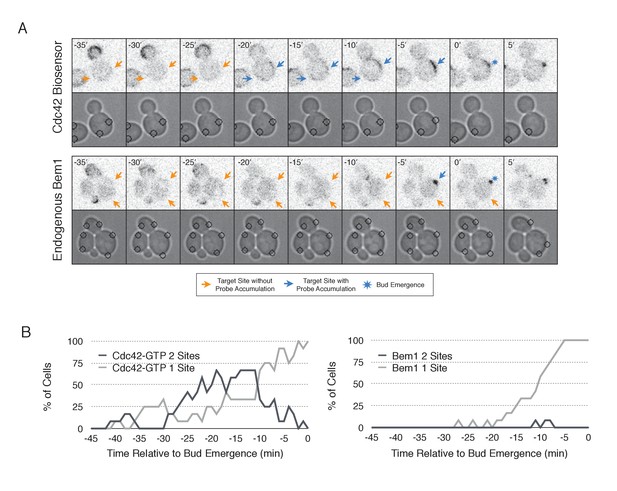
Nascent sites undergo competition to establish a single axis of polarity.
(A) Representative fluorescence and phase images in response to simultaneous recruitment of Cdc24 to two sites. Top panel depicts Cdc42-GTP response. Bottom panel depicts Bem1 response. Each image is 16.2 µm x 16.2 µm. Strains used: WYK8440 and WYK8301. (B) Percentage of cells with signal at one or both sites at any given time relative to bud emergence. Dark gray lines depict percentage of cells with activation at two sites simultaneously. Light gray lines represent percentage of cells with accumulation at only a single site. Bud emergence occurs at time = 0. Data are combined across multiple experiments (n experiments >= 2; N total cells > 20 for each condition).
-
Figure 9—source data 1
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26722.041
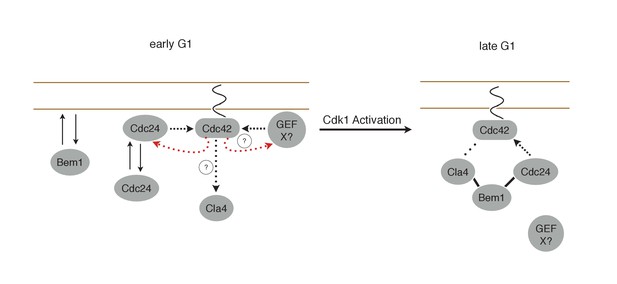
Working Model for polarity establishment.
In early G1, prior to Cdk1 activation, Cdc24, Bem1, and activated Cdc42 individually associate with the plasma membrane, but do not form stable complexes. With some frequency, Cdc24, and perhaps other Cdc42 GEFs, activate Cdc42 which can participate in a weak positive feedback loop with one or both GEFs. It is unclear whether Cdc42-GTP in early G1 interact with downstream effectors, such as Cla4, but if it does, it does not initiate Bem1-dependent positive feedback. Following Cdk1 activation, the Cla4-Bem1-Cdc24 complex assembles in late G1. This complex may amplify the preexisting focus of Cdc42-GTP, and ultimately undergo strong positive feedback to generate a single focus of Cdc42-GTP that subsequently triggers bud emergence.
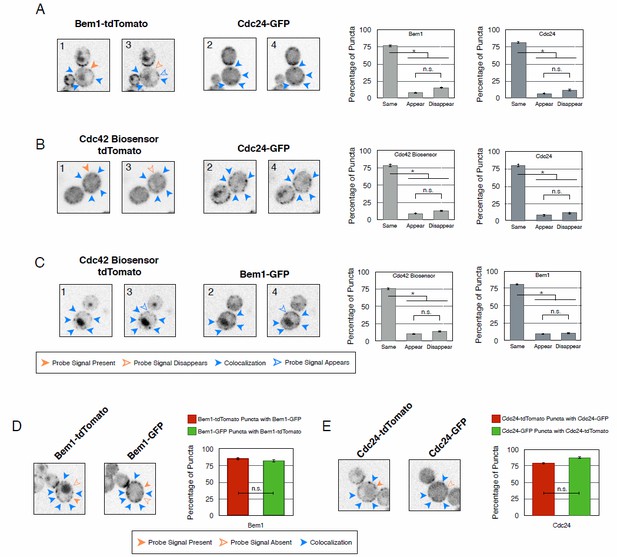
Recruitment of Cdc24 or Bem1 that cannot activate Cdc42 do not induce accumulation of wildtype Cdc24 or Bem1, respectively.
(A) Inverted fluorescent images depicting the pairwise combination of Bem1 and Cdc24 in early G1. All images are single planes and the number in the upper left corresponds to the order in which the images were acquired. Each image is 13.5 µm x 13.5 µm. Quantification corresponds to the percentage of puncta that remain the same, appear, or disappear between 1 and 3 or 2 and 4. Data are averages of all cells across multiple experiments (n experiments = 2; N cells > 50). Error bars S.E.M. n.s indicates populations not statistically different at p >= 0.05, * p < 0.05, Mann-Whitney U test. Strains used: WYK8551. (B) Inverted fluorescent images depicting the pairwise combination of the Cdc42 biosensor and Cdc24 in early G1. All images are single planes and the number in the upper left corresponds to the order in which the images were acquired. Each image is 13.5 µm x 13.5 µm. Quantification as in A. Data are averages of all cells across multiple experiments (n experiments = 2; N cells > 50). Error bars S.E.M. n.s indicates populations not statistically different at p >= 0.05, * p < 0.05, Mann-Whitney U test. Strains used: WYK8552. (C) Inverted fluorescent images depicting the pairwise combination of the Cdc42 biosensor and Bem1 in early G1. All images are single planes and the number in the upper left corresponds to the order in which the images were acquired. Each image is 13.5 µm x 13.5 µm. Quantification as in A. Data are averages of all cells across multiple experiments (n experiments = 2; N cells > 50). Error bars S.E.M. n.s indicates populations not statistically different at p >= 0.05, * p < 0.05, Mann-Whitney U test. Strains used: WYK8550. (D) Representative fluorescent images of early G1 cells co-expressing Bem1-tdTomato and Bem1-GFP. All images are Z projections of 0.25 𝜇m slices for the center 3 𝜇m. Each image is 13.5 µm x 13.5 µm. Quantification is the percentage of colocalization amongst puncta in early G1. Data are averages of all cells across multiple experiments (n experiments = 2; N cells > 75). Error bars S.E.M. n.s indicates populations not statistically different at p >= 0.05, * p < 0.05, Mann-Whitney U test. Strain used: WYK8554. (E) Representative fluorescent images of early G1 cells co-expressing Cdc24-tdTomato and Cdc24-GFP. All images and quantification as in D. Data are averages of all cells across multiple experiments (n experiments = 2; N cells > 75). Error bars S.E.M. n.s indicates populations not statistically different at p >= 0.05, * p < 0.05, Mann-Whitney U test. Strain used: WYK8553.
Videos
Photo-recruitment of Cdc24 is sufficient to activate Cdc42 and bias the bud site.
Representative phase contrast and fluorescent time-lapse images of the response to Cdc24 recruitment in cells expressing the Cdc42 biosensor. Left panel is the phase image with the position of the target defined by the black circle. Right panel is the Cdc42 biosensor. fps = 10.
Cdc42 activity can be dynamically repositioned in response to mobile sites of Cdc24 recruitment.
Representative phase contrast and fluorescent time-lapse images during dynamic repositioning experiments in cells expressing the Cdc42 biosensor. Left panel is the phase image with the position of the target defined by the black circle. Right panel is the Cdc42 biosensor. fps = 10.
Cdc42 activation can occur at two sites simultaneously in early G1
Representative phase contrast and fluorescent time-lapse images in cells expressing the Cdc42 biosensor when challenged with two sites of Cdc24 recruitment. Left panel is the phase image with the position of the target defined by the black circle. Right panel is the Cdc42 biosensor. fps = 10.
Bem1 accumulation is limited to a single site of Cdc24 recruitment.
Representative phase contrast and fluorescent time-lapse images in cells expressing Bem1-tdTomato when challenged with two sites of Cdc24 recruitment. Left panel is the phase image with the position of the target defined by the black circle. Right panel is the Cdc42 biosensor. fps = 10.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
This file contains table S1 containing the list of S. cerevisiae strains used in this study and Table S2 containing a list of plasmids used in this study.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26722.045
-
Supplementary file 2
This file contains a summary of the tests for statistical significance.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26722.046





