Viruses: Neutralizing SARS-CoV-2
November brought a weary world ample reasons for celebration, even as COVID-19 cases surged anew. Among the welcome tidings were reports that mRNA-based vaccines directed at the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein may have efficacies as high as 95%, including in the elderly and other important sub-populations (Jackson et al., 2020; Sahin et al., 2020; Walsh et al., 2020; Widge et al., 2020). In addition, there are early though less definitive suggestions that monoclonal antibodies – antibodies of single specificity generated by cloning and immortalizing a plasma B cell – that target the spike protein may be therapeutic if given early (Chen et al., 2020; Rogers et al., 2020), which is a welcome counterpoint to the generally disappointing results with convalescent plasma (that is, plasma from patients who have recovered from COVID-19; Simonovich et al., 2020). Much now depends upon understanding the human neutralizing antibody response to SARS-CoV-2.
One shortcoming of convalescent plasma is that the levels of neutralizing antibodies are extremely variable, and frequently very low (Muecksch et al., 2020), with higher levels of both immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin A correlating with more severe disease (Cervia et al., 2020). Levels also decline rapidly, by more than 50% in the first three months (Muecksch et al., 2020; Seow et al., 2020). On the other hand, monoclonals with potent neutralization capacity have been consistently obtainable from recovered COVID-19 patients and the relatively low levels of somatic hypermutation – the process by which B cells optimize antibody affinity – observed in these antibodies suggests that they might be readily elicited with the right vaccine (Robbiani et al., 2020; Yuan et al., 2020). However, it is important to understand the probability that SARS-CoV-2 may evolve to escape neutralizing antibodies, whether they are natural, vaccine-induced, or administered monoclonals.
Now, in eLife, Theodora Hatziioannou, Paul Bieniasz and co-workers – including Yiska Weisblum and Fabian Schmidt, both of Rockefeller University, as joint first authors – report data that are timely and important in this context (Weisblum et al., 2020). The researchers performed experiments in which human cells were infected, in the presence of antibodies, with a hybrid virus that mimics SARS-CoV-2. The only virus particles that could survive to propagate onward were those that had mutated in a way that allowed them to escape the antibodies. Specifically, the envelope glycoprotein of an innocuous rabies family virus was substituted with the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (Figure 1). The antibody neutralization sensitivity of this chimeric virus tracks remarkably close to that of SARS-CoV-2, and it also provides a number of additional advantages: it enables high-throughput analyses without requiring high levels of biosecurity; it can be monitored by GFP fluorescence; and it enables the rapid selection of escape mutants because the virus propagates to high titers and – unlike a coronavirus – does not proofread mistakes made during genome copying.
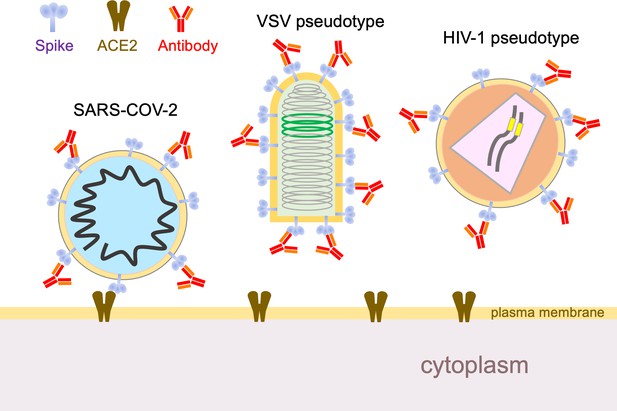
Using hybrid viruses to study SARS-CoV-2 escape from neutralizing antibodies.
The surface of the SARS-CoV-2 virion (left) contains spike proteins (pale blue) that bind to ACE2 receptors (brown), which leads to membrane fusion and entry into the cell. Neutralizing antibodies (red) can stop this happening by binding to the spike proteins, so viruses undergo reciprocal evolution to escape such antibodies. To better understand how viruses evolve to become resistant to different kinds of antibodies, Weisblum et al. developed two hybrid viruses that could be studied in the laboratory. The first was a hybrid rabies family virus (VSV, middle) that carries the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein rather than the normal envelope protein in its outer lipid envelope. This hybrid is replication-competent, carries a GFP transgene (green), and can be used for experiments in which it undergoes serial passage and selection in the presence of convalescent plasma or monoclonal antibodies. The second hybrid was an HIV-1 vector pseudotyped with the spike protein. This hybrid is replication-defective, carries a luciferase transgene (yellow), and completes a single cycle of infection. VSV: vesicular stomatitis virus.
In the presence of potent monoclonal antibodies that target the receptor binding domain of the spike protein, and some but not all convalescent plasmas, the researchers found that it took only two or three passages to select for specific resistance. (An excellent physical feel for these experiments can be had by looking at figure 1B in Weisblum et al., 2020 at higher magnification). When the escaped viruses were sequenced, mutations in the receptor binding domain – and some outside it as well – were identified. None of these mutations impaired replicative fitness in cultured cells in a discernible way.
Notably, mutations that potently blocked a given monoclonal antibody conferred little or no resistance to neutralization by plasma from the same individual (or others). Conversely, plasma from a given individual did not select for resistance to monoclonal antibodies derived from that individual. Finally, there was no overlap in the resistance selected by convalescent plasma from different individuals, suggesting that humoral immune responses are significantly heterogeneous between individuals. However, Weisblum et al. point out that they mostly tested immunoglobulin G in their experiments, whereas immunoglobulin A predominates in lung secretions and on the surfaces of respiratory epithelia, and may be particularly beneficial in the case of SARS-CoV-2 (Wang et al., 2020).
Weisblum et al. then asked an important question: do these mutant viruses exist in real SARS-CoV-2 in the general human population? For these experiments, they used a non-replicating hybrid virus, one based on HIV-1 (Figure 1). Moreover, in addition to the escape mutants selected in their first set of experiments, they used this system to test numerous naturally occurring mutations that have been identified in or near the ACE2 binding site (http://cov-glue.cvr.gla.ac.uk/#/home). This enabled them to identify additional escape mutants. Moreover, both sets of mutants are present, albeit at very low frequencies, in naturally circulating SARS-CoV-2. Thus, they 'pre-exist' and are available for selection to prominence under specific humoral immune pressure.
This situation brings to mind a lesson well learned about RNA viruses from HIV-1, which generates exceptional diversity. Not only is resistance to antiretroviral therapy quickly induced unless combinations of drugs are used, the virus in any one patient is virtually always resistant to the antibodies present in contemporaneous plasma. The problem is less severe for coronaviruses which, alone among RNA viruses, have the ability to proofread errors made during genome copying. Even so, it is likely that all possible single amino acid variants of SARS-CoV-2 currently exist many times over in the global population and perhaps even in many infected individuals. Following the paradigm of antiretroviral therapy, we can anticipate that combinations of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies will be required to securely prevent SARS-CoV-2 resistance. Indeed, Weisblum et al. go on to show that combinations of two antibodies can block the generation of resistance in vitro.
Whether antibody escape will become clinically significant for therapeutics or vaccines is not yet clear and depends on many factors, including the frequency of reinfection – which clearly happens with the four seasonal coronaviruses – and the duration of antibody responses after natural and vaccine-induced immunity. At present, however, there is no evidence that functionally significant SARS-CoV-2 variants have emerged as a result of immune pressure.
Finally, most patients – even those with low aggregate neutralizing activity in plasma – were found to have the ability to generate potent antibodies at low levels. Moreover, the genes of the potent monoclonal antibodies identified so far differ little from the germline sequence (Robbiani et al., 2020; Yuan et al., 2020). It thus seems likely that a properly designed vaccine can induce a durable and potent neutralizing antibody response, which is likely to be more effective and longer-lasting – and much more safely acquired – than responses that follow natural infection. The early mRNA vaccine clinical trial data certainly support initial effectiveness, with duration of immunity the major outstanding question to be answered.
One of the distinctive pleasures of being a virologist is the ability to see the most important and powerful idea in biology – natural selection – happen in real time. It’s even better when the experiments yield useful insights into an urgent medical problem. In this regard, Weisblum et al. have not disappointed.
References
-
Systemic and mucosal antibody responses specific to SARS-CoV-2 during mild versus severe COVID-19Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2020.10.040
-
SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with Covid-19New England Journal of Medicine.https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2029849
-
An mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 — preliminary reportNew England Journal of Medicine 383:1920–1931.https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2022483
-
Longitudinal analysis of serology and neutralizing antibody levels in COVID19 convalescentsThe Journal of Infectious Diseases jiaa659.https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiaa659
-
A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in Covid-19 severe pneumoniaNew England Journal of Medicine.https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2031304
-
Safety and immunogenicity of two RNA-Based Covid-19 vaccine candidatesNew England Journal of Medicine.https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2027906
-
Enhanced SARS-CoV-2 neutralization by dimeric IgAScience Translational Medicine eabf1555.https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.abf1555
-
Durability of responses after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 vaccinationNew England Journal of Medicine.https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc2032195
Article and author information
Author details
Publication history
- Version of Record published: December 15, 2020 (version 1)
Copyright
© 2020, Poeschla
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 2,346
- views
-
- 272
- downloads
-
- 4
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.
Download links
Downloads (link to download the article as PDF)
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools)
Further reading
-
- Evolutionary Biology
- Immunology and Inflammation
CD4+ T cell activation is driven by five-module receptor complexes. The T cell receptor (TCR) is the receptor module that binds composite surfaces of peptide antigens embedded within MHCII molecules (pMHCII). It associates with three signaling modules (CD3γε, CD3δε, and CD3ζζ) to form TCR-CD3 complexes. CD4 is the coreceptor module. It reciprocally associates with TCR-CD3-pMHCII assemblies on the outside of a CD4+ T cells and with the Src kinase, LCK, on the inside. Previously, we reported that the CD4 transmembrane GGXXG and cytoplasmic juxtamembrane (C/F)CV+C motifs found in eutherian (placental mammal) CD4 have constituent residues that evolved under purifying selection (Lee et al., 2022). Expressing mutants of these motifs together in T cell hybridomas increased CD4-LCK association but reduced CD3ζ, ZAP70, and PLCγ1 phosphorylation levels, as well as IL-2 production, in response to agonist pMHCII. Because these mutants preferentially localized CD4-LCK pairs to non-raft membrane fractions, one explanation for our results was that they impaired proximal signaling by sequestering LCK away from TCR-CD3. An alternative hypothesis is that the mutations directly impacted signaling because the motifs normally play an LCK-independent role in signaling. The goal of this study was to discriminate between these possibilities. Using T cell hybridomas, our results indicate that: intracellular CD4-LCK interactions are not necessary for pMHCII-specific signal initiation; the GGXXG and (C/F)CV+C motifs are key determinants of CD4-mediated pMHCII-specific signal amplification; the GGXXG and (C/F)CV+C motifs exert their functions independently of direct CD4-LCK association. These data provide a mechanistic explanation for why residues within these motifs are under purifying selection in jawed vertebrates. The results are also important to consider for biomimetic engineering of synthetic receptors.
-
- Genetics and Genomics
- Immunology and Inflammation
Transposable elements (TEs) are repetitive sequences representing ~45% of the human and mouse genomes and are highly expressed by medullary thymic epithelial cells (mTECs). In this study, we investigated the role of TEs on T-cell development in the thymus. We performed multiomic analyses of TEs in human and mouse thymic cells to elucidate their role in T-cell development. We report that TE expression in the human thymus is high and shows extensive age- and cell lineage-related variations. TE expression correlates with multiple transcription factors in all cell types of the human thymus. Two cell types express particularly broad TE repertoires: mTECs and plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs). In mTECs, transcriptomic data suggest that TEs interact with transcription factors essential for mTEC development and function (e.g., PAX1 and REL), and immunopeptidomic data showed that TEs generate MHC-I-associated peptides implicated in thymocyte education. Notably, AIRE, FEZF2, and CHD4 regulate small yet non-redundant sets of TEs in murine mTECs. Human thymic pDCs homogenously express large numbers of TEs that likely form dsRNA, which can activate innate immune receptors, potentially explaining why thymic pDCs constitutively secrete IFN ɑ/β. This study highlights the diversity of interactions between TEs and the adaptive immune system. TEs are genetic parasites, and the two thymic cell types most affected by TEs (mTEcs and pDCs) are essential to establishing central T-cell tolerance. Therefore, we propose that orchestrating TE expression in thymic cells is critical to prevent autoimmunity in vertebrates.






