Biochemical basis for the regulation of biosynthesis of antiparasitics by bacterial hormones
Figures
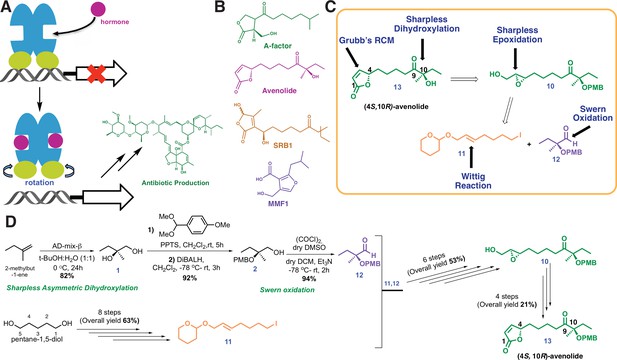
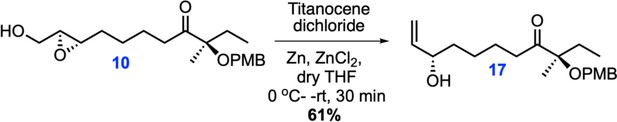
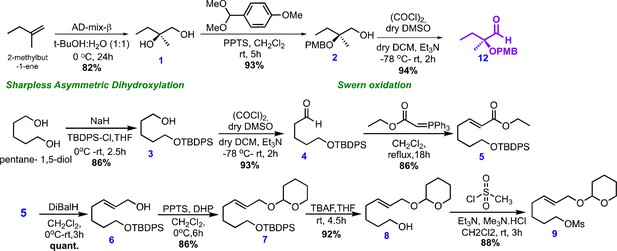
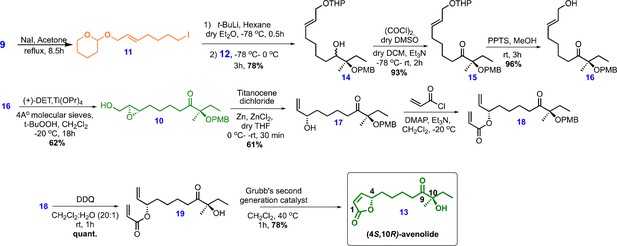
Chemical structures and retrosynthetic scheme for avenolide.
(A) Representation of the mechanism for hormone-induced transcriptional activation in bacteria. (B) Structures of representative compounds from the four known classes of bacterial hormones. A-factor is a γ-butyrolactone, avenolide is an alkylbutenolide, SRB1 is a 2-alkyl-3-methyl-4-hydroxybutenolide, and MMF1 is a 2-alkyl-4-hydroxymethylfuran-3-carboxylic acid. (C) Retrosynthetic scheme for avenolide synthesis involving five key reactions. (D) Overall summarized and synthetic scheme for total synthesis of (4S,10R)-avenolide with total number of steps and reaction yields.
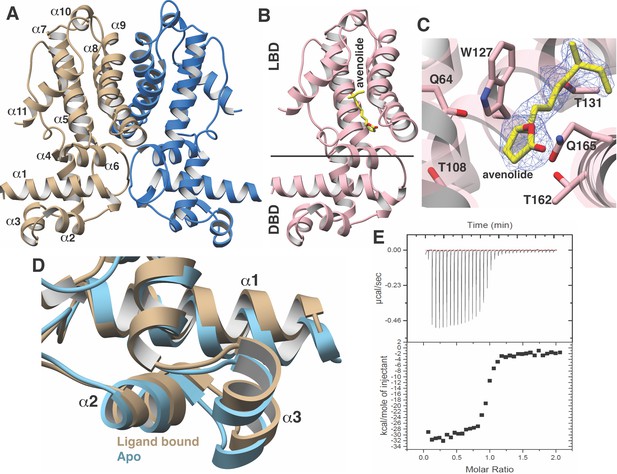
Structural characterization of the AvaR1-avenoide binding interaction.
(A) Structure of the AvaR1 homodimer in the absence of bound ligand. One monomer is shown colored in blue and another in brown. (B) Co-crystal structure of one monomer of AvaR1 (in pink) bound to (4S,10R)-avenolide (in yellow ball-and-stick). The ligand-binding domain (LBD) and the DNA-binding domain (DBD) are indicated. (C) Difference Fourier map (countered at 3 σ) calculated with coefficients |F(obs)|–|F(calc)| with the coordinates of the avenolide omitted prior to one round of refinement. The coordinates of the final structure are superimposed. (D) Superposition of the structures of the DBD of AvaR1 in the presence (brown) and absence (cyan) of bound ligand. Ligand binding induces a 10o shift in this domain that would preclude DNA binding. (E) Representative binding isotherm for the interaction of AvaR1 with (4S,10R)-avenolide indicative of a 1:1 binding stoichiometry.
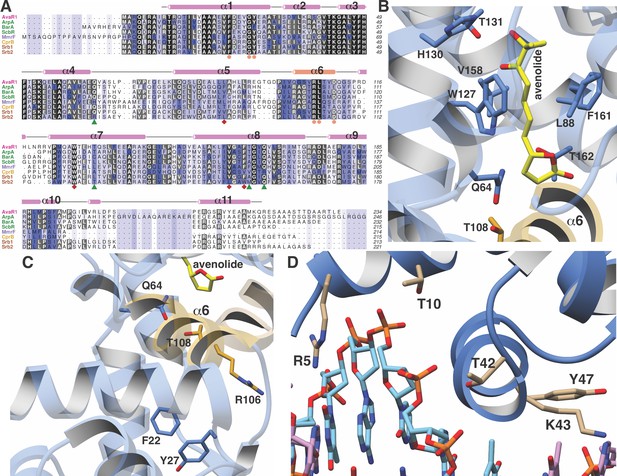
Close-up views of AvaR1-ligand and DNA structures.
(A) Multiple sequence alignment of various GBL-like receptors for which ligand specificity is known. The color-coding of the receptor names reflects the ligand class as colored in Figure 1B. Residues involved in interactions with the lactone are marked by green triangles, those interacting with the alkyl chain are marked by red diamonds, and those proposed to be involved in mediating hormone-dependent conformational movement are marked with orange circles. (B) Close-up view of the hormone-binding cavity showing residues that are in contact with the bound ligand. (C) Spatial orientation of conserved residues that are proposed to induce movement of the DBD in response to binding of the hormone at the ligand-binding domain. (D) Close-up view of the DBD of AvaR1 in complex with the aco ARE.
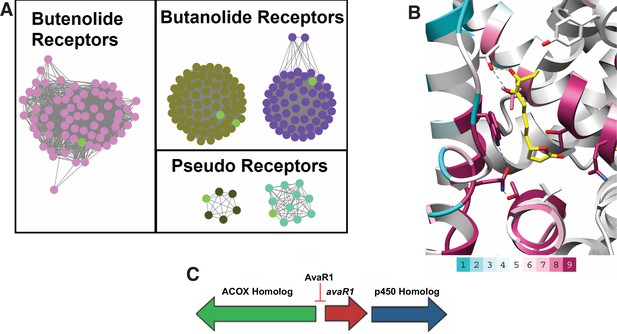
Sequence Similarity Networks of likely butenolide gene clusters.
(A) Sequence Similarity Networks (SSN) showing the relationship between different clades of putative butenolide receptors. Characterized receptors are shown in light green. (B) Conservation of sequences amongst the 90 putative butenolide receptors identified by bioinformatics mapped onto the structure of AvaR1. The color range indicates the least conserved (cyan) through to the most conserved (purple). (C) Genomic synteny used to cull sequences for the SSN.
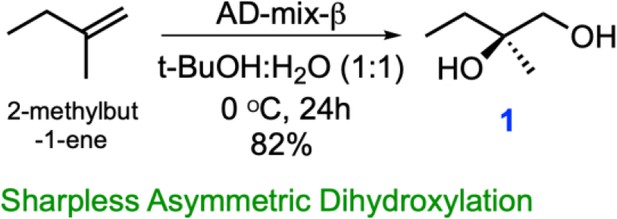
One step synthesis of (R)-2-Methylbutane-1,2-diol (1) from 2-methyl-1-butene via Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation.
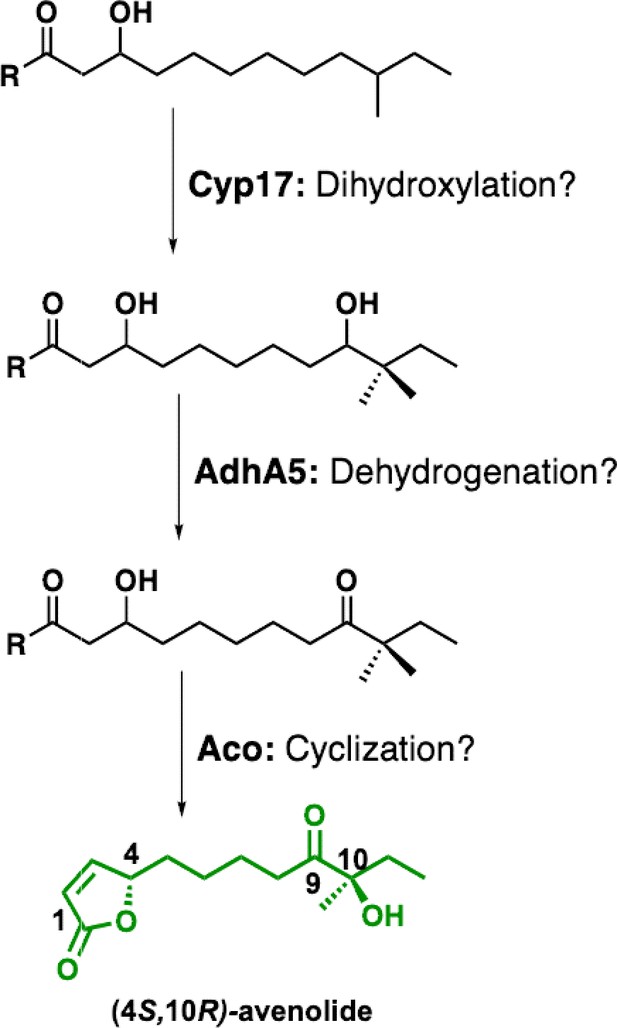
Proposed biosynthetic pathway for avenolide and putative roles of biosynthetic genes.
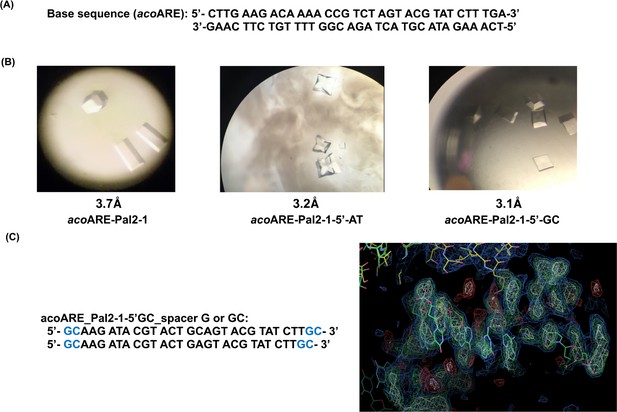
Crystallographic studies with DNA oligonucleotides.
(a) AvaR1 binding site in the upstream region of aco gene. (b) Crystals obtained with DNA Oligo Pal2-1 variant sequences; below the structure on the right is the screenshot from COOT depicting the electron density of the DNA oligo. (c) Proposed sequences containing linker with 1 bp or 2bp length.
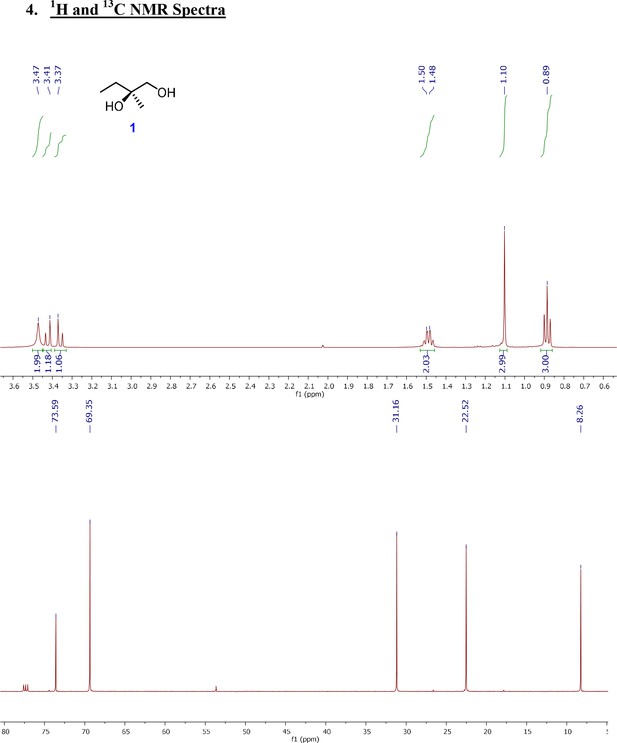
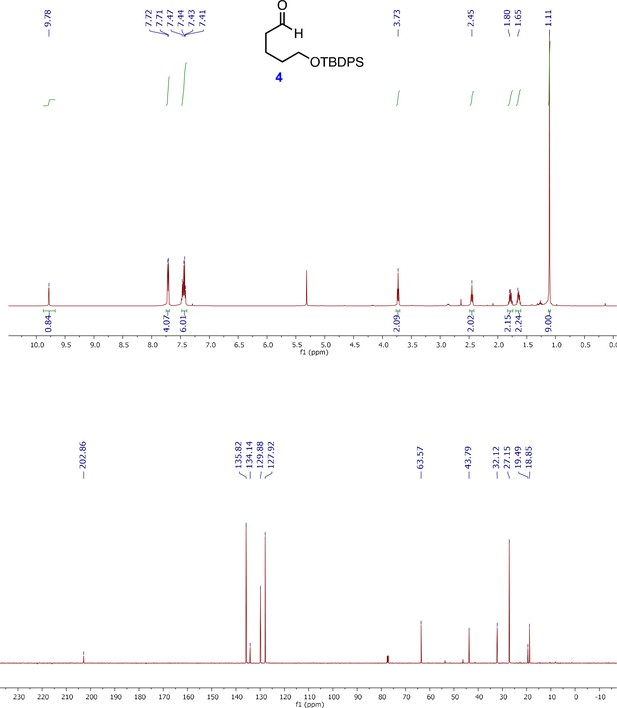
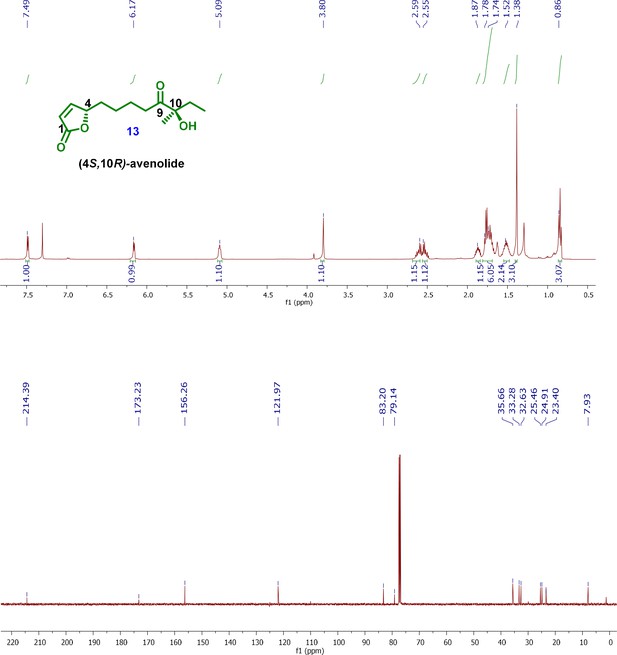
1H and 13C NMR spectra of key intermediates and final product (4S,10R)-avenolide.
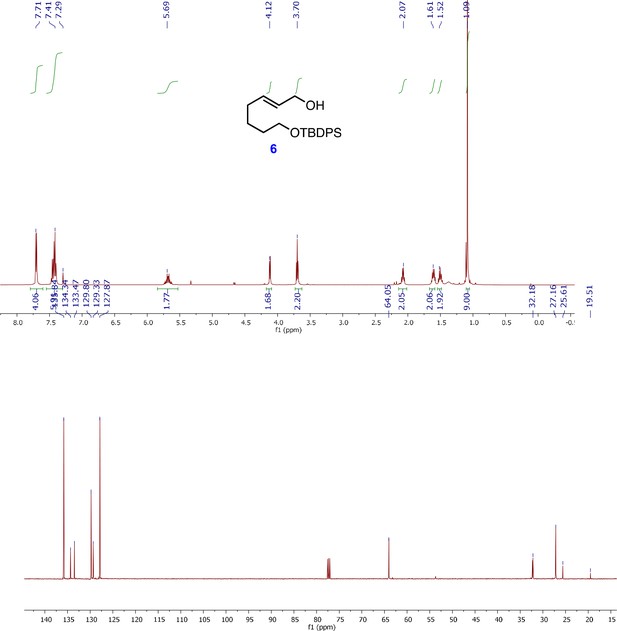
1H and 13C NMR spectra of (E)-7-((tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)oxy)hept-2-en-1-ol (6).
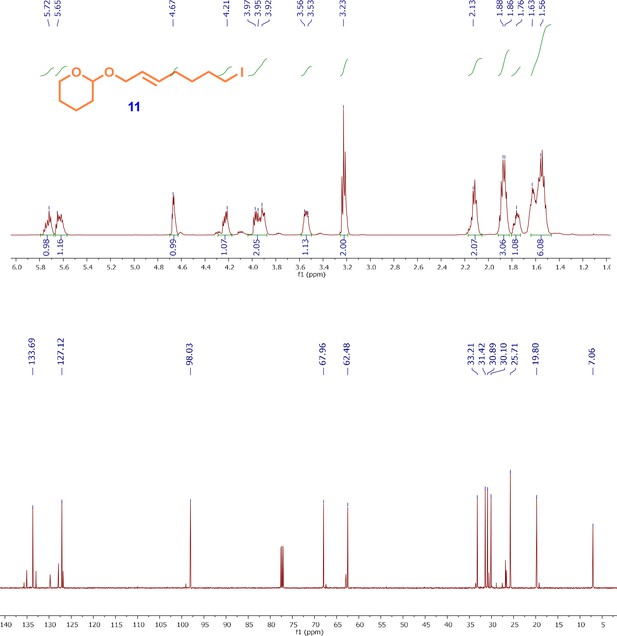
1H and13C NMR spectra of iodo-alkene intermediate; (E)-2-((7-iodohept-2-en-1-yl)oxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran (11).
1H and 13C NMR spectra of allyl alcohol intermediate; (R)-8-((2S,3S)3-(Hydroxymethyl)oxiran-2-yl)3-((4-methoxybenzyl)oxy)3-methyloctan-4-one (17).
1H and 13C NMR spectra of acrylyl alkene intermediate; (3S,9R)-9-((4-methoxybenzyl)oxy)-9-methyl-8-oxoundec-1-en-3-yl acrylate (18).
Tables
List of all of the acoARE oligonucleotides tried for co-crystallization with AvaR1.
Pal in the name denotes the palindromic sequences that have been designed using the first or the second half of the symmetric sequence, which are self-annealing. The first half of the sequence is complementary to the second half.
Target sequence (acoARE): 5′-CTTGAAGACAAAACCGTCTAGTACGTATCTTTGA-3′ 3′-GAACTTC TGTTTTGGCAGATCATGCATAGAAACT- 5′
| Aco_ARE_Oligo | Sequence |
|---|---|
| acoARE +1 | 5′-GAAGACAAAACCGTCTAGTACGTATCTTTGA-3′ 3′-CTTC TGTTTTGGCAGATCATGCATAGAAACT-5′ |
| acoARE +4 | 5′-CTTGAAGACAAAACCGTCTAGTACGTATCTTTGACCT-3′ 3′-GAACTTC TGTTTTGGCAGATCATGCATAGAAACTGGA-5′ |
| acoARE +5 | 5′-ACTTGAAGACAAAACCGTCTAGTACGTATCTTTG ACCTC-3′ 3′-TGAACTTC TGTTTTGGCAGATCATGCATAGAAACTGGAG-5′ |
| acoARE_pal1 | 5′-TTG AAG ACA AAA CCG TCT AGA CGG TTT TGT CTT CAA-3′ |
| acoARE_pal2 | 5′-TCA AAG ATA CGT ACT AGT ACG TAT CTT TGA- 3′ |
| acoARE_pal1 +one each | 5′-CTTG AAG ACA AAA CCG TCT AGA CGG TTT TGTCTTCAAG-3′ |
| acoARE_pal2 +one each | 5′-GTCA AAG ATA CGT ACT AGT ACG TAT CTT TGAC-3′ |
| acoARE_pal1-5' over A | 5′-ATTG AAG ACA AAA CCG TCT AGA CGG TTT TGT CTT CAA-3′ |
| acoARE_pal2 5' over A | 5′-ATCA AAG ATA CGT ACT AGT ACG TAT CTT TGA-3′ |
| acoARE_pal1-2 each | 5′- G AAG ACA AAA CCG TCT AGA CGG TTT TGT CTT C-3′ |
| acoARE_pal2-1 each | 5′- CA AAG ATA CGT ACT AGT ACG TAT CTT TG- 3′ |
| acoARE_pal2-2 each | 5′- A AAG ATA CGT ACT AGT ACG TAT CTT T- 3′ |
| acoARE_pal2-1-3’G | 5′- CA AAG ATA CGT ACT AGT ACG TAT CTT T- 3′ |
| acoARE_pal2-1each-5’C | 5′- CCA AAG ATA CGT ACT AGT ACG TAT CTT TG- 3′ |
| acoARE_pal2-1each-3’G | 5′- CA AAG ATA CGT ACT AGT ACG TAT CTT TGG- 3′ |
| acoARE_pal2 −1e+GCpair | 5′- GCA AAG ATA CGT ACT AGT ACG TAT CTT TGC- 3′ |
| acoARE_Pal2-3each | 5′-AAG ATA CGT ACT AGT ACG TAT CTT- 3′ |
| acoARE_Pal2-1-5'CG | 5′-CGAAG ATA CGT ACT AGT ACG TAT CTT CG- 3′ |
| acoARE_Pal2-1-5'GC | 5′- GCAAG ATA CGT ACT AGT ACG TAT CTT GC- 3′ |
| acoARE_Pal2-1-5'TA | 5′- TAAAG ATA CGT ACT AGT ACG TAT CTT TA- 3′ |
| acoARE_Pal2-1-5'AT | 5′-ATAAG ATA CGT ACT AGT ACG TAT CTT AT- 3′ |
| acoARE_Pal2-1-5'GC-Mid G | 5′- GCAAG ATA CGT ACTG AGT ACG TAT CTT GC- 3′ |
| acoARE_Pal2-1-5'GC-Mid GC | 5′- GCAAG ATA CGT ACTGC AGT ACG TAT CTT GC- 3′ |
List of identified Streptomyces strains with homology to aco, avar1, and cyp genes involved in avenolide biosynthesis in S. avermitilis.
Strains are from the genus Streptomyces unless otherwise noted.
| Receptor | Aco | Cyp450 | Strain |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADK59_29015 | ADK59_RS28945 | ADK59_RS28935 | XY332 |
| ADK54_RS22575 | ADK54_RS22580 | ADK54_RS22570 | WM6378 |
| SPRI_RS01555 | SPRI_RS01560 | SPRI_RS01550 | S. pristinaespiralis |
| SPRI_RS34865/spbR | SPRI_RS34860 | SPRI_RS34870 | S. pristinaespiralis |
| AVL59_26260 | AVL59_RS26265 | AVL59_RS26255 | S. griseochromogenes strain ATCC 14511 |
| ASE41_15570/scaR | ASE41_RS08690 | ASE41_RS08700 | Streptomyces sp. Root264 |
| B446_03460 | B446_RS03395 | B446_RS03385 | S. collinus (strain DSM 40733/Tu 365) |
| SAZU_2710 | AOQ53_RS12925 | AOQ53_RS12915 | S. azureus strain ATCC 14921 |
| tylP | orf18 | orf16 | S. fradiae |
| TU94_00975 | TU94_RS00980 | TU94_RS00965 | S. cyaneogriseus subsp. noncyanogenus |
| AT728_21175 | AT728_RS06415 | AT728_RS06425 | S. silvensis |
| SSFG_07848 | SSFG_07849 | SSFG_07847 | S. viridosporus ATCC 14672 |
| AQJ91_00095 | AQJ91_RS00090 | AQJ91_RS00100 | RV15 |
| SGLAU_25540 | SGLAU_RS25200 | SGLAU_RS25210 | S. glaucescens |
| AQI88_17505 | AQI88_RS17500 | AQI88_RS17510 | S. cellostaticus |
| avaR1 | aco/SM007_06205 | cyp17 | S. avermitilis |
| BEN35_RS25960 | BEN35_RS25965 | BEN35_RS25955 | S. fradiae strain Olg4R |
| SGM_6044 | SGM_6045 | SGM_6043 | S. griseoaurantiacus M045 |
| AQJ66_RS29075 | AQJ66_29065 | AQJ66_RS29080 | S. bungoensis |
| BIV23_RS09990 | BIV23_RS09995 | BIV23_RS09985 | MUSC 1 |
| OP17_RS26145 | OP17_RS26140 | OP17_RS26150 | S. aureofaciens strain NRRL B-1286 |
| AOK23_RS06340 | AOK23_RS06335 | AOK23_RS06345 | S. torulosus strain NRRL B-3889 |
| AOK12_RS18690 | AOK12_RS18695 | AOK12_RS18685 | S. kanamyceticus strain NRRL B-2535 |
| AOK14_RS28840 | AOK14_RS28845 | AOK14_RS28835 | S. neyagawaensis strain NRRL B-3092 |
| JHAT_RS31450 | JHAT_RS31455 | JHAT_RS31445 | JHA26 |
| IG92_RS0101750 | IG92_RS0101755 | IG92_RS0101745 | S. cacaoi subsp. cacaoi NRRL S-1868 |
| IH57_RS0113175 | IH57_RS0113170 | IH57_RS0113180 | NRRL F-5053 |
| TR46_RS36115 | TR46_RS36110 | TR46_RS36120 | Streptacidiphilus carbonis strain NBRC 100919 |
| AWZ10_RS30605 | AWZ10_RS30600 | AWZ10_RS30610 | S. europaeiscabiei strain 96–14 |
| AMK31_RS05975 | AMK31_RS05980 | AMK31_RS05970 | TSRI0107 |
| OQI_RS18015 | OQI_RS18020 | OQI_RS18010 | S. pharetrae CZA14 |
| AOK15_RS33540 | AOK15_RS33545 | AOK15_RS33535 | S. ossamyceticus strain NRRL B-3822 |
| AOK17_RS00790 | AOK17_RS00795 | AOK17_RS00785 | S. phaeochromogenes strain NRRL B-1248 |
| B079_RS0125750 | B079_RS0125745 | B079_RS0125755 | LaPpAH-108 |
| AMK33_RS39295/AMK33_38290 | AMK33_RS39290 | AMK33_RS39300 | CB02400 |
| ASC56_RS07050 | ASC56_RS07055 | ASC56_RS07045 | TP-A0356 |
| BEK98_43205 | BEK98_43200 | BEK98_RS44190 | S. diastatochromogenes |
| SAMN04487983_101174 | SAMN04487983_101173 | SAMN04487983_101175 | yr375 |
| B5181_21375 | B5181_21380 | B5181_21370 | 4F |
| B9W62_10200 | B9W62_10205 | B9W62_10195 | CS113 |
| SAMN05216260_11022 | SAMN05216260_11023 | SAMN05216260_11021 | S. jietaisiensis |
| BN2145_RS03090 | BN2145_RS03095 | BN2145_RS03085 | S. leeuwenhoekii |
| KY5_6076 | KY5_6075 | KY5_6077 | S. formicae |
| CW362_40715/CW362_RS40740 | CW362_40710 | CW362_40720 | S. populi |
| SAMN05421806_12721 | SAMN05421806_12722 | SAMN05421806_12720 | S. indicus |
| CTU88_08915 | CTU88_08920 | CTU88_08910 | JV178 |
| BX282_0700 | BX282_0701 | BX282_0699 | 1121.2 |
| SAMN06272765_6800 | SAMN06272765_6799 | SAMN06272765_6801 | Ag109_G2-15 |
| CJD44_11095 | CJD44_11100 | CJD44_11090 | alain-838 |
| C3488_RS02995 | C3488_RS03000 | C3488_RS02990 | Ru72 |
| C6Y14_RS06395 | C6Y14_06390 | C6Y14_RS06400 | A217 |
| IF73_RS0131080 | IF73_RS0131075 | IF73_RS0131085 | NRRL F-5727 |
| C6N75_16870/C6N75_RS16880 | C6N75_16875 | C6N75_RS16865 | ST5x |
| VO63_07870 | VO63_07865 | VO63_07875 | S. showdoensis |
| IF54_RS0133395 | IF54_RS0133390 | IF54_RS0133400 | NRRL B-3229 |
| EW58_RS46355 | EW58_RS46360 | EW58_RS46350 | S. mirabilis |
| BG482_RS07255 | BG482_RS07260 | BG482_RS07250 | LUP30 |
| STEPF7_RS00065 | STEPF7_RS00060 | STEPF7_RS00070 | F-7 |
| C6376_26350 | C6376_26345 | C6376_26355 | P3 |
| BS75_RS38740 | BS75_RS38735 | BS75_RS38745 | Streptacidiphilus albus JL83 |
| SMA5143A_3910 | SMA5143A_3909 | SMA5143A_3911 | MA5143a |
| SLUN_38640 | SLUN_38645 | SLUN_38635 | S. lunaelactis |
| CLW08_6960/CLW08_RS34500 | CLW08_6959 | CLW08_6961 | 69 |
| CLW15_0573 | CLW15_0574 | CLW15_0572 | 73 |
| DC095_032510 | DC095_032505 | DC095_032515 | S. xinghaiensis |
| C8R36_7975 | C8R36_7974 | C8R36_7976 | 3212.5 |
| CLW07_7979 | CLW07_7978 | CLW07_7980 | 67 |
| BX279_8804 | BX279_8803 | BX279_8805 | Ag82_O1-9 |
| C8R37_8029 | C8R37_8028 | C8R37_8030 | 3212.4 |
| DT_019_27550 | DT_019_27545 | DT_019_27555 | SDr-06 |
| EDD87_5077 | EDD87_5076 | EDD87_5078 | S. ossamyceticus |
| C4J65_35580 | C4J65_35585 | C4J65_35575 | CB09001 |
| DI272_14555 | DI272_14560 | DI272_14550 | Act143 |
| DKG34_25265 | DKG34_25260 | DKG34_25270 | NWU49 |
| CLW14_9027 | CLW14_9026 | CLW14_9028 | 75 |
| EDE03_1306 | EDE03_1307 | EDE03_1305 | Ag82_G5-5 |
| E2B92_31970 | E2B92_31965 | E2B92_31975 | WAC05374 |
| FE633_RS10505 | FE633_RS10500 | FE633_RS10510 | NEAU-C151 |
| FGD71_RS00515 | FGD71_RS00510 | FGD71_RS00520 | NEAU-SSA 1 |
| FNX44_RS06285 | FNX44_RS06290 | FNX44_RS06280 | OF1 |
| E4K73_RS21075 | E4K73_RS21070 | E4K73_RS21080 | IB201691-2A2 |
| EV585_RS00830 | EV585_RS00825 | EV585_RS00835 | BK335 |
| EV288_RS22310 | EV288_RS22315 | EV288_RS22305 | BK215 |
| DN402_06475 | DN402_06480 | DN402_06470 | SW4 |
| F3T56_RS11975 | F3T56_RS11980 | F3T56_RS11970 | TRM68348 |
| EV298_RS42585 | EV298_RS42590 | EV298_RS42580 | BK042 |
| ESG85_RS18290 | ESG85_RS18295 | ESG85_RS18285 | TRM44457 |
| EV588_RS28855 | EV588_RS28860 | EV588_RS28850 | BK141 |
| B9W62_10200 | B9W62_10205 | B9W62_10195 | CS113 |
| FB157_RS34410 | FB157_RS34405 | FB157_RS34415 | BK340 |
| TNCT1_RS20710 | TNCT1_RS20705 | TNCT1_RS20715 | 1–11 |
| Sri02f_RS33870 | Sri02f_RS33865 | Sri02f_RS33875 | S. rishiriensis strain NBRC 13407 |
Crystallographic refinement parameters.
| SeMet AvaR1 | AvaR1-avenolide | AvaR1-DNA | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data collection | |||
| Space group | P21 | P21 | P42 |
| Cell: a, b, c (Å)/β (o) | 42.0, 78.9, 130.2/93.3 | 44.4, 232.5, 87.7/92.7 | 130.5, 130.5, 180.6 |
| Resolution (Å)* | 50–2.4 (2.5–2.40) | 116–2.0 (2.0–1.99) | 130–3.08 (3.13–3.08) |
| Total reflections | 166,803 | 570,056 | 836,259 |
| Completeness (%) | 99.9 (98.9) | 95.9 (65.4) | 100 (100) |
| Rsym (%) | 8.8 (62.8) | 13.4 (62.1) | 7.7 (127.5) |
| Redundancy | 5.2 (5.2) | 4.8 (5.5) | 15.1 (15.2) |
| I /σ(I) | 7.6 (1.8) | 10.5 (2.5) | 25.9 (2.2) |
| Refinement | |||
| Resolution (Å) | 39.3–2.4 | 25.0–2.0 | 25.0–3.09 |
| Number reflections | 31,643 | 110,860 | 52,651 |
| Rwork/Rfree† | 22.3/27.5 | 19.9/24.1 | 19.5/26.3 |
| Number of atoms | |||
| Protein | 6843 | 13,313 | 13,169 |
| Water | 249 | 1299 | – |
| DNA/ligand | – | 136 | 1148 |
| B-factors | |||
| Protein | 54.3 | 22.9 | 105.3 |
| Water | 44.6 | 31.7 | – |
| DNA/ligand | – | 15.8 | 82.3 |
| R.M.S. deviations | |||
| Bond lengths (Å) | 0.012 | 0.009 | 0.010 |
| Bond Angles (o) | 1.58 | 1.48 | 1.69 |
-
*Highest resolution shell is shown in parenthesis.
†R-factor = Σ(|Fobs|-k|Fcalc|)/Σ |Fobs| and R-free is the R value for a test set of reflections consisting of a random 5% of the diffraction data not used in refinement.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Key resources table.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57824/elife-57824-supp1-v2.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57824/elife-57824-transrepform-v2.docx