Shared neural underpinnings of multisensory integration and trial-by-trial perceptual recalibration in humans
Figures
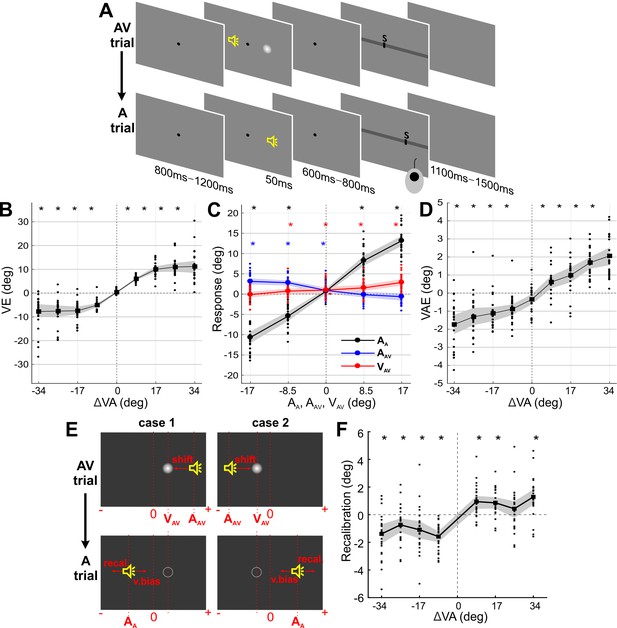
Paradigm and behavioral results (N = 24).
(A) Experimental design. Participants localized auditory (or visual) targets and indicated the perceived location using a mouse cursor. Audio-visual (AV) and auditory (A) trials alternated. (B) Response bias induced by the ventriloquist effect (VE) as a function of audio-visual discrepancy in the AV trial. VE: the difference between the reported location (RAV) and the location at which the sound (AAV) was actually presented (RAV - AAV). (C) Sound localization response in the A trial was significantly influenced by the current sound (AA; black), the previous sound (AAV; blue) and the previous visual (VAV; red) stimulus. (D) Response bias induced by the ventriloquist effect (VAE) as a function of audio-visual discrepancy in the AV trial. VAE: the difference between the reported location (RA) minus the mean reported location for all trials of the same stimulus position (RA – mean(RA)). (E) Example trials dissociating a pure visual bias from a genuine multisensory bias in the VAE. Trials for which the expected visual (v.bias) and multisensory (recal) biases are in opposite directions were selected; these satisfied either case 1: VAV - AAV < 0 and AA ≤VAV or case 2; VAV - AAV > 0 and AA ≥VAV. (F) Recalibration bias for trials from (E). Solid lines indicate mean across participants. Shaded area is the estimated 95% confidence interval based on the bootstrap hybrid method. Dots denote individual participants. Asterisks denote p-values<0.05 from two-sided Wilcoxon signed rank tests, corrected with the Holm method for multiple comparisons, AA: sound location in A trial. AAV: sound location in AV trial. VAV: visual location in AV trial. Deposited data: Data_behav (folder).
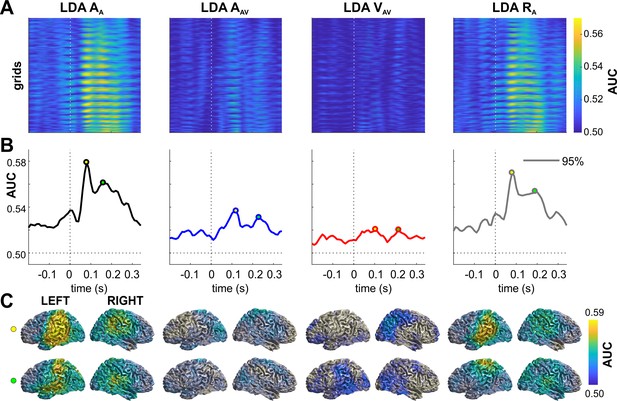
Neural representation of current and previous sensory information and upcoming responses.
The figure shows the performance (AUC) of linear discriminants for different variables of interest. (A) Time-course of discriminant performance for all grid points in source space. (B) Time-course of the 95th percentile across source locations. (C) Surface projections of significant (p≤0.01; FWE corrected across multiple tests using cluster-based permutation) performance at the peak times extracted from panel B (open circles). The performance of LDA VAV was not significant when tested across all source locations, and the maps for VAV are not masked with significance. AA: sound location in A trial. AAV: sound location in AV trial. VAV: visual location in AV trial. Deposited data: Atrial_LDA_AUC.mat.
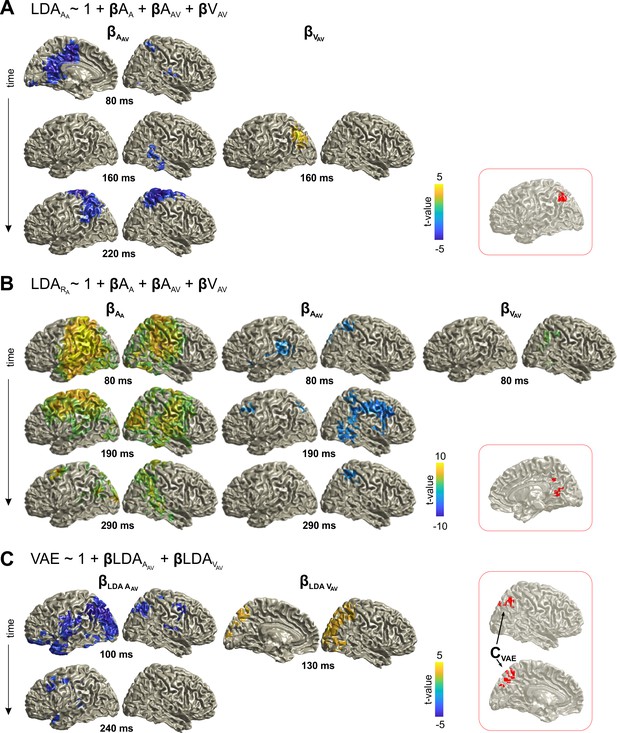
Neural correlates of trial-by-trial recalibration (VAE bias).
(A) Contribution of previous stimuli to the neural representation of the sound (AA) in the A trial (here the effect for AA itself is not shown). (B) Contribution of current and previous stimuli to the neural representation of the response (RA) in the A trial. (C) Ventriloquist–aftereffect in the A trial predicted by the neural representation of information about previous stimuli. Red insets: Grid points with overlapping significant effects for both AAV and VAV (A, B), and for both LDAA_AV and LDAV_AV (C) across time. Surface projections were obtained from whole-brain statistical maps (at p≤0.05, FWE corrected). See Table 1 for detailed coordinates and statistical results. AA: sound location in A trial. AAV: sound location in AV trial. VAV: visual location in AV trial. Deposited data: Atrial_LDA_AUC.mat; Atrial_LDA_beta.mat; VAE_beta.mat.
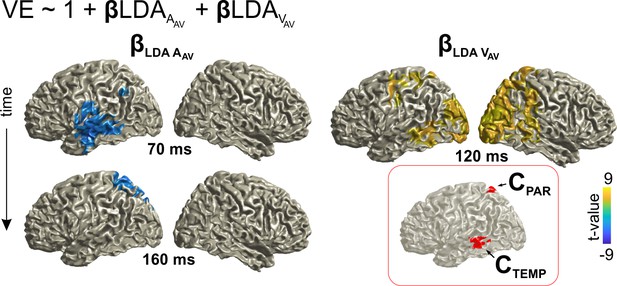
Neural correlates of audio-visual integration within a trial (VE bias).
Contribution of the representations of acoustic and visual information to the single trial bias in the AV trial. Red inset: Grid points with overlapping significant effects for both LDAA_AV and LDAV_AV. Surface projections were obtained from whole-brain statistical maps (at p≤0.05, FWE corrected). See Table 2 for detailed coordinates and statistical results. AAV: sound location in AV trial. VAV: visual location in AV trial. Deposited data: AVtrial_LDA_AUC.mat; VE_beta.mat.
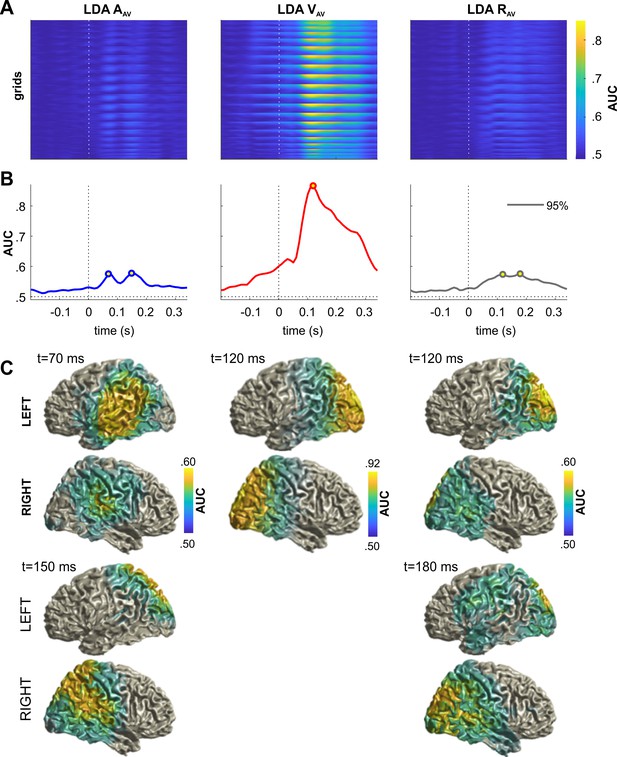
Neural representation of sensory information in AV trials.
The figure shows the performances (AUC) of linear discriminants for variables of interest, applied to the MEG data from the AV trial. (A) Time-courses of discriminant performance for all points in source space. (B) Time-courses of the 95th percentile across source locations. (C) Surface projections of significant (p≤0.01; FWE corrected across multiple tests using cluster-based permutation) performance at the peak times extracted from panel B (open circles). Classification performance peaked around 70 ms and 150 ms for sound location (AAV), around 120 ms for visual location (VAV), and around 120 ms and 180 ms for the response (RAV). Deposited data: AVtrial_LDA_AUC.mat.
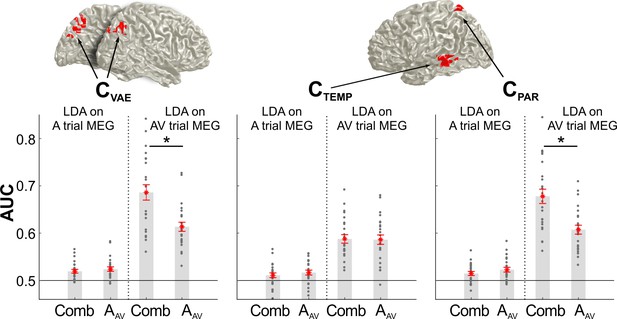
Classification performance for unisensory and combined multisensory information.
The bar graphs show the classification performance for each cluster of interest (CVAE from Figure 3C, CPAR and CTEMP from Figure 4) based on the activity in the AV trial or the A trial. Classification was applied to either the sound location in the AV trial (AAV), or the combined multisensory information in the AV trial (Comb), derived from the participant specific VE bias (derived from model mi3;VE ~ 1 + β⋅AAV + β⋅VAV for the behavioral data). Asterisks denote p<0.01, two-sided paired t-test, FDR corrected for multiple comparisons at p≤0.05. Gray dots are individual participant values averaged within each cluster, red stars are the mean across participants, and red lines are standard errors of mean. AAV: sound location in AV trial. VAV: visual location in AV trial. Deposited data: LDA_AUC_comb.mat.
Tables
Neuro-behavioral modeling of the VAE.
The significance of each predictor was tested at selected time points at the whole-brain level (p≤0.05, FWE corrected). The table provides the peak coordinates of significant clusters, the anatomical regions contributing to significant clusters (based on the AAL Atlas), as well as beta and cluster-based t-values (df = 23). The overlap was defined as grid points contributing to both a significant effect for AAV and VAV (at any time). The effect of AA is not indicated, as this was significant for a large part of the temporal and parietal lobe, and was not of primary interest. L: left hemisphere; R: right hemisphere. BA: Brodmann area. **sum of 2 spatially separate clusters, ***sum of 4 clusters.
| Regressor | Post-stim. time (ms) | Anatomical labels | MNI coord. (peak) Brodmann Area | β t-value (tsum) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDAA_A ~ 1 + AA + AAV + VAV | ||||
| AAV | 80 | L/R: Cingulum Mid., Precuneus L: Supp. Motor Area | −3,–20, 29 BA 23 | −5.6 (−1220) |
| 160 | R: Fusiform, Temporal Mid/Inf | 28,–39, −20 BA 37 | −3.8 (−203) | |
| 220 | L/R: Postcentral L: Parietal Inf/Sup R: Precentral, Supp. Motor Area | −24,–36, 77 BA 03 | −6.6 (−1560) | |
| VAV | 160 | L: Occipital Mid/Sup, Parietal Inf/Sup | −40,–76, 37 BA 19 | 5.3 (246) |
| overlap | - | L: Angular, Parietal Inf., Occipital Mid. | −40,–62, 47 BA 39 | - |
| LDAR_A ~ 1 + AA + AAV + VAV | ||||
| AA | 80 | L: Angular, Temporal Mid. L/R: Postcentral, Precuneus | −40,–52, 21 BA 39 | 17.9 (13862) |
| 190 | R: Precuneus, Lingual Temporal Sup. L: Pre/Postcentral, Precuneus | 8,–51, 5 BA 30 | 9.3 (8323) | |
| 290 | L: Occipital Mid/Sup. R: Temporal Mid/Sup., Parietal Sup. | −24,–100, 5 BA 17 | 6.9 (2390) | |
| AAV | 80 | L: Lingual, Precuneus R: Lingual, Parietal Sup. | −24,–52, 13 BA 17 | −5.8 (−1152) |
| 190 | R: Frontal Mid/Inf, Precentral | 33, 21, 21 BA 48 | −6.1 (−1343) | |
| 290 | R: Precuneus, Cingulum Mid/Post. Parietal Inf/Sup., Postcentral | 16,–42, 41 BA 23 | −4.2 (−256) | |
| VAV | 80 | R: Fusiform, Angular, Parietal Inf. Temporal Mid.Inf, Precuneus | 32,–51, −3 BA 37 | 4.3 (225) |
| overlap | - | R: Calcarine, Precuneus, Cingulum Mid. | 17,–67, 23 BA 18 | - |
| VAE ~ 1 + LDAA_AV + LDAV_AV | ||||
| LDAA_AV | 100 | L: Occipital Mid/Sup., Temporal Inf., Parietal Mid/Sup L/R: Precuneus | −32,–87, 37 BA 19 | −7.4 (−3571)** |
| 240 | L: Precentral, Frontal Mid, Precuneus, Temporal Pole Sup | −32,–20, 45 BA 03 | −4.7 (−413)*** | |
| LDAV_AV | 130 | R: Occipital Mid/Sup, Parietal Inf/Sup, Angular | 24,–95, 29 BA 18 | 4.7 (579) |
| overlap (CVAE) | - | L/R: Precuneus R: Angular | −3,–65, 51 BA 07 | - |
Neuro-behavioral modeling of the VE.
The significance of each predictor was tested at selected time points at the whole-brain level (p≤0.05, FWE corrected). The table provides the peak coordinates of significant clusters, the anatomical regions contributed to significant clusters (based on the AAL Atlas), peak beta values and cluster-based t-values (df = 23). The overlap was defined as grid points contributing to both a significant effect for LDAA_AV and LDAV_AV (at any time). L: left hemisphere; R: right hemisphere. BA: Brodmann area. **sum of 2 spatially separate clusters.
| VE ~ 1 + LDAA_AV + LDAV_AV | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regressor | Post-stim. time (ms) | Anatomical labels | MNI coord. (peak) Brodmann Area | β t-value (tsum) |
| LDAA_AV | 70 | L: Temporal Mid/Sup., Rolandic Oper, Postcentral, Heschl | −47,–19, −19 BA 20 | −4.1 (−392) |
| 160 | L: Parietal Inf/Sup., Precuneus, Cuneus Occipital Sup | −24,–60, 69 BA 07 | −4.0 (−181) | |
| LDAV_AV | 120 | L/R: Occipital Mid., Calcarine R: Occipital Sup., Temporal Mid., Lingual, Cuneus | 24,–92, 13 BA 18 | 9.1 (7188)** |
| overlap (CTEMP, CPAR) | - | L: Temporal Mid Parietal Sup, Cuneus, Precuneus | −58,–41, −6 (CTEMP, BA 21) −14,–60, 70 (CPAR, BA 05, 07) | - |
Overlapping neural substrates for integration and recalibration.
Both neuro-behavioral models, VE and VAE (Equations 4/5), were tested within the clusters significantly contributing to the VAE effect (from Figure 3C, CVAE) and the two clusters contributing to the VE effect (from Figure 4, CTEMP, CPAR). The table lists regression betas and group-level t-values. The expected effects (based on Figure 3C and Figure 4) are shown in normal font, the effects of interest (cross-tested) in BOLD. We directly compared the effect strengths between clusters (one-sided paired t-test, p<0.05, FDR adjusted). Significant results are indicated by *. In particular, both CVAE and CPAR have significant VAE and VE effects (tcrit = 2.81, and their respective effect sizes do not differ between clusters (ns beta differences).
| Model | VAE ~ 1 + β*LDAA_AV + β*LDAV_AV | VE ~ 1 + β*LDAA_AV + β*LDAV_AV | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster | CVAE | CTEMP | CPAR | CVAE | CPAR |
| t-value (βLDAA_AV) | −3.29 (−0.12) | −2.86 (−0.13)ns | −2.97 (−0.09)ns | −2.50 (−0.30)ns | −3.31 (−0.32) |
| t-value (βLDAV_AV) | 3.17 (0.12) | 0.91 (0.03)* | 2.23 (0.08)ns | 6.61 (3.88)ns | 6.93 (3.35) |
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species (Human) | Participants | Volunteers recruited from adverts | ||
| Software, algorithm | MATLAB R2017A | MathWorks | https://www.mathworks.com/ | |
| Software, algorithm | Psychtoolbox-3 | Brainard, 1997; Pelli, 1997 | http://psychtoolbox.org/ | |
| Software, algorithm | SPM8 | Wellcome Trust | http://www.fil.ion.ucl.ac.uk/spm/software/spm8/ | |
| Software, algorithm | FreeSurfer | Fischl, 2012 | https://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/ | |
| Software, algorithm | PKU and IOA HRTF database | Qu et al., 2009 | http://www.cis.pku.edu.cn/auditory/Staff/Dr.Qu.files/Qu-HRTF-Database.html | |
| Software, algorithm | Fieldtrip | Oostenveld et al., 2011 | http://www.fieldtriptoolbox.org/ | |
| Other | Behavioral data | This paper | https://dx.doi.org/10.5061/dryad.t0p9c93 | data generated in this study |
| Other | MEG data | This paper | https://dx.doi.org/10.5061/dryad.t0p9c93 | data generated in this study |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.47001.012





