A dynamic interaction between CD19 and the tetraspanin CD81 controls B cell co-receptor trafficking
Figures
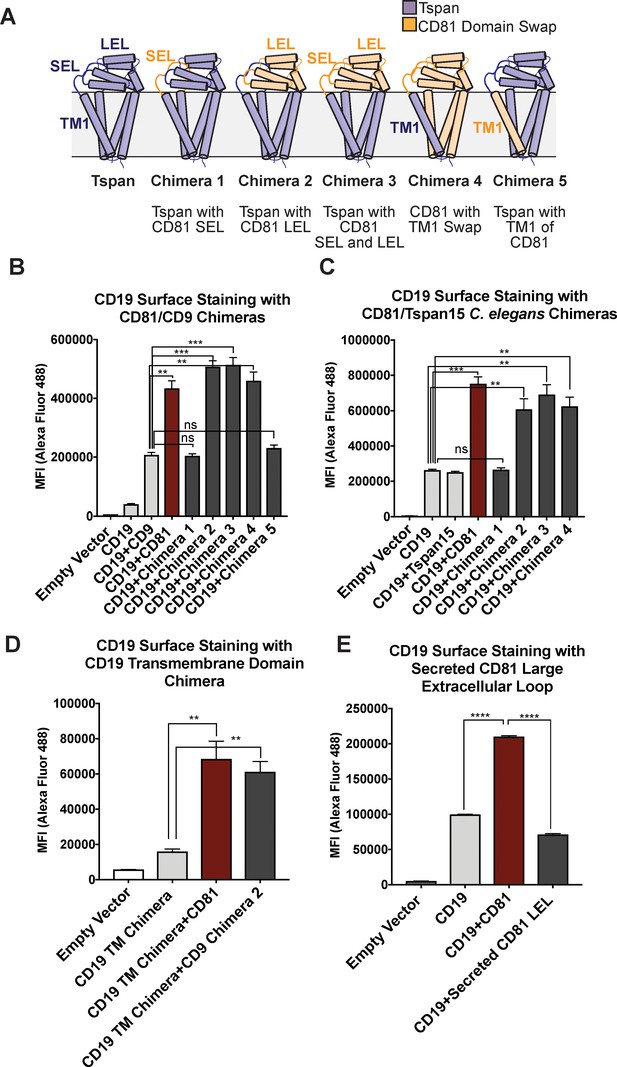
CD81 chimera design and CD19 Export Assay.
(A) Design of CD81 Chimeras used in export assay experiments. (B) Export assay with CD81/CD9 chimeras. (C) Export assay with CD81/Tspan15 C. elegans chimeras. (D) Export assay with CD19/ σ1 receptor transmembrane domain chimera. (E) Export assay with a secreted construct of the CD81 large extracellular loop. For the data in panels (B – E), surface CD19 was detected by flow cytometry using an Alexa 488-coupled anti-CD19 antibody. Each figure represents three independent experiments. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed in GraphPad Prism using an unpaired two-tailed t test. **p<0.01; ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
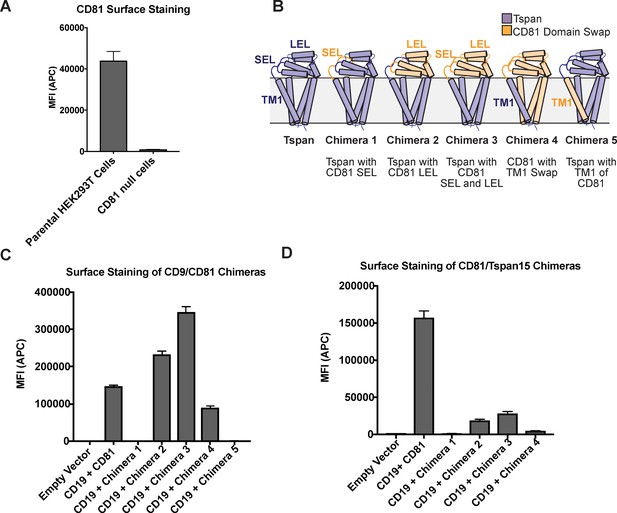
Surface staining of CD81 chimeras used in the CD19 Export Assay.
Expression was analyzed using an anti-CD81 antibody, so only chimeras with the large extracellular loop of CD81 are detectable. (A) CD81 surface staining of parental HEK293T cells compared to CRISPR knockout cells. (B) Panel of CD81 chimeras used in export assay. (C) CD81 surface staining of CD9/CD81 chimeras detected with 5A6 antibody. (D) CD81 surface staining of CD81/Tspan15 C. elegans chimeras detected with 5A6 antibody. Error bars represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments.
Representative gating strategy for CD81 null 293 T cells used in the CD19 export assay and CD19-CD81 fusion protein validation experiments.
Cells were first gated on live cells and then on singlet cells.
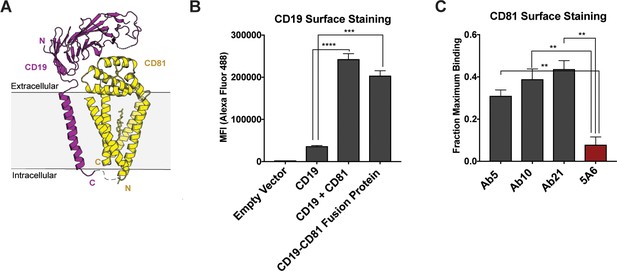
Design and evaluation of a CD19-CD81 fusion protein.
(A) Cartoon representing the designed CD19-CD81 fusion protein. The model was created based on known structures of the CD19 ectodomain (PDB 6AL5) and CD81 (PDB 5TCX). A short Gly-Ser linker (dashed lines) connects P329 of the intracellular portion of CD19 to the N-terminus of CD81. (B) Analysis of CD19 surface staining in CD81-null cells expressing the CD19-CD81 fusion protein. Surface staining for the CD19-CD81 fusion is compared to staining of cells expressing only CD19, and to staining of cells expressing both CD19 and CD81, using an Alexa 488-coupled anti-CD19 antibody. (C) Binding of various CD81 antibodies to the CD19-CD81 complex, analyzed by flow cytometry. ‘Fraction maximum binding’ was calculated by dividing the average MFI of antibody bound to CD19-CD81 by the average MFI of antibody bound to CD81. An anti-human IgG-Alexa 488 secondary antibody was used to detect CD81 antibody bound to the cell surface. For the data in panel B and C, each figure represents three independent experiments and error bars represent mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed in GraphPad Prism using an unpaired t test. **p<0.01; ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
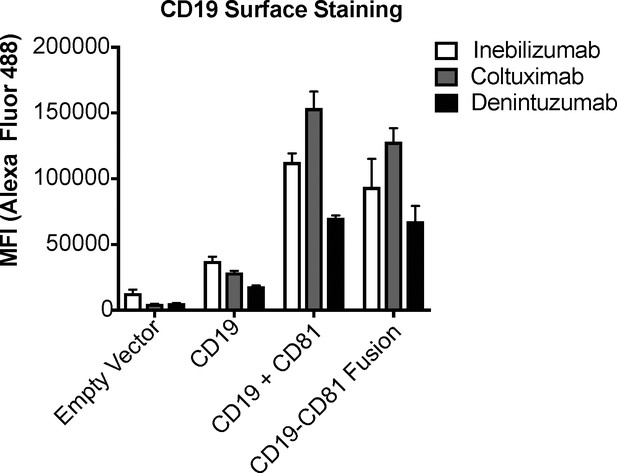
Validation of the CD19-CD81 fusion protein with a panel of CD19 antibodies.
A panel of CD19 antibodies recognizes the CD19-CD81 fusion to the same degree as it recognizes wild type CD19, providing further evidence that the fusion protein is properly folded. Error bars represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments.
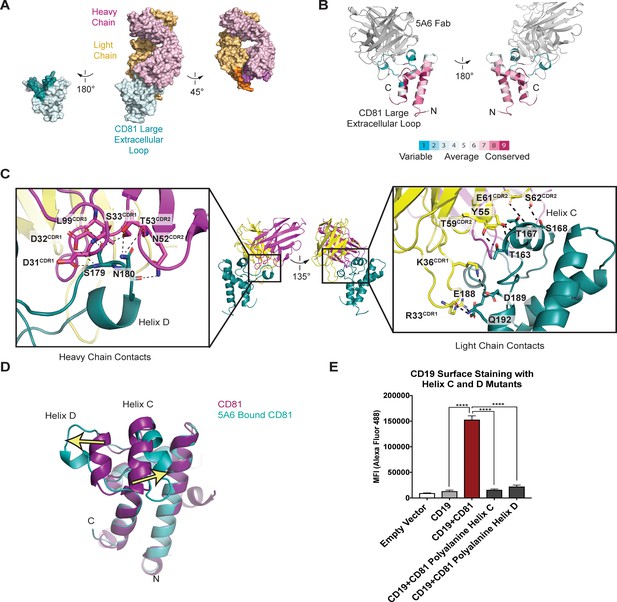
Structure of the 5A6 Fab-CD81 Large Extracellular Loop Complex (PDB 6U9S).
(A) Surface representation of the 5A6-CD81 complex. CD81 is blue, the 5A6 Fab light chain is yellow, and the heavy chain is magenta. Residues at the binding interface are colored in a darker shade. (B) CD81 colored by evolutionary conservation score using the top 50 CD81-related sequences determined by Consurf (Landau et al., 2005).(C) 5A6 Fab-CD81 binding interface. Heavy chain (left panel) and light chain (right panel) contacts are shown. Hydrogen bonding interactions are indicated with dotted lines. (D) Structural superposition of 5A6 bound CD81 on full length CD81. Arrows indicate positional shifts of the variable helices C and D in the 5A6-bound structure. (E) CD19 Export Assay with Helix C and D Mutants. Surface CD19 was detected by flow cytometry using an Alexa 488-coupled anti-CD19 antibody. Expression of helix C and D mutants was confirmed by flow cytometry (Figure 3—figure supplement 3). For the data in panel E, error bars represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed in GraphPad Prism using an unpaired t test. **p<0.01; ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
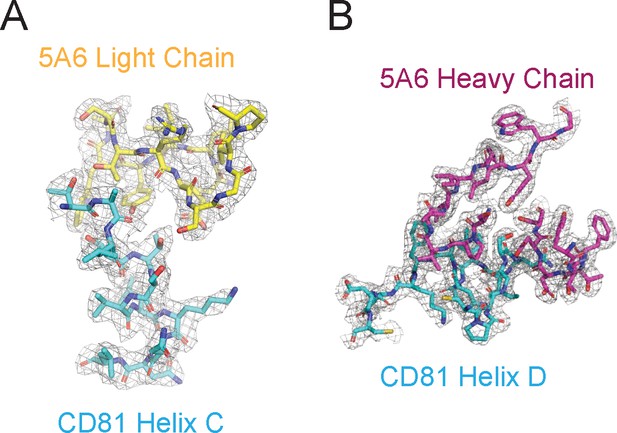
Representative Density in the CDRs of 5A6 Fab.
(A–B) Composite omit 2Fo-Fc electron density map contoured at 1.0 σ for CD81 Helix C (A) and CD81 Helix D (B).
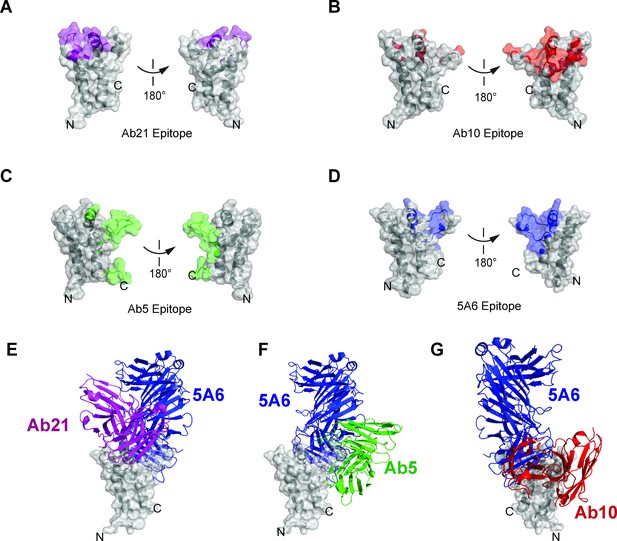
Epitope comparison of Ab5, Ab10, Ab21, and 5A6.
(A) Surface representation of CD81 large extracellular loop colored purple for residues within 4 Å of Ab21 (PDB 5DFW). (B) Surface representation of CD81 large extracellular loop colored red for residues within 4 Å of Ab10 (PDB 6EK2). (C) Surface representation of CD81 large extracellular loop colored green for residues within 4 Å of Ab5 (PDB 6EJM). (D) Surface representation of CD81 large extracellular loop colored blue for residues within 4 Å of 5A6. (E) Superposition of Ab21 and 5A6 complexes, comparing binding sites and angles of approach for Ab21 and 5A6. (F) Superposition of Ab5 and 5A6 complexes, comparing binding sites and angles of approach for Ab5 and 5A6. (G) Superposition of Ab10 and 5A6 complexes, comparing binding sites and angles of approach for Ab10 and 5A6.
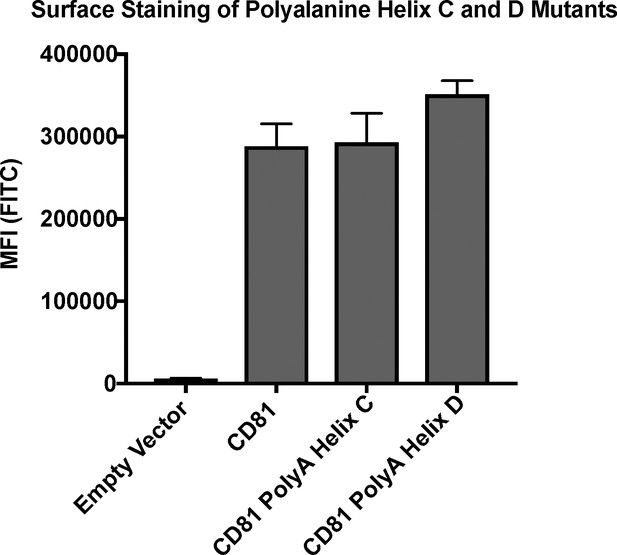
CD81 surface staining of polyalanine mutants detected with Ab21.
Error bars represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments.
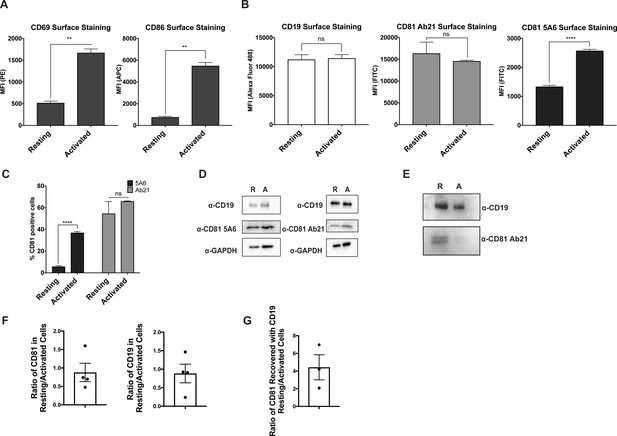
CD81 antibody labeling experiments in resting and activated primary human B cells.
(A) Surface staining of the B cell activation markers, CD86 and CD69, in resting B cells and cells activated with IgM, IgG Fab’2. (B) Surface staining of CD19 and CD81 with antibody 5A6 and Ab21. (C) Percent of CD81 positive cells labeled with 5A6 or Ab21. (D) Western blots of total protein lysate. ‘R’ represents resting cells and ‘A’ represents activated cells. (E) Immunopurification of CD19 from resting and activated primary human B cells, followed by western blotting for CD19, and for CD81 using Ab21. ‘R’ represents resting cells and ‘A’ represents activated cells. (F) Densitometry analysis of western blots of whole cell lysates shown in Panel D. (G) Densitometry analysis of western blots of CD19-CD81 co-immunoprecipitation shown in Panel E. For all panels, data are shown as mean ± SEM. Three replicates were performed for CD81 5A6 and Ab21 staining, and two replicates were performed for CD19, CD69, and CD86 staining conditions. Statistical analysis was performed in GraphPad Prism using an unpaired t test. **p<0.01; ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
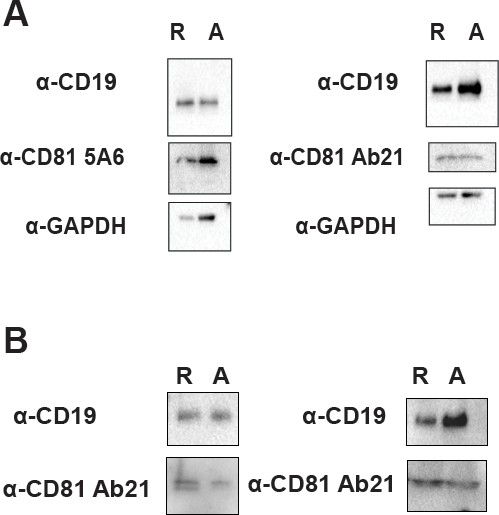
Replicate western blots.
(A) Replicate western blots of total protein lysate from Figure 4D. ‘R’ represents resting cells and ‘A’ represents activated cells. (B) Replicate immunoprecipitations of CD19 from resting and activated primary human B cells, followed by western blotting for CD19, and for CD81 using Ab21. ‘R’ represents resting cells and ‘A’ represents activated cells.
Representative gating strategy for primary human B cells.
Cells were first gated on live cells, then on singlet cells, and then on CD20+ cells.
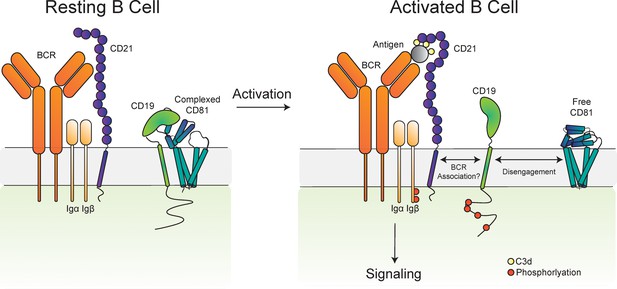
Proposed model for the disengagement of the CD81 during B cell activation.
Upon B cell activation, dissociation of the B cell co-receptor complex could allow CD19 to freely diffuse in the membrane and interact with the BCR, leading to amplified signaling through the BCR and activation of the B cell.
Tables
X-ray crystallography data collection and refinement statistics.
Refined coordinates and structure factors are deposited in the Protein Data Bank under accession code 6U9S.
| Data collection | 5A6-CD81 LEL |
|---|---|
| Wavelength (Å) | 0.9792 |
| Space Group | P 21 21 21 |
| Number of crystals | 1 |
| Unit cell dimensions | |
| a,b,c | 40.003, 96.858, 297.091 |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 90, 90 |
| Resolution (Å) (last shell) | 49.5–2.4 (2.54–2.4) |
| No. of reflections (total/unique) | 293920/46497 |
| Completeness (%) (last shell) | 99.1 (96.8) |
| I/σ(I) (last shell) | 7.94 (0.46) |
| Rmeas (%) (last shell) | 20.5% (355.7%) |
| CC1/2 (%) (last shell) | 99.5 (16.6) |
| Multiplicity | 6.3 |
| Refinement | |
| Number of atoms (protein/solvent) | 7974/358 |
| Rwork/Rfree (%) | 21.44/28.08 |
| R.M.S. deviation (Å) | |
| Bond length | 0.003 |
| Bond angles | 0.537 |
| Ramachandran statistics | |
| Favored | 96.94 |
| Allowed | 3.06 |
| Outliers | 0.00 |
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody | Rabbit Polyclonal CD19 antibody | Cell Signaling | Cat#3574S; RRID:AB_2275523 | 1:500 (western blot) |
| Antibody | CD19 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (SJ25-C1), Alexa Fluor 488 | Thermo-Fisher | Cat#MHCD1920; RRID:AB_389313 | 2 µg/mL (flow cytometry) |
| Antibody | GAPDH (D16H11) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (HRP Conjugate) | Cell Signaling | Cat#8884S; RRID:AB_11129865 | 1:10,000 (western blot) |
| Antibody | APC Mouse Monoclonal anti-human CD81 | BioLegend | Cat#349510; RRID:AB_2564020 | 2 µg/mL (flow cytometry) |
| Antibody | Human Monoclonal CD81 Clone Ab5 | Recombinant; Nelson et al., 2018 | 2 µg/mL (flow cytometry) | |
| Antibody | Human Monoclonal CD81 Clone Ab10 | Recombinant; Nelson et al., 2018 | 2 µg/mL (flow cytometry) | |
| Antibody | Human Monoclonal CD81 Clone Ab21 | Recombinant; Nelson et al., 2018 | 2 µg/mL (flow cytometry) 1:1000 (western blot) | |
| Antibody | Human Monoclonal CD81 Clone 5A6 | Recombinant; WO 2017/218691 A1 | 2 µg/mL (flow cytometry) 1:100 (western blot) | |
| Antibody | Human Monoclonal CD19 (Coltuximab) | Recombinant; Therapeutic Antibody Database | 2 µg/mL (flow cytometry) | |
| Antibody | Human Monoclonal CD19 (Denintuzumab) | Recombinant; Therapeutic Antibody Database | 2 µg/mL (flow cytometry) | |
| Antibody | Human Monoclonal CD19 (Inebiliziumab) | Recombinant; Therapeutic Antibody Database | 2 µg/mL (flow cytometry) | |
| Antibody | APC Mouse Monoclonal CD86 antibody | BioLegend | Cat#374208; RRID:AB_2721449 | 2 µg/mL (flow cytometry) |
| Antibody | APC Mouse Monoclonal CD20 Clone L27 | BD Biosciences | Cat#340941; RRID:AB_1645724 | 1 µg/mL (flow cytometry) |
| Antibody | Donkey anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) HRP Conjugate | Sigma Aldrich | Cat#GENA934-1ML; RRID:AB_2722659 | 1:5000 (western blot) |
| Antibody | Rabbit Anti-Human IgG H and L HRP Conjugate | Abcam | Cat#ab6759; RRID_:AB_955434 | 1:5000 (western blot) |
| Antibody | F(ab')2-Goat anti-Human IgG, IgM (H+L), Functional Grade | Thermo-Fisher | Cat#16-5099-85 | 20 µg/mL (B cell activation) |
| Biological sample (human) | Leuko-reduction Collar | Brigham and Women’s Hospital Crimson Core | ||
| Commercial assay or kit | QuickExtract DNA Extraction Solution | VWR | Cat#76081–766 | |
| Chemical compound | Valproic Acid Sodium Salt | Sigma Aldrich | Cat#P4543-25G | |
| Chemical compound, drug | D-(+)-Glucose solution | Sigma Aldrich | Cat#G8769-100ML | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Magnesium Formate DiHydrate | Hampton Research | Cat#HR2-537 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | StockOptions Sodium Acetate | Hampton Research | Cat#HR2-933-01 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Polyethylene Glycol Monomethyl Ether 550 | Hampton Research | Cat#HR2-611 | |
| Other | MicroTools | Hampton Research | Cat#HR4-837 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | RosetteSep Human B Cell Enrichment Cocktail | STEMCELL Technologies | Cat#15024 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Lymphoprep density gradient medium | STEMCELL Technologies | Cat#07851 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Nutridoma-SP | Sigma Aldrich | Cat#11011375001 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | n-Dodecyl-B-D-maltoside (DDM) | Anatrace | Cat#D310 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Cholesteryl Hemisuccinate | Sigma Aldrich | Cat#C6512 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Iodoacetamide | Sigma Aldrich | Cat# I1149-5G | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Benzonase nuclease | Sigma Aldrich | Cat# E1014-25KU | |
| Commercial assay or kit | In-Fusion HD Cloning Plus | Clontech | Cat# 638911 | |
| Cell line (human) | Expi293F Cells | Thermo-Fisher | Cat#A14527 | |
| Cell line (human) | CD81 null HEK293T cells | This paper | HEK293T cells with CD81 knocked out using CRISPR/Cas9 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | gRNA forward primer for CD81 knockout cell line generation | Integrated DNA Technologies | CACCGATGCGCTGCGTCTGCGGCG | |
| Sequence-based reagent | gRNA reverse primer for CD81 knockout cell line generation | Integrated DNA Technologies | AAACCGCCGCAGACGCAGCGCATC | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pcDNA3.1 (+) Mammalian Expression Vector | Thermo-Fisher | Cat#V79020 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pFUSE-hIgG1-Fc2 | InvivoGen | Cat#pfuse-hg1fc2 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pD2610-v5 CMV(v5)-ORF Mamm-ElecD | ATUM | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | gBlocks | Integrated DNA Technologies | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pSpCas9(BB)−2A-GFP (PX458) | Addgene | Cat#48138 | |
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism 8.0 | N/A | http://www.graphpad.com/scientific-software/prism/ | |
| Software, algorithm | BD Accuri C6 Plus software | BD Accuri C6 Plus | http://www.bdbiosciences.com/en-us/instruments/research-instruments/research-cell-analyzers/accuri-c6-plus | |
| Software, algorithm | SB Grid Consortium | Morin et al., 2013 | https://sbgrid.org/software/ | |
| Software, algorithm | XDS | Kabsch, 2010 | https://sbgrid.org/software/ | |
| Software, algorithm | Phenix | Afonine et al., 2012 | https://sbgrid.org/software/ | |
| Software, algorithm | Coot | Emsley and Cowtan, 2004 | https://sbgrid.org/software/ | |
| Software, algorithm | PyMOL | DeLano, 2010 | https://sbgrid.org/software/ |





