Genetic surveillance in the Greater Mekong subregion and South Asia to support malaria control and elimination
Figures
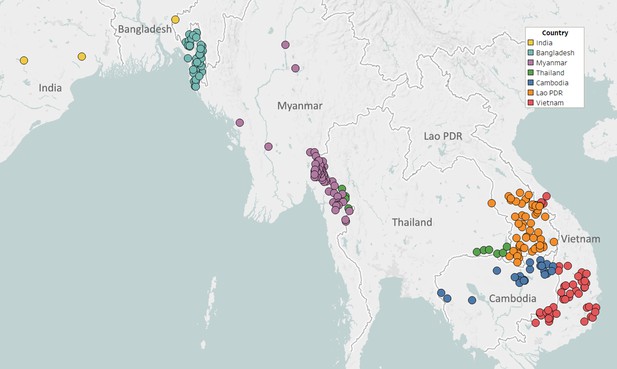
Map of GenRe-Mekong sample collection sites in Asia.
Sites markers are colored by country. One site in Kinshasa (DR Congo) not shown.
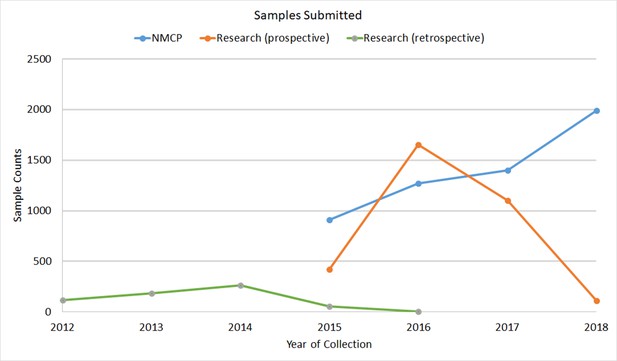
Trends in sample collections over time.
Numbers of samples collected prospectively each year by surveillance projects (blue) and research studies (orange) are compared. Sample counts submitted retrospectively by research projects (green) are also shown.
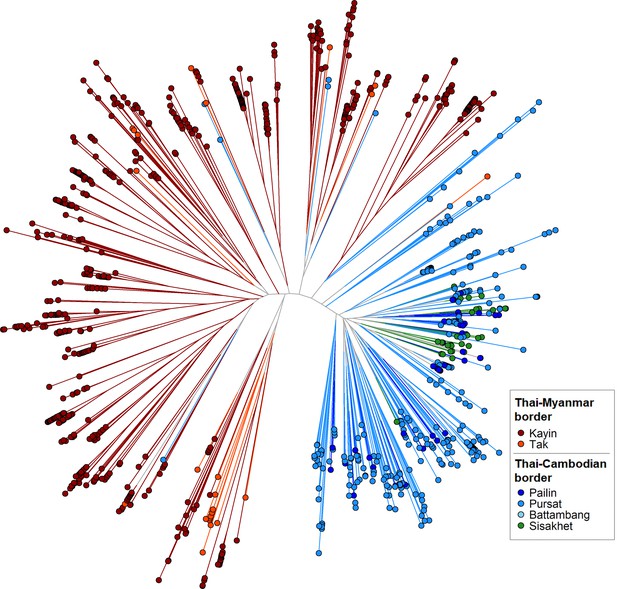
Neighbor-joining tree using barcode data to show genetic differentiation between parasites in the Thai-Myanmar and Thai-Cambodian border regions.
The tree was derived from a matrix distance matrix, computed by comparing the genetic barcodes of samples. The branch length separating each pair of parasites represents the amount of genetic differentiation between them: individuals separated by shorter branches are more similar to each other. Samples from provinces/states of Myanmar, Thailand, and Cambodia near to the borders were included. Each circular marker represents a sample, colored by the province/state of origin.
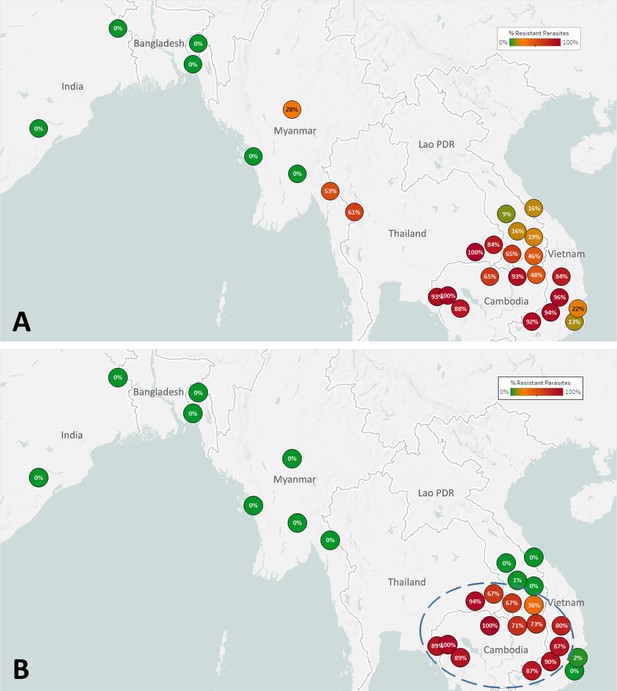
Map of the spread of (A) artemisinin resistance (ART-R) and (B) dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine resistance (DHA-PPQ-R) in Asian countries.
Marker text and color indicate the proportion of sample classified as resistant in each province/state/division surveyed. A total of 6762 samples were included in (A) and 3395 samples in (B), after excluding samples with undetermined phenotype prediction. The results are summarized in Table 3.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Proportions of parasites predicted to be resistant to artemisinin and to the DHA-PPQ combination therapy in each province/state/division.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/62997/elife-62997-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
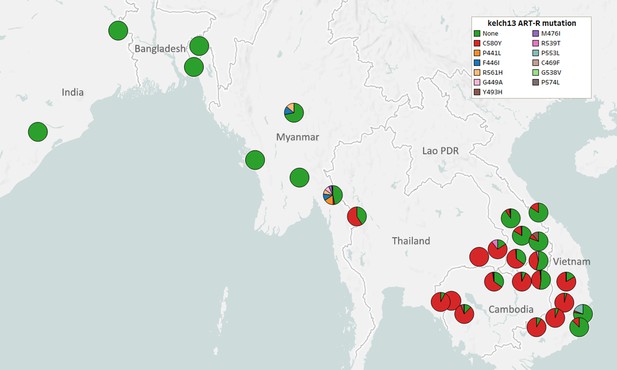
kelch13 allele diversity in Asian countries.
We show a pie chart for each province/state/division surveyed, indicating the relative proportion of different nonsynonymous mutations found in the resistance domains of kelch13. A total of 6758 samples were included in this analysis, after excluding samples where the kelch13 genotype could not be called, and those with undetermined ART-R phenotype prediction. For display clarity, mutations that we only found in singleton samples are also excluded (n=18).
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Sample frequencies for different kelch13 alleles at each province/state/division.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/62997/elife-62997-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
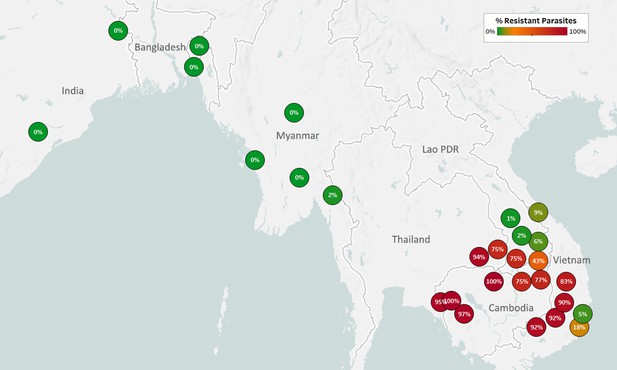
Map of Piperaquine Resistance (PPQ-R) in Asian countries.
Marker text and color indicate the proportion of sample classified as resistant in each province/state/division surveyed. A total of 3552 samples were included in this analysis, after excluding samples where plasmepsin 2/3 copy number could not be determined. The results are summarized in Table 3.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Proportions of parasites predicted to be resistant to piperaquine in each province/state/division.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/62997/elife-62997-fig3-figsupp2-data1-v1.xlsx
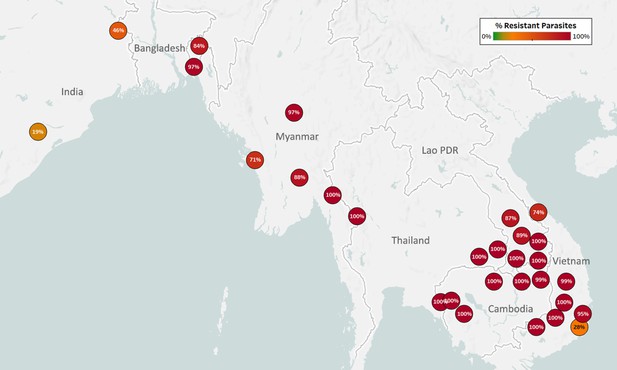
Map of Chloroquine Resistance (CQ-R) in Asian countries.
Marker text and color indicate the proportion of sample classified as resistant in each province/state/division surveyed. A total of 6458 samples were included in this analysis, after excluding samples where the crt core haplotype could not predict a phenotype. The results are summarized in Table 3.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 3—source data 1
Proportions of parasites predicted to be resistant to chloroquine in each province/state/division.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/62997/elife-62997-fig3-figsupp3-data1-v1.xlsx
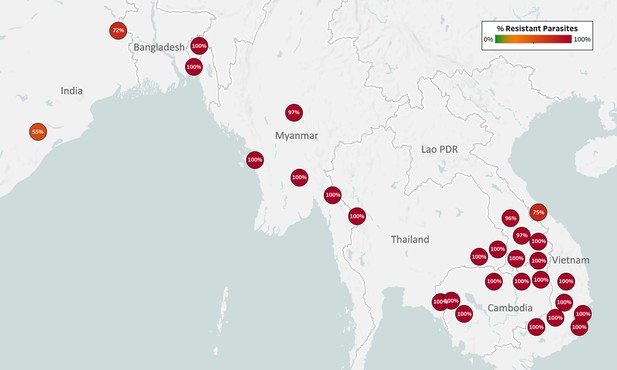
Map of Pyrimethamine Resistance (PYR-R) in Asian countries.
Marker text and color indicate the proportion of sample classified as resistant in each province/state/division surveyed. A total of 7208 samples were included in this analysis, after excluding samples where the dhfr core haplotype could not predict a phenotype. The results are summarized in Table 3.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 4—source data 1
Proportions of parasites predicted to be resistant to pyrimethamine in each province/state/division.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/62997/elife-62997-fig3-figsupp4-data1-v1.xlsx
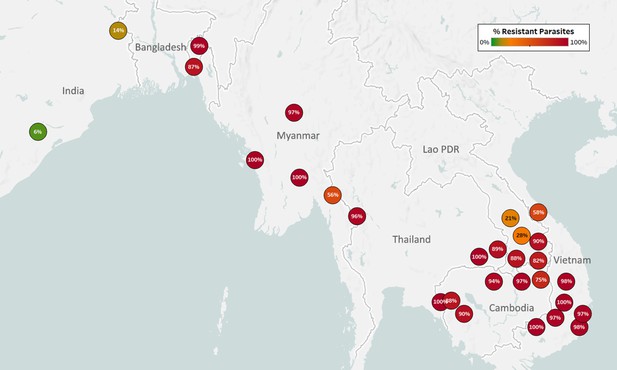
Map of Sulfadoxine Resistance (SD-R) in Asian countries.
Marker text and color indicate the proportion of sample classified as resistant in each province/state/division surveyed. A total of 7095 samples were included in this analysis, after excluding samples where the dhps core haplotype could not predict a phenotype.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 5—source data 1
Proportions of parasites predicted to be resistant to sulfadoxine in each province/state/division.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/62997/elife-62997-fig3-figsupp5-data1-v1.xlsx
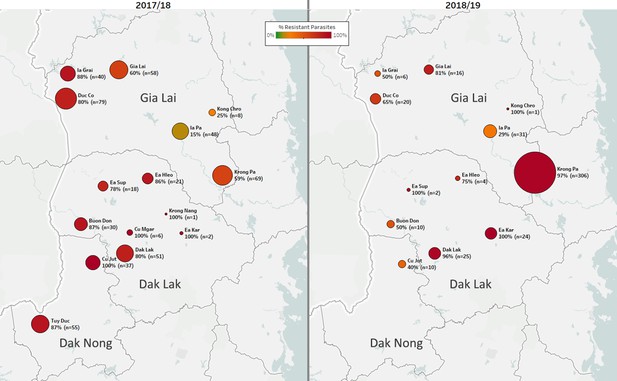
Longitudinal sample counts and proportions of DHA-PPQ-R parasites in three provinces of Central Vietnam.
The same geographical area (Gia Lai, Dak Lak, and Dak Nong provinces) is shown for two malaria seasons: 2017/18 (12 months from May 2017, n=523) and 2018/2019 (the following 12 months, n=455). Districts are represented by markers whose size is proportional to the number of samples, and whose color indicates the frequency of samples carrying both the kelch13 C580Y mutation and the plasmepsin2/3 amplification, and thus predicted to be DHA-PPQ-R. Marker labels show district name, resistant parasite frequency, and sample count.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Proportions of samples predicted to be resistant to DHA-PPQ in districts of Vietnam, in the seasones 2017/18 and 2018/19.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/62997/elife-62997-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
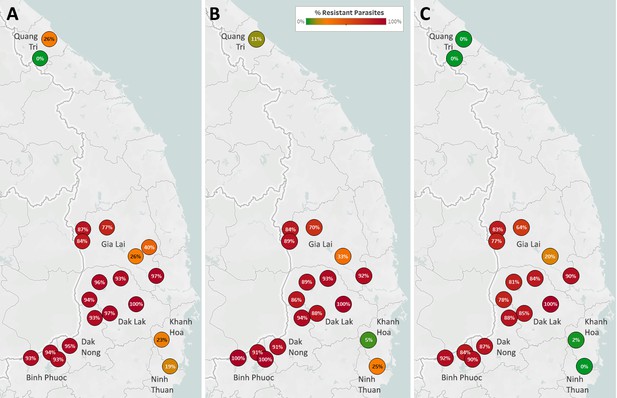
Frequencies of ART-R and PPQ-R parasites in Vietnam.
The three maps show frequencies of predicted resistance to artemisinin (A, n=1543), piperaquine (B, n=1380), and DHA-piperaquine (C, n=1372). Samples are aggregated by district, represented by a marker; estimates are shown only for districts with more than 10 collected samples. Marker text and color indicate the proportion of sample classified as resistant in each district. Labels show the names of the seven provinces where samples were collected.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Counts and proportions of samples predicted to be resistant to artemisinin, piperaquine and DHA-PPQ in provinces of Vietnam.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/62997/elife-62997-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
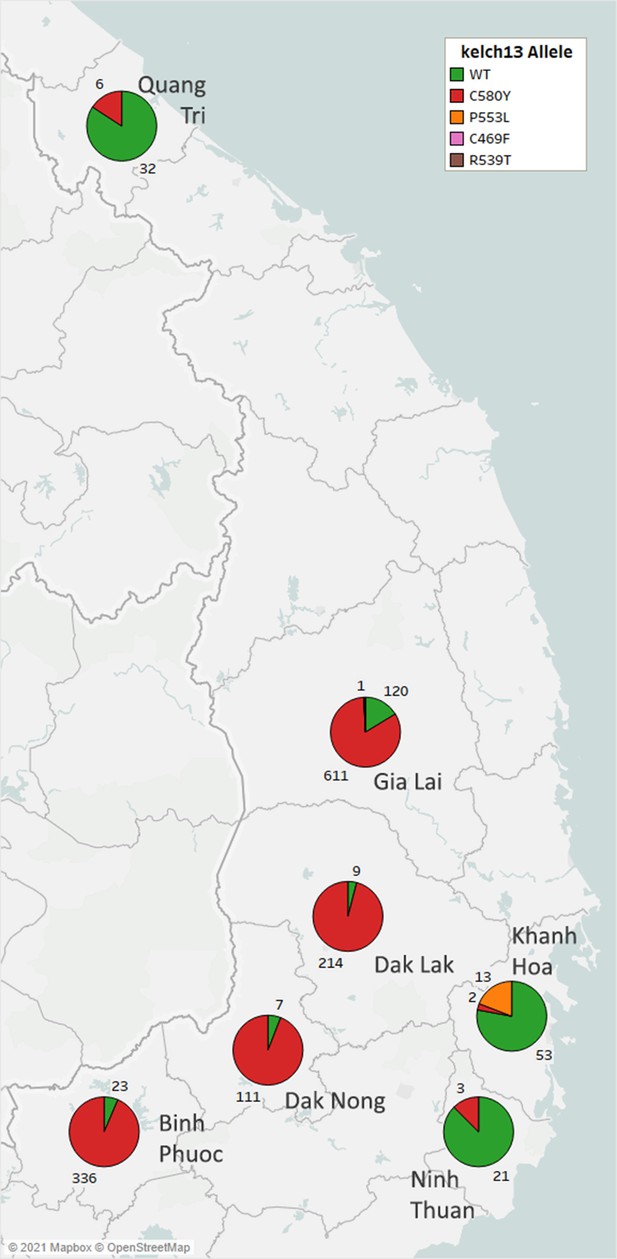
Distribution of kelch13 alleles in seven provinces of Vietnam.
Each pie chart shows the proportions of kelch13 alleles in samples collected in each province. Numbers by each pie slice indicate the actual number of samples carrying that allele. Samples with heterozygous kelch13 calls were disregarded. A total of 1567 samples with kelch13 genotypes were analyzed.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Sample frequencies for different kelch13 alleles in provinces of Vietnam.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/62997/elife-62997-fig4-figsupp2-data1-v1.xlsx
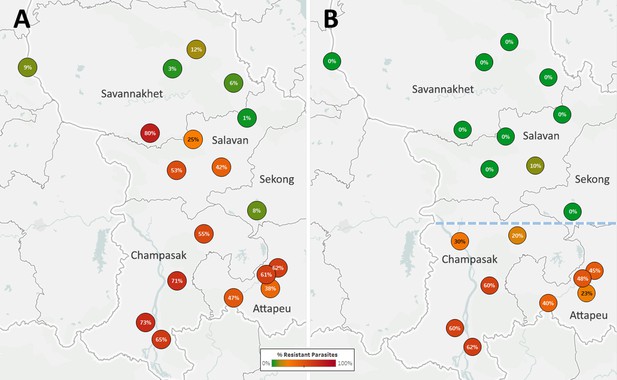
Proportions of ART-R and KEL1/PLA1 parasites in southern Laos districts.
Districts in five provinces of southern Laos are represented by markers whose color and label indicates the frequency of samples classified as ART-R (A) and as DHA-PPQ-R, i.e. possessing markers of resistance to both artemisinin and piperaquine (B). Only districts with more than 10 samples with valid genotypes are shown. In panel (B), a dashed line denotes a hypothetical demarcation line between a Lower Zone, where DHA-PPQ-R strains have spread, and an Upper Zone, where they are absent and ART-R parasites belong to different strains.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Counts and proportions of samples predicted to be resistant to artemisinin and DHA-PPQ in districts of Laos.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/62997/elife-62997-fig5-data1-v1.xlsx
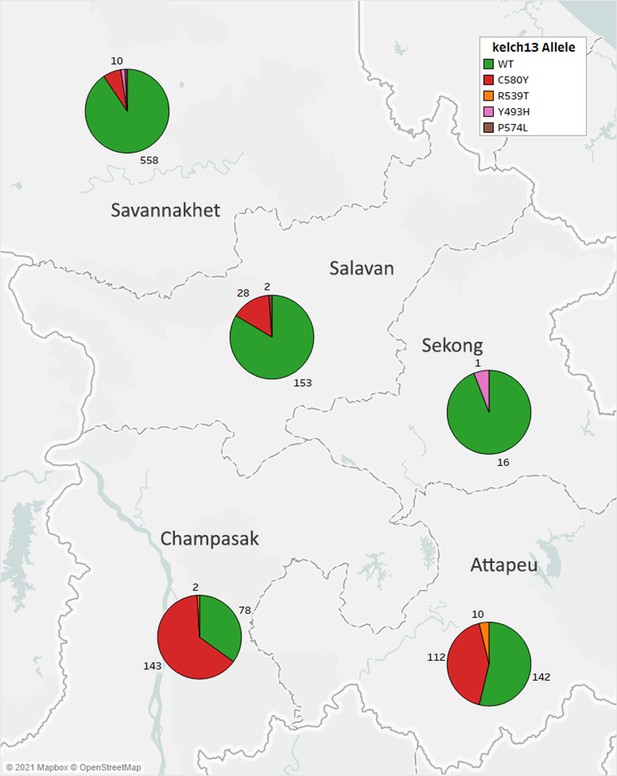
Frequencies Distribution of kelch13 alleles in five provinces of Laos.
Each pie chart shows the proportions of kelch13 alleles in samples collected in each province. Numbers by each pie slice indicate the actual number of samples carrying that allele. Samples with heterozygous kelch13 calls were disregarded. A total of 1303 samples with kelch13 genotypes were analyzed.
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Sample frequencies for different kelch13 alleles in provinces of Laos.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/62997/elife-62997-fig5-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
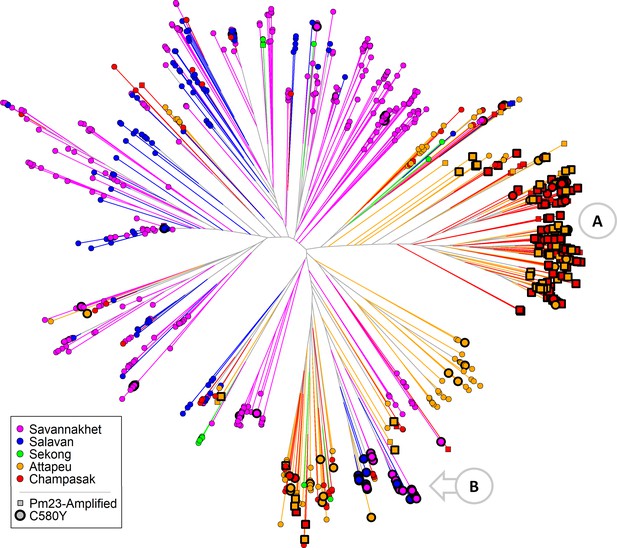
Neighbour-joining tree using barcode data to show genetic differentiation between groups of parasites collected in Southern Laos.
The tree was derived from a genetic distance matrix, computed by comparing the genetic barcodes of samples collected in the Lao PDR (n=1332). Each marker represents a parasite sample, coloured by province. The branch length separating each pair of parasites represents the amount of genetic differentiation between them: individuals separated by shorter branches are more similar to each other. Thicker marker borders indicate parasites carrying thekelch13C580Y mutation, while square markers indicate samples withplasmepsin2/3amplification. Orange circular callouts show notable features of this tree. (A) Shows a large cluster of parasites from the Lower Zone (Attapeu and Champasak provinces) carrying both C580Y andplasmepsin2/3amplification (DHA-PPQ-R). (B) Indicates that C580Y mutants from the Upper Zone (Savannakhet and Salavan provinces) are genetically distinct from the DHA-PPQ-R strains, but also from Upper Zone wild-type parasites.
Tables
Participating studies in GenRe-Mekong.
For each study, we list the NMCP and Research partners involved, the type of study, the geographical region covered and the number of collection sites. In the last two columns, we show the total number of samples submitted, and the number included in the final set of quality-filtered samples used in epidemiology analyses.
| NMCP partner | Research / technical partner | Study type | Regions surveyed | Sites | Submitted samples | Filtered samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Center for Malaria Parasitology and Entomology of Lao PDR (CMPE) | Lao-Oxford-Mahosot Hospital-Wellcome Trust Research Unit (LOMWRU), Vientiane | Genetic Surveillance | South Laos (five provinces) | 51 | 1555 | 1387 |
| Institute of Malariology, Parasitology, and Entomology Quy Nhon (IMPE-QN), Vietnam | Oxford University Clinical Research Unit (OUCRU), Ho Chi Minh City | Genetic Surveillance | Central Vietnam (seven provinces) | 51 | 1632 | 1492 |
| National Institute of Malariology, Parasitology, and Entomology (NIMPE), Vietnam | Vysnova Partners, Mahidol-Oxford Research Unit (MORU) | Epidemiological Study | South Vietnam (three provinces) | 19 | 292 | 265 |
| National Center for Parasitology, Entomology, and Malaria Control (CNM), Cambodia | Genetic Surveillance | Northeast Cambodia (two provinces) | 19 | 182 | 174 | |
| Bangladesh National Malaria Control Programme | Mahidol-Oxford Research Unit (MORU) | Epidemiological Study | Bangladesh (Chittagong Division) | 55 | 2055 | 1575 |
| - | Mahidol-Oxford Research Unit (MORU) | Clinical Efficacy Study | Cambodia, Vietnam, Thailand, Lao PDR, Myanmar, Bangladesh, India, DR Congo | 17 | 1875 | 1123 |
| - | National Institutes of Health (NIH) | Clinical Efficacy Study | Cambodia | 3 | 592 | 502 |
| - | Oxford University Clinical Research Unit (OUCRU) | Epidemiological Study | South Vietnam | 4 | 184 | 175 |
| - | Mahidol-Oxford Research Unit (MORU) | Elimination Study | West Cambodia | 1 | 69 | 32 |
| - | Mahidol-Oxford Research Unit (MORU) | Epidemiological Study | Northeast Thailand | 7 | 87 | 60 |
| - | Shoklo Malaria Research Unit (SMRU) | Clinical Efficacy Study | Thailand (Tak province) | 4 | 29 | 28 |
| - | Shoklo Malaria Research Unit (SMRU) | Elimination Study | Myanmar (Kayin State) | 51 | 1071 | 813 |
| Total | 9623 | 7626 | ||||
Drug resistance-related SNPs genotyped by GenRe-Mekong (excludes kelch13).
| Chromosome | Position | Gene Id | Gene Description | Mutation | Reference | Alternate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pf3D7_04_v3 | 748239 | PF3D7_0417200 | dhfr (bifunctional dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase) | N51I | A | T |
| Pf3D7_04_v3 | 748262 | C59R/Y | T | C | ||
| Pf3D7_04_v3 | 748263 | C59R/Y | G | A | ||
| Pf3D7_04_v3 | 748410 | S108N/T | G | AC | ||
| Pf3D7_04_v3 | 748577 | I164L | A | T | ||
| Pf3D7_05_v3 | 958145 | PF3D7_052300 | mdr1 (multidrug resistance protein 1) | N86Y | A | T |
| Pf3D7_05_v3 | 958440 | Y184F | A | T | ||
| Pf3D7_05_v3 | 961625 | D1246Y | G | T | ||
| Pf3D7_07_v3 | 403623 | PF3D7_0709000 | crt (chloroquine resistance transporter) | N75D/E | T | A |
| Pf3D7_07_v3 | 403625 | K76T | A | C | ||
| Pf3D7_07_v3 | 405362 | N326S | A | G | ||
| Pf3D7_07_v3 | 405600 | I356T | T | C | ||
| Pf3D7_08_v3 | 549681 | PF3D7_0810800 | dhps (dihydropteroate synthetase) | S436A/Y/F/G | T | GC |
| Pf3D7_08_v3 | 549682 | S436A/Y/F/G | C | TAG | ||
| Pf3D7_08_v3 | 549685 | A437G | G | C | ||
| Pf3D7_08_v3 | 549993 | K540E/N | A | GT | ||
| Pf3D7_08_v3 | 549995 | K540E/N | A | TG | ||
| Pf3D7_08_v3 | 550117 | A581G | C | G | ||
| Pf3D7_08_v3 | 550212 | A613S/T | G | TA | ||
| Pf3D7_13_v3 | 748395 | PF3D7_1318100 | fd (ferredoxin) | D193Y | C | A |
| Pf3D7_13_v3 | 2504560 | PF3D7_1362500 | exo (exonuclease) | E415G | A | G |
| Pf3D7_14_v3 | - | PF3D7_1408000 and PF3D7_1408100 | pm23 (plasmepsin 2 and plasmepsin 3) | Breakpoint | - | - |
| Pf3D7_14_v3 | 1956225 | PF3D7_1447900 | mdr2 (multidrug resistance protein 2) | T484I | G | A |
| Pf3D7_14_v3 | 2481070 | PF3D7_1460900 | arps10 (apicoplast ribosomal protein S10) | V127M | G | A |
| Pf3D7_14_v3 | 2481073 | D128Y/H | G | TC |
Frequencies of resistant parasites in provinces/states/divisions surveyed, for different antimalarials.
| Country | Province, State, or Division | ART-R | PPQ-R | DHA-PPQ-R | CQ-R | PYR-R | SD-R | SP-R | SP-R (IPTp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| India | Odisha | 0% | 0% | 0% | 18% | 57% | 6% | 1% | 0% |
| West Bengal | 0% | 0% | 0% | 47% | 71% | 14% | 5% | 0% | |
| Tripura | 0% | 0% | 0% | 85% | 100% | 99% | 55% | 0% | |
| Bangladesh | Chittagong | 0% | 0% | 0% | 97% | 100% | 87% | 46% | 16% |
| Myanmar | Rakhine | 0% | 0% | 0% | 71% | 100% | 100% | 51% | 26% |
| Bago | 1% | 0% | 0% | 88% | 100% | 100% | 91% | 74% | |
| Mandalay | 29% | 0% | 0% | 96% | 98% | 98% | 29% | 24% | |
| Kayin | 54% | 2% | 0% | 100% | 100% | 56% | 73% | 27% | |
| Thailand | Tak | 61% | - | 0% | 100% | 100% | 96% | 100% | 88% |
| Sisakhet | 100% | 90% | 90% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | |
| Ubon Ratchathani | 80% | 75% | 56% | 100% | 100% | 85% | 100% | 17% | |
| Cambodia | Pailin | 93% | 97% | 90% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 56% |
| Battambang | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 88% | 100% | 29% | |
| Pursat | 88% | 98% | 67% | 100% | 100% | 92% | 98% | 44% | |
| Preah Vihear | 61% | 100% | 11% | 100% | 100% | 94% | 98% | 21% | |
| Steung Treng | 93% | 75% | 70% | 100% | 100% | 97% | 100% | 0% | |
| Ratanakiri | 49% | 79% | 42% | 99% | 100% | 76% | 90% | 5% | |
| Laos | Champasak | 66% | 75% | 56% | 100% | 100% | 88% | 94% | 12% |
| Attapeu | 46% | 43% | 31% | 100% | 100% | 82% | 100% | 18% | |
| Sekong | 26% | 6% | 0% | 100% | 100% | 91% | 74% | 5% | |
| Salavan | 17% | 2% | 1% | 89% | 97% | 28% | 38% | 1% | |
| Savannakhet | 10% | 1% | 0% | 87% | 96% | 21% | 41% | 2% | |
| Vietnam | Binh Phuoc | 92% | 93% | 83% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 14% |
| Dak Nong | 94% | 92% | 88% | 100% | 100% | 97% | 96% | 22% | |
| Dak Lak | 96% | 90% | 86% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 99% | 15% | |
| Gia Lai | 84% | 83% | 76% | 99% | 100% | 98% | 95% | 4% | |
| Khanh Hoa | 22% | 5% | 2% | 95% | 100% | 97% | 74% | 2% | |
| Ninh Thuan | 13% | 18% | 0% | 28% | 100% | 98% | 75% | 0% | |
| Quang Tri | 16% | 9% | 0% | 75% | 76% | 59% | 26% | 5% | |
| Congo PDR | Kinshasa | 0% | 0% | 0% | 58% | 98% | 72% | 88% | 0% |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
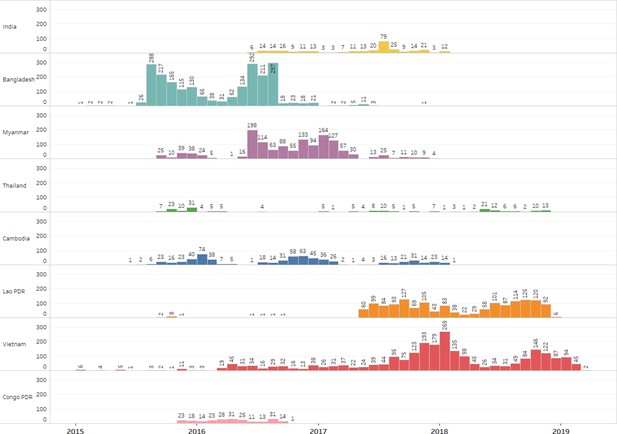
Geographical breakdown by year of samples processed by GenRe-Mekong.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/62997/elife-62997-supp1-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
Counts of processed samples, by province/state/division of origin.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/62997/elife-62997-supp2-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 3
Number of samples carrying mutations in the resistance domains of kelch13 by province/state/division.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/62997/elife-62997-supp3-v1.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/62997/elife-62997-transrepform-v1.docx