The LRR-TM protein PAN-1 interacts with MYRF to promote its nuclear translocation in synaptic remodeling
Figures
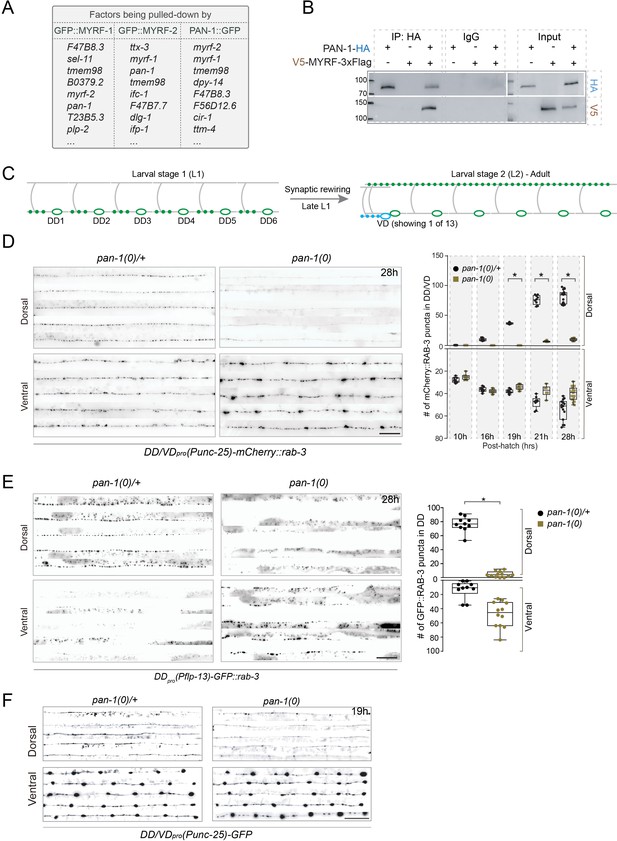
pan-1 mutants exhibit blocked synaptic rewiring.
(A) Top of list for factors interacting with MYRF-1, MYRF-2, and PAN-1, identified by co-IP and Mass-Spec analysis. The factors are ranked by specificity of the binding. The strains used are myrf-1(ju1121); myrf-1pro-GFP::myrf-1::Flag (ybqEx164), myrf-2(ybq42); myrf-2pro-GFP::myrf-2 (ybqIs128), and pan-1GFP (ybq47). Complete list of IP-MS results can be found in Supplementary file 1 for MYRF-1, Supplementary file 2 for MYRF-2, and Supplementary file 3 for PAN-1. (B) Co-immunoprecipitation of PAN-1 and MYRF in HEK293T cells. Rabbit anti-HA was used in co-IP, and the target bands in Western Blot were visualized using murine anti-HA and murine anti-V5. (C) Illustration of synaptic rewiring in six DDs. The presynaptic sties, indicated by green dots, are localized in ventral processes at L1, and become localized in dorsal processes after the rewiring is complete. The rewiring begins from late L1 and is complete by late L2. Ventral D (VD) is a class of GABAergic neurons analogous to DDs and born at late L1. Presynaptic sites of VDs form in their ventral processes. (D) Deficient synaptic remodeling in pan-1(gk142) mutants. The presynaptic sites in DD/VD are labeled by unc-25pro-mCherry::rab-3(juIs236). Images of five ventral and dorsal cords are vertically tiled. At 28 hr, the synaptic remodeling was complete in control animals pan-1(gk142)/mT1, marked by the formation of dorsal synapses. In contrast, there was few clear clusters in dorsal cord of pan-1 mutants. Scale bar, 20 μm. In quantification graph, the number of synapses in DD/VD of pan-1(gk142) and control animals pan-1(gk142)/mT1 were counted, which is shown as Mean ± SEM (t test. *, p<0.001). (E) Deficient synaptic remodeling in pan-1(gk142) mutants. The presynaptic sites in DD are labeled by flp-13pro-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs46). Images of five ventral and dorsal cords are vertically tiled. At 28 hr, the synaptic remodeling was complete in control animals pan-1(gk142)/mT1, marked by the formation of dorsal synapses and disappearance of ventral synapses. In contrast, there was few clear clusters in dorsal cord of pan-1 mutants while ventral synapses were retained. Scale bar, 20 μm. In quantification graph, the number of synapses in DD of pan-1(gk142) and control animals pan-1(gk142)/mT1 were counted, which is shown as Mean ± SEM (t test. *, p<0.001). (F) Axon morphology of DD neurons is normal in pan-1(gk142) mutants. The axons were labeled by unc-25pro-GFP(juIs76). It is normal that a gap is present between dorsal processes of DD3 and DD4 in a subset of animals of this stage. More than 15 animals were examined for each genotype. Images of five ventral and dorsal cord were vertically tiled. Scale bar, 20 μm.
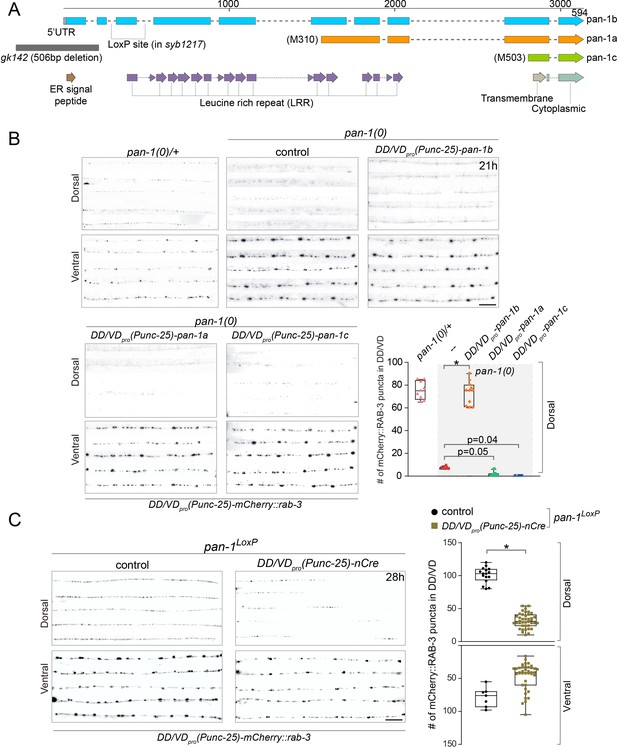
PAN-1 functions cell-autonomously in synaptic rewiring.
(A) Illustration of pan-1 gene and protein domains. Three pan-1 transcripts are produced via trans-splicing. gk142 deletion eliminates the promoter and all three transcripts. The insertion sites of LoxP insertion in pan-1(syb1217) are indicated. (B) Deficient synaptic remodeling in pan-1(gk142) was rescued by DD/VD-expressing pan-1b, but not pan-1a or pan-1c. The presynaptic sites in DD/VD are labeled by unc-25pro-mCherry::rab-3(juIs236). The stage of animals was 21 post-hatch hours. Images of five ventral and dorsal cords are vertically tiled. Scale bar, 20 μm. The number of synapses in DD/VD of genotype-indicated animals was counted and shown as Mean ± SEM (t test. *, p<0.001). Expressed were three isoforms of pan-1: unc-25pro-pan-1b::GFP(ybqIs131); unc-25pro-pan-1a(ybqEx624); unc-25pro-pan-1c(ybqEx626). (C) DD/VD-specific gene inactivation of pan-1. pan-1LoxP(syb1217) animals with or without DD/VD-expressed nCre transgene, unc-25pro-nCre(tmIs1073). Two LoxP sequences are inserted inside the flanking introns of the third exon of pan-1 gene. Animals are labeled by presynaptic marker in DD/VD, unc-25pro-mCherry::rab-3(juIs236). In the presence of nCre, segments of synapses are missing in dorsal cords. Images of five ventral and dorsal cords are vertically tiled. Scale bar, 20 μm. The number of synapses in DD/VD of genotype-indicated animals was counted and shown as Mean ± SEM (t test. *, p<0.001).
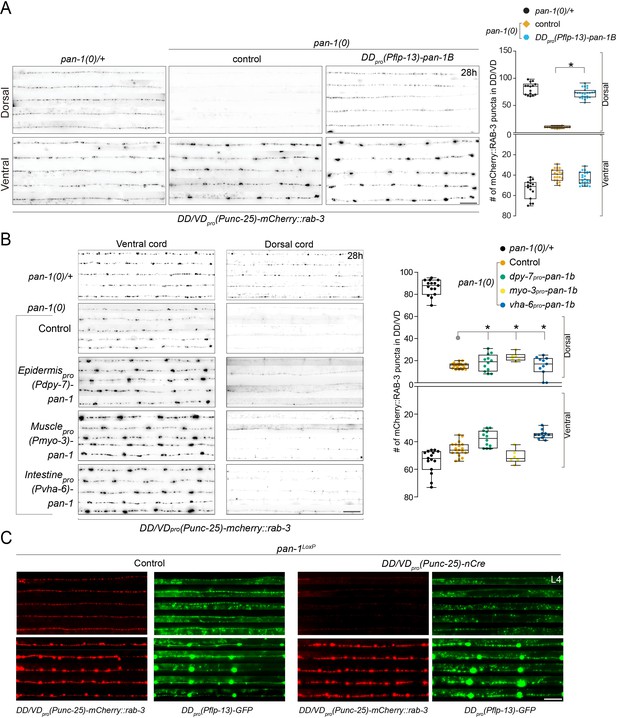
PAN-1 acts cell-autonomously.
(A) Synpatic remodeling defects in pan-1(0) is rescued by flp-13pro-driven pan-1. flp-13pro is specifically expressed in DDs among ventral cord motor neurons, even though it is also expressed in a number of head neurons. Images of five ventral and dorsal cord were vertically tiled. Scale bar, 20 μm. At right was quantification of synapse number in DD/VD of indicated genotypes, which was shown as Mean ± SEM (t test. *, p<0.00.0001). (B) Synaptic remodeling in control animals (pan-1(gk142)/mT1) and pan-1(gk142) mutants carrying transgene of pan-1 expressed in epidermis (dpy-7pro-pan-1b (ybqEx741)), muscle (myo-3pro-pan-1b (ybqEx737)), and intestine (vha-6pro-pan-1b (ybqEx739)). Animals were labeled by presynaptic marker in DD/VD, unc-25pro-mCherry::rab-3(juIs236). Images of five ventral and dorsal cord were vertically tiled. Deficient synaptic remodeling in pan-1(gk142) mutants could not rescued by either of the transgenes. Scale bar, 20 μm. At right was quantification of synapse number in DD/VD of indicated genotypes, which was shown as Mean ± SEM (t test. ns, p>0.05). (C) Axon morphology of DDs are normal in pan-1LoxP(syb1217), unc-25pro-nCre(tmIs1073) animals. The animals were colabeled by presynaptic marker in DD/VD, unc-25pro-mCherry::rab-3(juIs236) and axonal marker, flp-13pro-GFP(juIs145). Note that dorsal synapses were largely absent in nCre-expressing animals, but the DD axons were all present. Images of five ventral and dorsal cords are vertically tiled. Shown are red and green channels of the same individuals. Scale bar, 20 μm.
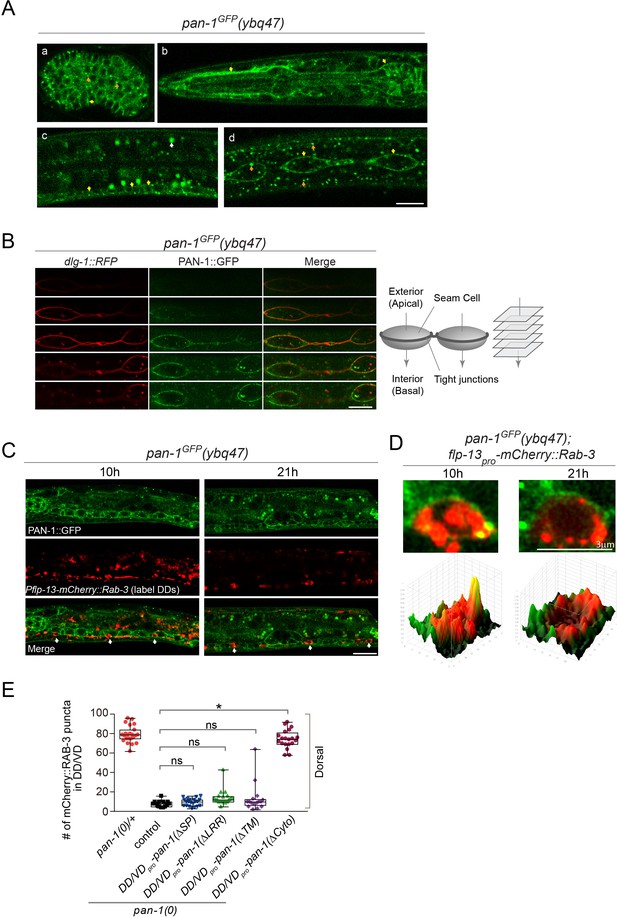
PAN-1 localizes on the cell membrane.
(A) Signals of PAN-1GFP in pan-1GFP(ybq47) (knock-in) animals. a, embryo. b, head region of L2 larva. c and d, trunk region of L2 larva with a focus on ventral cord neurons (yellow arrows) and seam cells (yellow arrows), respectively. Yellow arrow, GFP at the cell membrane. Orange arrow, GFP as cytoplasmic puncta. White arrow, auto-fluorescence. Images are single optical slices by confocal microscopy. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) Localization of PAN-1GFP(ybq47) in respect to tight junction protein DLG-1::RFP(mcIs46) in seam cells. Shown are a consecutive series of confocal optical sections (0.36-μm-thick section at 0.7 μm interval on Z-axis). PAN-1 partially overlaps with DLG-1, but primarily localizes at basal lateral membrane of seam cell (towards the interior). Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) Colocalization of PAN-1GFP and DD neuron marker. The animals pan-1GFP(ybq47); Pflp-13-mCherry::rab-3(ybqIs1) at 10, 21 post-hatch hours were imaged by Airyscan confocal microscopy. The animals carry glo-1(zu391) to reduce auto-fluorescence. RAB-3 is localized in cytoplasm, while PAN-1 is enriched on the cell membrane. White arrow, soma of DDs. Scale bar, 10 μm. (D) Shown are the magnified images of DD soma from the colabeling experiment (C), and 3-D intensity plots of green and red signals in the upper image. (E) Quantification of the synaptic remodeling in pan-1(gk142) carrying transgenes of DD/VD-expressed pan-1 variants. The number of synapses in DD/VD of animals of indicated genotypes were counted and shown as Mean ± SEM (t test. ns, p>0.05. *, p<0.001.). Expressed in the transgenes are unc-25pro-pan-1ΔSP(ybqEx643); unc-25pro-pan-1ΔLRR(ybqEx642); unc-25pro-pan-1ΔTM (ybqEx644); unc-25pro-pan-1ΔCyto(ybqEx645).
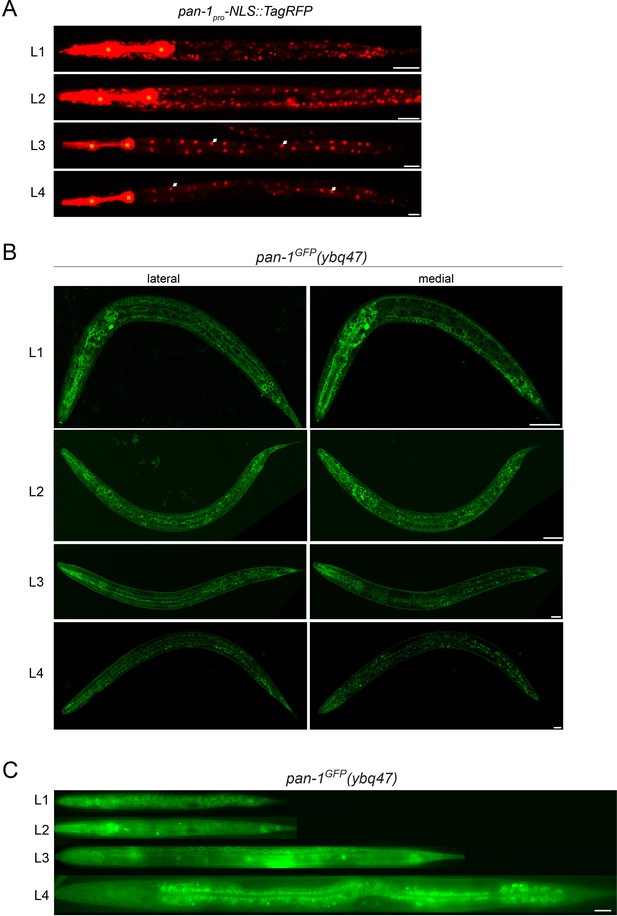
pan-1 expression is temporally regulated during development.
(A) Expression of pan-1 transcription reporter (pan-1pro-NLS::tagRFP(ybqIs138)) at four larval stages. RFP is observed broadly at L1 and L2, but downregulated at L3 in most of tissues except for intestine (white arrows). * marks the signals of co-injection marker myo-2pro-mCherry that is expressed in pharynx. Scale bar, 20 μm. (B) Signals of PAN-1GFP in pan-1GFP(ybq47) animals at four larval stages. These are Airyscan Images of sagittal section of animal. Lateral and medial positions of the same animals are shown. The strain carries Pflp-13-mCherry::rab-3(ybqIs1); the transgene has a co-injection marker Pttx-3-RFP, the fluorescence of which could leak into green channel. The strain also carries glo-1(zu391) to reduce auto fluorescence. Scale bar, 20 μm. (C) Signals of PAN-1GFP in pan-1GFP(ybq47) animals at four larval stages. The images were acquired by wide-field microscope. The display parameters for all images are identical. The strain carries glo-1(zu391) to reduce auto fluorescence. Scale bar, 20 μm.
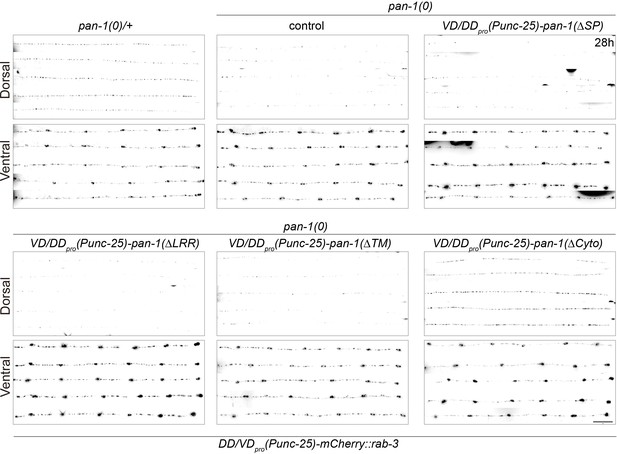
LRR region and TMD of PAN-1 are important for synaptic rewiring.
Representative images from pan-1(gk142)/mT1, pan-1(gk142), and pan-1(gk142) carrying transgene unc-25pro-pan-1ΔSP(ybqEx643); unc-25pro-pan-1ΔLRR(ybqEx642); unc-25pro-pan-1ΔTM (ybqEx644); unc-25pro-pan-1ΔCyto(ybqEx645). Presynaptic sites in DD/VD are labeled by unc-25pro-mCherry::rab-3(juIs236). Images of five ventral and dorsal cords are vertically tiled. Scale bar, 20 μm.
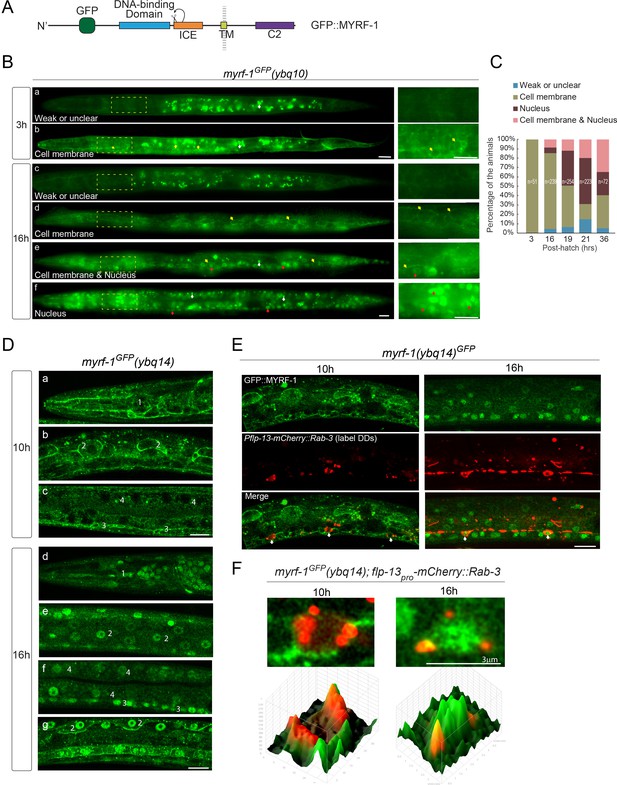
MYRF localizes on the cell membrane and is cleaved at specific stages.
(A) Illustration of functional domains of MYRF. GFP is inserted after Ala171 within the N-MYRF. (B) MYRF-1GFP signals in animals of early and late L1 imaged using wide-field microscope and sCMOS camera. GFP was primarily observed at the cell membrane in myrf-1GFP(ybq10) (Knock in) animals at three post-hatch hours (b). Three types of GFP patterns were observed within a population of the animals at 16 post-hatch hours, that is primarily on the cell membrane (d), primarily in the nucleus (f), and in both (e). A small population of animals showed weak, unclear, or inconsistent signals throughout the body (a, c). The panels on the right show the framed areas in a-f (dotted lines) with higher magnification. White arrow, auto-fluorescence. Yellow arrow, GFP at the cell membrane. Red arrow, GFP in the nucleus. Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) Quantification of animals showing particular pattern of MYRF-1GFP (as in (B)) at various stages. (D) Single optical-plane images of MYRF-1GFP(ybq14) at 10, 16 post-hatch hours acquired by Airyscan confocal microscopy. ybq14 is made by knocking in 3xFlag at C’ of myrf-1 in ybq10 background (Meng et al., 2017). ybq10 and ybq14 are of no difference in MYRF-1GFP signals. All sections are sagittal. a, d, head region. b, e, g, lateral (left-right) section of the middle (head-tail) segment of animal. c, f, medial (left-right) section of the middle (head-tail) segment of animal. a, b, c, GFP at the cell membrane. d, e, f, GFP in the nucleus. g, GFP at the cell membrane and in the nucleus. Number 1–4 labels selective anatomical structures and cell types, including the position of metacorpus –the middle part of pharynx (1), seam cell (2), ventral nerve cord (3), intestine (4). Scale bar, 10 μm. (E) Colocalization of MYRF-1GFP and DD neuron marker. The animals myrf-1GFP(ybq14); Pflp-13-mCherry::rab-3(ybqIs1) at 10, 16 post-hatch hours were imaged by Airyscan confocal microscopy. The animals carry glo-1(zu391) to reduce auto-fluorescence. RAB-3 is localized in cytoplasm. White arrow, soma of DDs. Scale bar, 10 μm. (F) Shown are the magnified image of DD soma from the colabeling experiment (E), and 3-D intensity plots of green and red signals in the upper image.
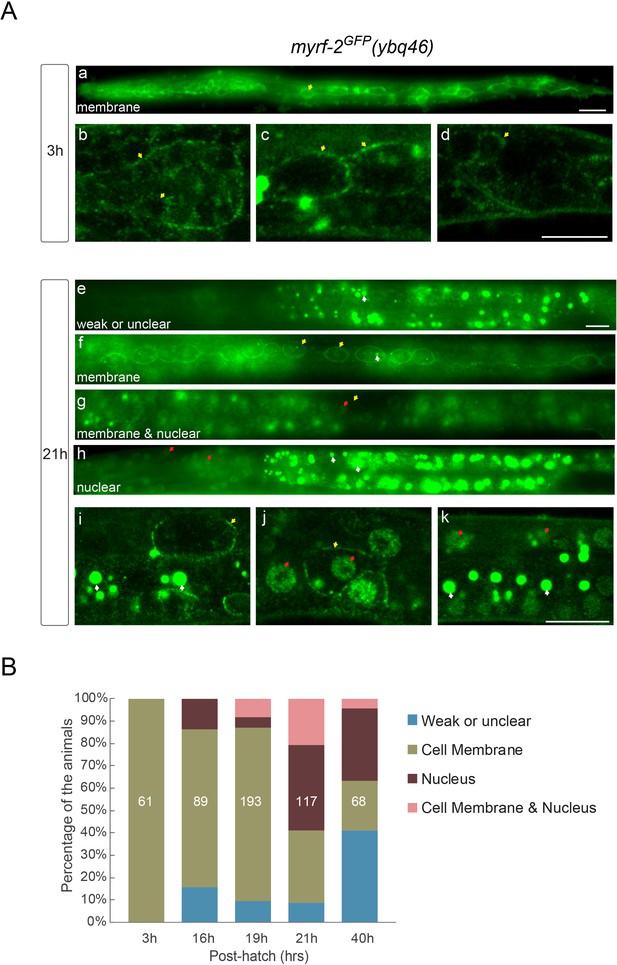
MYRF-2 is localized at cell membrane.
(A) MYRF-2GFP signals in myrf-2GFP(ybq46) +(Knock in) animals were detected during larval development. At early L1 (three post-hatch hours) (a–d), GFP signals are detected primarily at cell membrane. a, wild-field image of a whole 3 hr larva. b-d, single optical slices by Airyscan confocal microscopy. b, pharynx. c, seam cells. d, tail. At early L2 (21 hr) (e–k), GFP signals within a population of animals exhibit three patterns – primarily on the cell membrane, primarily in the nucleus, and in both. e-h, wild-field microscope images. i-k, single optical slices by Airyscan confocal microscopy. e, weak or unclear signals are detected. f and i, cell membrane signals. g and j, cell membrane and nuclear signals. h and k, nuclear signals. Yellow arrow, GFP at the cell membrane. Red arrow, GFP in the nucleus. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) Quantification of animals showing particular pattern of MYRF-2GFP (as in (A)) at various stages.
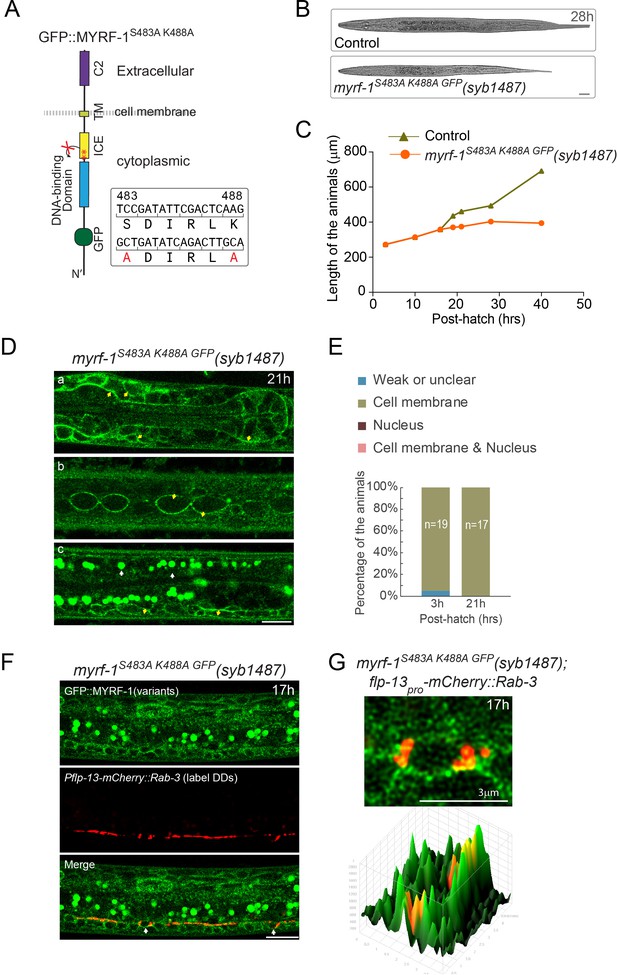
Loss-of-cleavage variant of MYRF stays on cell membrane.
(A) Illustration of loss-of-cleavage MYRF-1 mutant protein encoded by myrf-1S483A K488A GFP(syb1487) allele. With the two critical catalytic residues of ICE domain mutated, MYRF-1 cannot be cleaved, and GFP signals are expected to remain at cell membrane. (B) DIC images of myrf-1S483A K488A GFP(syb1487) and control myrf-1(syb1487)/mIn1 animals. At 28 post-hatch hours, the mutants were alive but shorter because they arrested at earlier stages. Scale bar, 20 μm. (C) Body length of myrf-1S483A K488A GFP(syb1487) and control animals myrf-1(syb1487)/mIn1 was quantified and shown as Mean. n = 15. (D) GFP signals in different body regions of myrf-1S483A K488A GFP(syb1487) animals. GFP was primarily detected at the cell membrane in the mutant at 21 hr. All optical sections are sagittal. a, head region. b, lateral (left-right) section of trunk region showing seam cells (yellow arrows). c, medial (left-right) section of trunk region showing ventral cord neurons (yellow arrows). White arrow, auto-fluorescence. Yellow arrow, GFP at the cell membrane. Images are single optical slices by Airyscan confocal microscopy. Scale bar, 10 μm. (E) Quantification of animals showing particular pattern of MYRF-1S483A K488A GFP (as in (D)) at indicated stages. (F) Colocalization of MYRF-1S483A K488A GFP and DD neuron marker. The animals myrf-1S483A K488A GFP(syb1487); Pflp-13-mCherry::rab-3(ybqIs1) at 17 post-hatch hours were imaged by confocal microscopy. RAB-3 is localized in cytoplasm. White arrow, soma of DDs. Scale bar, 10 μm. (G) Shown are the magnified image of DD soma from the colabeling experiment (F), and 3-D intensity plots of green and red signals in the upper image.
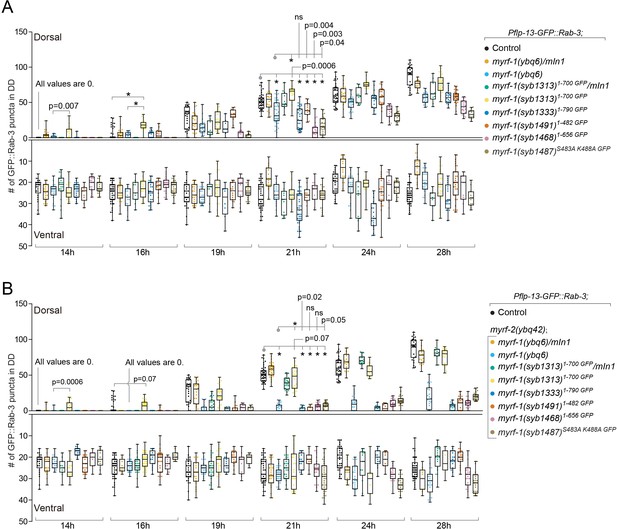
Analysis of synaptic rewiring in myrf-1 mutants.
Quantifications of the ventral and dorsal synapses in myrf-1 single mutants (A) and myrf-1; myrf-2 double mutants (B). Wild-type control (marker only) is flp-13pro-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47). The allele genotypes of each mutant are indicated in the figure. All mutants carry ybqIs47 marker. The number of synapses in DDs were counted and shown as Mean ± SEM (t test. ns, p>0.05. *, p<0.0001.). Indicated time points are post-hatch hours. p-Values for comparison between all genotypes can be found in Supplementary file 4.

Synaptic rewiring in myrf-1 mutants at 14 hr.
Representative images myrf-1 single mutants at 14 post-hatch hours. The allele genotypes of each mutant are indicated in the figure. Five ventral and dorsal cords are vertically tiled. All animals carry synpatic marker flp-13pro-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47). Scale bar, 20 μm.

Synaptic rewiring in myrf-1 mutants at 16 hr.
Representative images myrf-1 single mutants at 16 post-hatch hours. The allele genotypes of each mutant are indicated in the figure. Five ventral and dorsal cords are vertically tiled. All animals carry synpatic marker flp-13pro-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47). Scale bar, 20 μm.

Synaptic rewiring in myrf-1 mutants at 19 hr.
Representative images myrf-1 single mutants at 19 post-hatch hours. The allele genotypes of each mutant are indicated in the figure. Five ventral and dorsal cords are vertically tiled. All animals carry synpatic marker flp-13pro-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47). Scale bar, 20 μm.

Synaptic rewiring in myrf-1 mutants at 21 hr.
Representative images myrf-1 single mutants at 21 post-hatch hours. The allele genotypes of each mutant are indicated in the figure. Five ventral and dorsal cords are vertically tiled. All animals carry synpatic marker flp-13pro-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47). Scale bar, 20 μm.

Synaptic rewiring in myrf-1 mutants at 24 hr.
Representative images myrf-1 single mutants at 24 post-hatch hours. The allele genotypes of each mutant are indicated in the figure. Five ventral and dorsal cords are vertically tiled. All animals carry synpatic marker flp-13pro-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47). Scale bar, 20 μm.

Synaptic rewiring in myrf-1 mutants at 28 hr.
Representative images myrf-1 single mutants at 28 post-hatch hours. The allele genotypes of each mutant are indicated in the figure. Five ventral and dorsal cords are vertically tiled. All animals carry synpatic marker flp-13pro-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47). Scale bar, 20 μm.

Synaptic rewiring in myrf-1; myrf-2 double mutants at 14 hr.
Representative images myrf-1; myrf-2 double mutants at 14 post-hatch hours. The allele genotypes of each mutant are indicated in the figure. Five ventral and dorsal cords are vertically tiled. All animals carry synpatic marker flp-13pro-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47). Scale bar, 20 μm.

Synaptic rewiring in myrf-1; myrf-2 double mutants at 16 hr.
Representative images myrf-1; myrf-2 double mutants at 16 post-hatch hours. The allele genotypes of each mutant are indicated in the figure. Five ventral and dorsal cords are vertically tiled. All animals carry synpatic marker flp-13pro-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47). Scale bar, 20 μm.

Synaptic rewiring in myrf-1; myrf-2 double mutants at 19 hr.
Representative images myrf-1; myrf-2 double mutants at 19 post-hatch hours. The allele genotypes of each mutant are indicated in the figure. Five ventral and dorsal cords are vertically tiled. All animals carry synpatic marker flp-13pro-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47). Scale bar, 20 μm.

Synaptic rewiring in myrf-1; myrf-2 double mutants at 21 hr.
Representative images myrf-1; myrf-2 double mutants at 20 post-hatch hours. The allele genotypes of each mutant are indicated in the figure. Five ventral and dorsal cords are vertically tiled. All animals carry synpatic marker flp-13pro-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47). Scale bar, 20 μm.

Synaptic rewiring in myrf-1; myrf-2 double mutants at 24 hr.
Representative images myrf-1; myrf-2 double mutants at 24 post-hatch hours. The allele genotypes of each mutant are indicated in the figure. Five ventral and dorsal cords are vertically tiled. All animals carry synpatic marker flp-13pro-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47). Scale bar, 20 μm.

Synaptic rewiring in myrf-1; myrf-2 double mutants at 28 hr.
Representative images myrf-1; myrf-2 double mutants at 28 post-hatch hours. The allele genotypes of each mutant are indicated in the figure. Five ventral and dorsal cords are vertically tiled. All animals carry synpatic marker flp-13pro-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47). Scale bar, 20 μm.
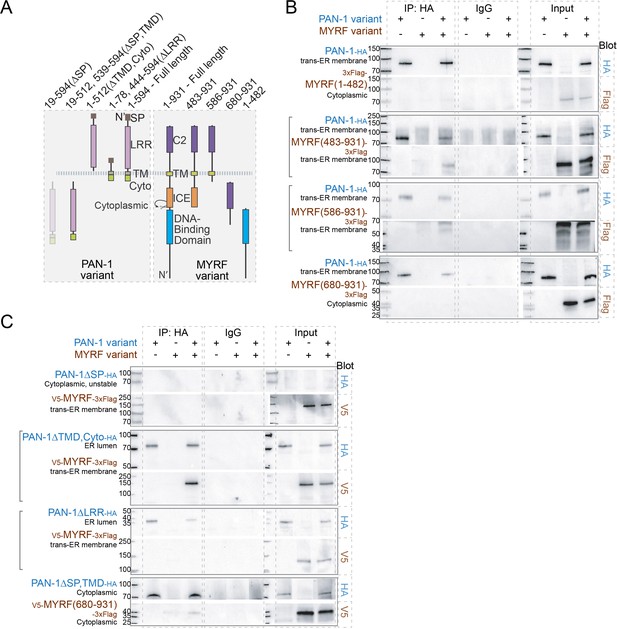
MYRF and PAN-1 interact through extracellular domains in HEK293T cells.
(A) Illustration of PAN-1 and MYRF protein variants (used in B and C) that were expressed in HEK293T cells, showing predicted topology on membrane. (B) PAN-1 interacted with the non-cytoplasmic region of MYRF-1. Co-IP of PAN-1 and MYRF-1 variants from the lysate of HEK293T cells was performed. Rabbit anti-HA was used in co-IP, and the target bands in western blot were detected using murine anti-HA, murine anti-V5 or murine anti-Flag. The subcellular compartment for each expressed protein has been indicated in the figure. Square brackets indicate the pairs that showed positive interaction. (C) The LRR of PAN-1 interacted with the non-cytoplasmic region of MYRF-1. Co-immunoprecipitation of PAN-1 variants and MYRF form the lysate of HEK293T cells was performed similarly to (B).
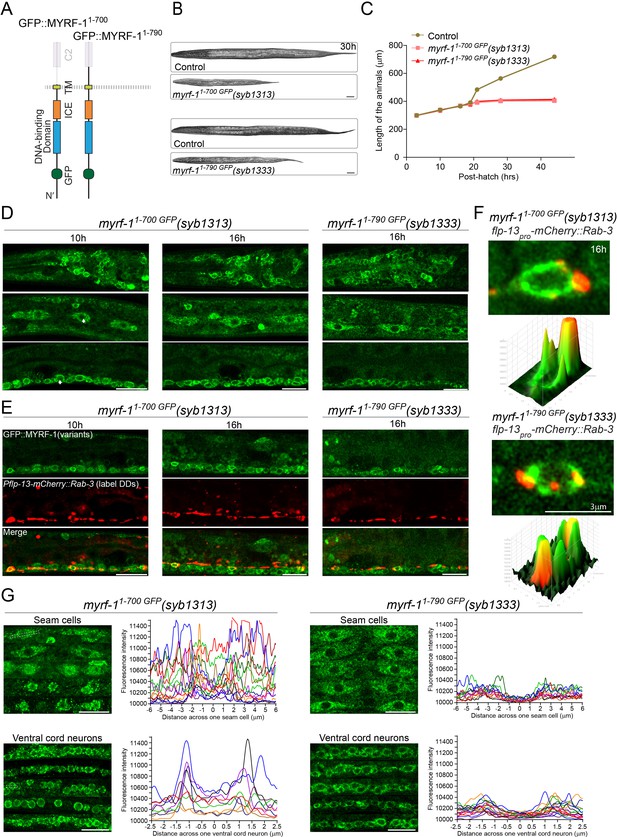
Extracellular region is required for MYRF’s cell-membrane localization and function.
(A) Illustration of truncate MYRF-1 proteins encoded by myrf-11-700 GFP(syb1313) and myrf-11-790 GFP(syb1333), with in-frame deletion of the whole and the part of the extracellular region of MYRF-1, respectively. (B) DIC images of myrf-11-700 GFP(syb1313) and control myrf-1(syb1313)/mIn1 animals (top); myrf-11-790 GFP(syb1333) and control myrf-1(syb1333)/mIn1 animals (bottom). At 30 post-hatch hours, the mutants were shorter because they arrested at earlier stages. Scale bar, 20 μm. (C) Body length of myrf-11-700 GFP(syb1313), myrf-11-790 GFP(syb1333), and control animals myrf-1(syb1313)/mIn1 was measured and shown as Mean, n = 15. (D) GFP signals in different body regions of myrf-11-700 GFP(syb1313) and myrf-11-790 GFP(syb1333) mutants. GFP signals were primarily localized in the cytoplasm in both mutants. Weak GFP signals were also detected in the nuclei of myrf-11-700 GFP(syb1313) (white arrows), but not in those of myrf-11-790 GFP(syb1333). Little cell membrane signals were observed in either mutant. Images are single sagittal optical slices obtained by AiryScan confocal microscopy. Top row, head regions. Middle row, lateral (left-right) section of middle (head-tail) segment with a focus on seam cells. Bottom row, medial (left-right) section of middle (head-tail) segment with a focus on ventral nerve cord. Scale bar, 10 μm. (E) Colabeling MYRF-11-700 GFP(syb1313) and MYRF-11-790 GFP(syb1333) with DD neuron marker Pflp-13-mCherry::rab-3(ybqIs1) at 10, 16 post-hatch hours. The animals carry glo-1(zu391) to reduce auto-fluorescence. Shown are single optical slices by Airyscan confocal microscopy. RAB-3 is localized in cytoplasm. White arrow, soma of DDs. Scale bar, 10 μm. (F) Shown are the magnified image of DD soma from the colabeling experiment (E), and 3-D intensity plots of green and red signals in the upper image. (G) Analysis of GFP intensity across individual seam cells and ventral cord neurons of myrf-11-700 GFP(syb1313) and myrf-11-790 GFP(syb1333) animals. Images excerpts from five independent animals are vertically tiled. Each graph line represents average GFP intensity along a bar ROI across single seam cell (or ventral cord neuron) from independent individual animals. X-axis, position on the bar ROI. 0 on X-axis denotes the center of the cell analyzed. An example of ROI was drawn in the figure as a white dot line square. Scale bar, 10 μm.
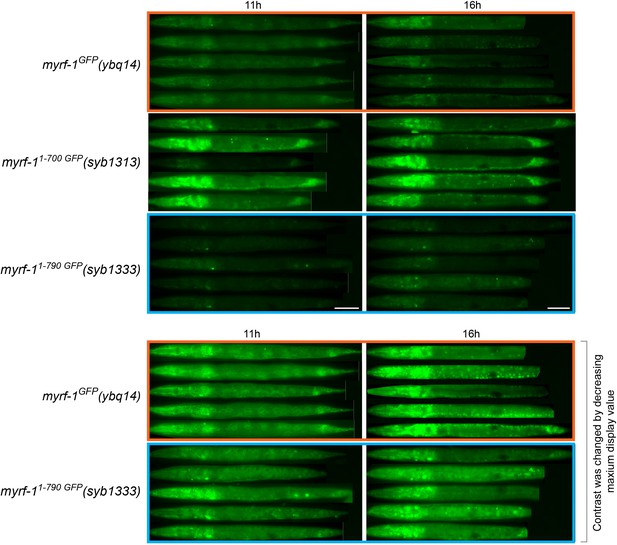
Comparing the signal intensity in MYRF-11-700 GFP(syb1313) and MYRF-11-790 GFP(syb1333).
MYRF-1GFP(ybq14), MYRF-11-700 GFP(syb1313), and MYRF-11-790 GFP(syb1333) animals were imaged under wide-field microscope. Images of five animals were vertically tiled. The display parameters for images of top three rows were identical. Note that MYRF-11-700 GFP(syb1313) was stronger than the other two. Bottom two rows showed the same images (indicated by orange and blue box) processed using different display parameters (the maximum display value was decreased to 1/3 of the upper image value). Scale bar, 20 μm.
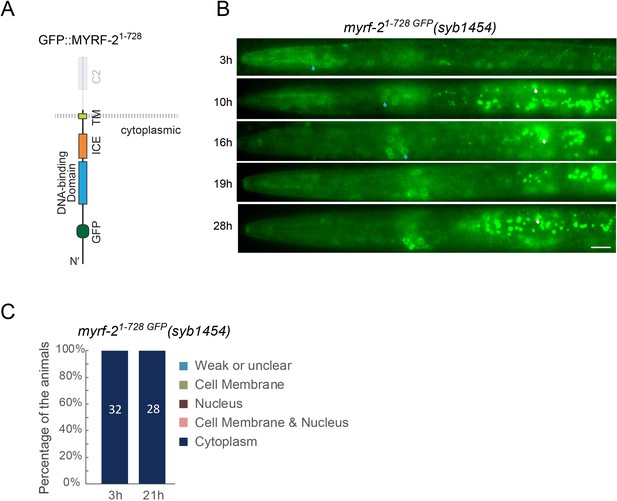
Extracellular domain of MYRF-2 is required for its cell-membrane localization.
(A) Illustration of myrf-21-728 GFP(syb1454) with in-frame deletion of the whole extracellular region of MYRF-2. (B) GFP signals in myrf-21-728 GFP(syb1454) mutants at different post-hatch hours. Shown are anterior half of the animals. Images were acquired using wide-field microscopy. Blue arrow, GFP in cytoplasm. White arrow, auto-fluorescence. Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) Quantification of animals showing particular pattern of MYRF-21-728 GFP as in (B).
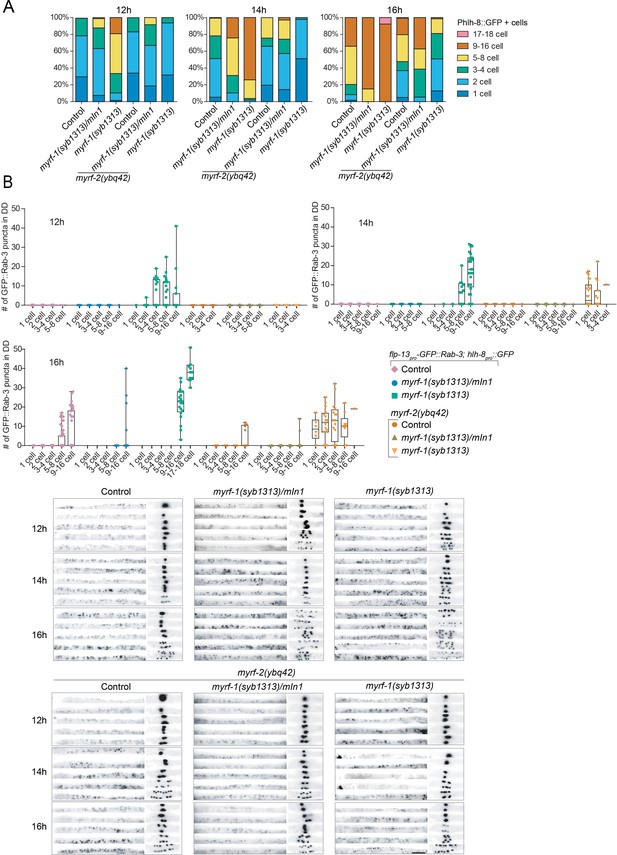
myrf-11-700 GFP(syb1313) exhibits precocious, yet discordant synaptic rewiring and M-cell division.
(A) Percentage of animals showing the particular number of M-cell progenies labeled by hlh-8pro-GFP(ayIs6) at 12, 14, 16 post-hatch hours. (B) Quantification of dorsal synapse number of DDs in individuals subgrouped by the number of M-cell progenies. The synapses of DDs were labeled by flp-13pro-GFP::Rab-3(ybqIs47). At bottom are representative images showing dorsal cord and M-cell progenies simultaneously. Scale bar, 20 μm.
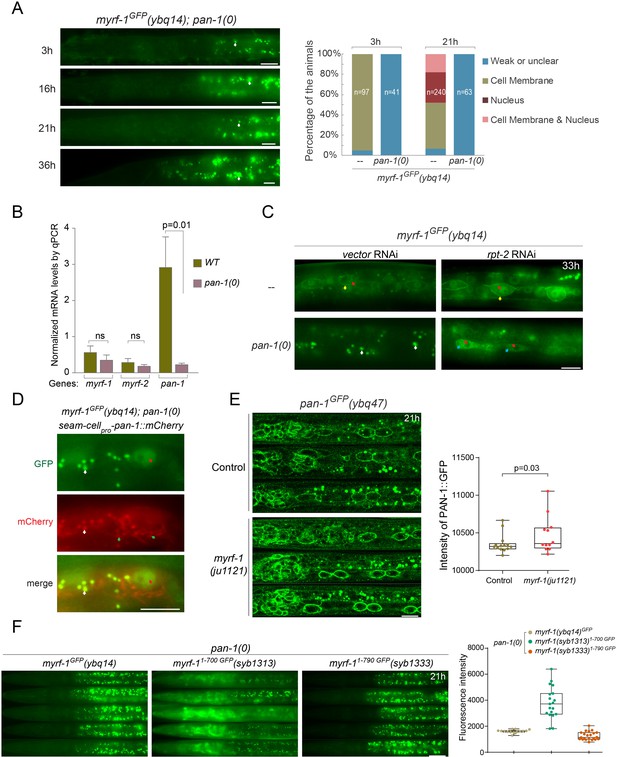
PAN-1 is required for MYRF’s cell-membrane and nuclear localization.
(A) Signals of MYRF-1GFP(ybq14) in pan-1(gk142) animals at different post-hatch hours. No clear GFP signals are detected in pan-1 mutants. White arrow, auto-fluorescence. Images are acquired by wide-field microscopy, showing anterior half of each animal. Scale bar, 10 μm. The graph at right shows the percentage of animals with particular MYRF-1GFP pattern in pan-1 mutants and control animals at 3, 21 post-hatch hours. (B) Transcripts levels of myrf and pan-1 in pan-1(gk142) and control animals (only with markers) (unc-25pro-mCherry::rab-3(juIs236); hlh-8pro-GFP(ayIs6)) by qPCR. Mean normalized transcript level of three replicates were shown (Mean ± SEM, t test. ns, p>0.05.). Transcript level of Internal control gene pmp-3 was used as normalization reference. The animals were 21 post-hatch hours, which were staged with the help of M-cell division marker (hlh-8pro-GFP). (C) Signals of MYRF-1GFP(ybq14) in pan-1(gk142) animals under treatment of rpt-2 RNAi. rpt-2 is a component of ubiquitin proteasome system. MYRF-1GFP signals are not detected in pan-1 mutants, but are detected when treated by rpt-2 RNAi. The GFP signals are observed in cytoplasm (blue arrows) in pan-1(gk142); rpt RNAi, in contrast to on the cell membrane (yellow arrows) and in the nucleus (red arrows) in wild-type animals. Scale bar, 10 μm. (D) Signals of MYRF-1GFP(ybq14) in seam cells of pan-1(gk142) mutants can be restored by seam-cell specifically expressed pan-1 transgene, SCMpro-pan-1::mCherry(ybqEx778). Red arrow, GFP signals in the nucleus of seam cells. Green arrow, signals of exogenous expressed PAN-1::mCherry in seam cells. White arrow, auto-fluorescence. Scale bar, 10 μm. (E) Signals of PAN-1GFP in control (pan-1(ybq47)GFP only) and myrf-1(ju1121) mutants, showing anterior half of animal body. Images are single slices acquired by Airyscan. Shown are lateral position of sagittal sections focusing on seam cells. Images excerpts from three independent animals are vertically tiled. Scale bar, 10 μm. The graph at right shows the intensity of PAN-1GFP on cell membrane of seam cells. Each data point represents independent individual animals. Shown are Mean ± SEM (t test). (F) MYRF-1GFP(ybq14), MYRF-11-700 GFP(syb1313), and MYRF-11-790 GFP(syb1333) signals in pan-1(gk142) mutants. Images are captured on wide-field microscope and show the anterior half of animal body. Images excerpts from five independent animals are vertically tiled. Scale bar, 20 μm. The graph at right shows the average intensity of head region (which is free of intestinal auto-fluorescence). Each data point represents individual animal.
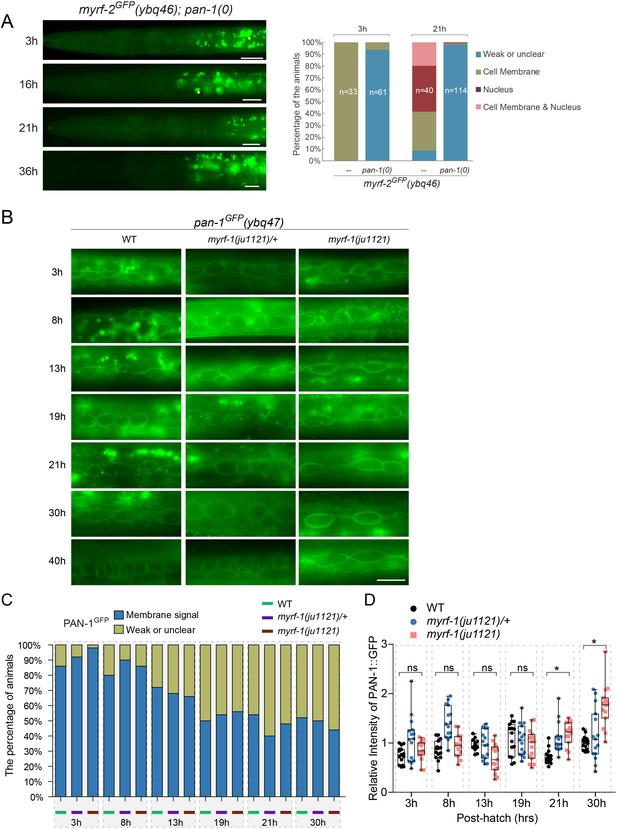
pan-1 is required for cell-membrane localization of MYRF.
(A) No clear MYRF-2GFP(ybq46) signals were detected in pan-1(gk142) animals at various post-hatch hours. Images were taken under wide-field microscope, showing anterior half of each animal. Yellow arrow, auto-fluorescence. Scale bar, 10 μm. At right was quantification of animals showing particular pattern of MYRF-2GFP in pan-1 mutants and control animals at 3, 21 post-hatch hours. (B) Signals of PAN-1GFP(ybq47) in wild type, myrf-1(ju1121), and myrf-1(ju1121)/mIn1 animals, with a focus on seam cells. Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) Percentage of animals with detectable PAN-1GFP(ybq47) in wild type, myrf-1(ju1121)/mIn1, and myrf-1(ju1121) animals at different post-hatch hours. Patterns of GFP signals were categorized into two types: consistent cell membrane signals throughout the animals; unclear signals. At least 50 animals are analyzed for each stage. (D) Relative intensity of PAN-1GFP in myrf-1(ju1121) and control animals (as in B). Measured was intensity of GFP signals at the cell membrane of seam cells. Shown are Mean ± SEM (t test. ns, p>0.05. *, p<0.001).
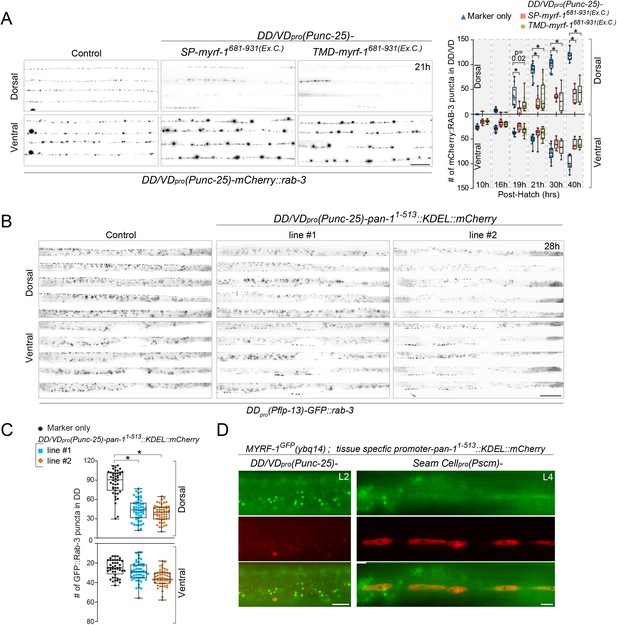
MYRF-PAN-1 interaction is important for synaptic remodeling.
(A) Synaptic remodeling in animals with extracellular domain of MYRF overexpressed. Expressed in transgenes were unc-25pro-SP-MYRF-1Ex.C. (ybqEx752) and unc-25pro-TMD-MYRF-1Ex.C. (ybqEx754). SP-, 1-40aa of MIG-17. TMD-, 1-51aa of NEP-2. Ex.C., extracellular region (681-931aa) of MYRF-1. Synaptic remodeling was labeled by unc-25pro-mCherry::rab-3(juIs236). Scale bar, 20 μm. The graph shows the number of synapses at various post-hatch hours. Shown as Mean ± SEM (t test. *, p<0.001.). (B) Synaptic remodeling in animals with ER-retained PAN-1 overexpressed. Expressed in transgenes were unc-25pro-pan-111-513::KDEL::mCherry, line#1 ybqEx815, line#2 ybqEx817. Synaptic remodeling was labeled by flp-13pro-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47). Images of five ventral and dorsal cords were vertically tiled. Scale bar, 20 μm. (C) Quantification of the number of synapses in (B), shown as Mean ± SEM (t test. *, p<0.0001.). (D) MYRF-1GFP was trapped in cytoplasm by overexpression of ER-retained PAN-1. unc-25pro-pan-111-513::KDEL::mCherry(ybqEx807), SCMpro-pan-111-513::KDEL::mCherry(ybqEx820) was overexpressed in myrf-1GFP(ybq14) background. The MYRF-1GFP signals were greatly increased in mCherry positive cells and localized in cytoplasm, while MYRF-1GFP was normally localized on cell membrane and nucleus at L2 (left panel), or largely down-regulated at L4 (right panel). The images were taken using wide-field microscope. Scale bar, 10 μm.
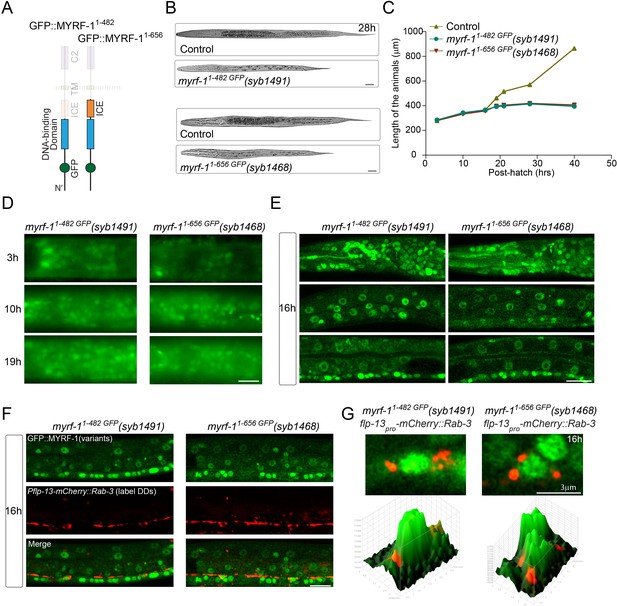
N-terminal MYRF alone is insufficient for MYRF’s function.
(A) Illustration of truncated MYRF-1 proteins encoded by myrf-11-482 GFP(syb1491) and myrf-11-656 GFP(syb1468), with in-frame deletion of the whole (starting from cleavage point) and the part (starting from the end of ICE region) of the C-terminal region of MYRF-1, respectively. (B) DIC images of myrf-11-482 GFP(syb1491) and control myrf-1(syb1491)/mIn1 animals (top); myrf-11-656 GFP(syb1468) and myrf-1(syb1468)/mIn1 animals (bottom). At 28 post-hatch hours, the mutants were alive but shorter because they arrested at earlier stage. Scale bar, 20 μm. (C) Body length of myrf-11-482 GFP(syb1491),myrf-11-656 GFP(syb1468), and control animals myrf-1(syb1491)/mIn1 was measured and shown as Mean, n = 15. (D) GFP signals in myrf-11-482 GFP(syb1491) and myrf-11-656 GFP(syb1468) mutants at 3, 10, 16 post-hatch hours. GFP signals were primarily observed in the nuclei (more than 20 animals were imaged and analyzed for each developmental stage). Images show head regions, and were acquired by wide-filed camera. Scale bar, 10 μm. (E) Single optical-plane images of MYRF-11-482 GFP(syb1491) and MYRF-11-656 GFP(syb1468) at 16 post-hatch hours acquired by Airyscan confocal microscopy. All sections are sagittal. Top row, head region. Middle row, lateral (left-right) section of the middle (head-tail) segment. Bottom row, medial (left-right) section of the middle (head-tail) segment with a focus on ventral nerve cord. Scale bar, 10 μm. (F) Colabeling MYRF-11-700 GFP(syb1313) and MYRF-11-790 GFP(syb1333) with DD neuron marker Pflp-13-mCherry::rab-3(ybqIs1) at 16 post-hatch hours. The animals carry glo-1(zu391) to reduce auto-fluorescence. Shown are single optical slices by Airyscan confocal microscopy. RAB-3 is localized in cytoplasm. White arrow, soma of DDs. Scale bar, 10 μm. (G) Shown are the magnified image of DD soma from the colabeling experiment (F), and 3-D intensity plots of green and red signals in the upper image.
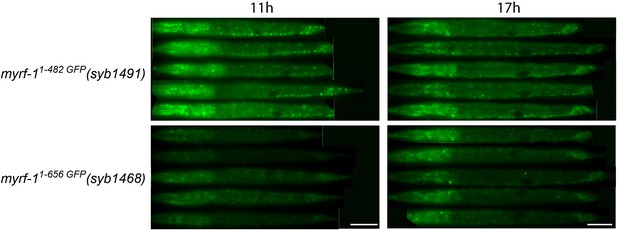
Comparing the signal intensity in MYRF-11-482 GFP(syb1491) and MYRF-11-656 GFP(syb1468).
MYRF-11-482 GFP(syb1491) and MYRF-11-656 GFP(syb1468) animals were imaged under wide-field microscope. Images of five animals were vertically tiled. The display parameters for all images were identical. Scale bar, 20 μm.
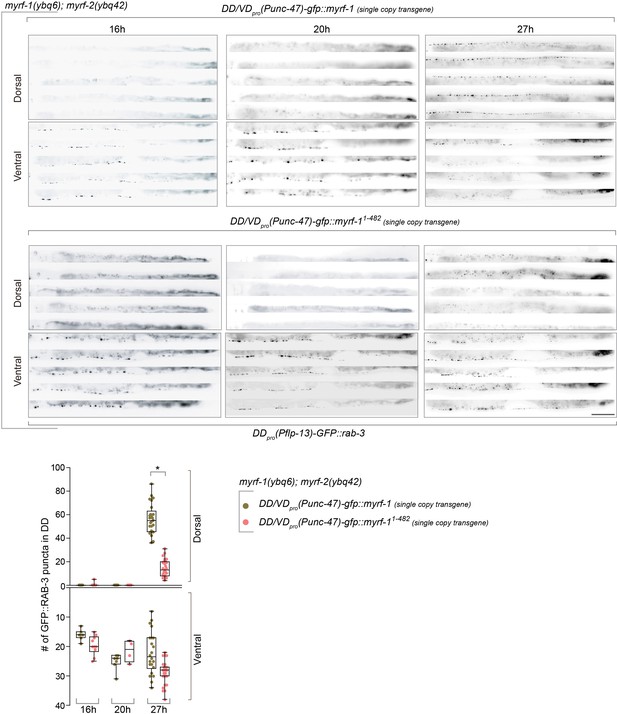
Single-copy-transgene of MYRF-11-482 (N-MYRF-1) in DDs does not rescue synaptic rewiring defects.
(A) Synaptic remodeling in myrf-1(ybq6); myrf-2(ybq42) double mutants carrying single-copy transgene unc-47pro-gfp::myrf-1(ybqIs92), unc-47pro-gfp::myrf-11-482(ybq99). unc-47pro is expressed in DD/VDs among ventral cord motor neurons. The presynaptic sites in DD are labeled by flp-13pro-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47). Full-length myrf-1 rescued synpatic rewiring defects in myrf-1; myrf-2 double mutants, while myrf-11-482 did not. Images of five ventral and dorsal cord were vertically tiled. Scale bar, 20 μm. (B) Quantification of synapse number in DDs of indicated genotypes as in (A), which was shown as Mean ± SEM (t test. *, p<0.0001).
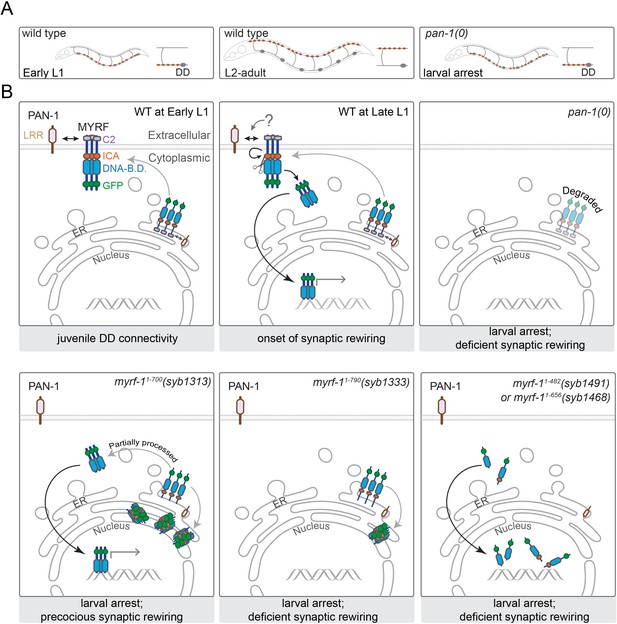
A model for how PAN-1 and MYRF interact to regulate synaptic rewiring.
(A) Illustration of synaptic rewiring in wild type and pan-1(0) mutants. Synapses in DDs are indicated by brown-color dots. (B) PAN-1 and MYRF interaction via extracellular domains is required for cell-membrane localization of MYRF. The release of N-MYRF occurs at late L1, coinciding the timing when MYRF is critically required for driving L1-L2 larval transition and synaptic remodeling in DD neurons. In the absence of PAN-1, MYRF is degraded, which leads to larval arrest and blocked DD synaptic remodeling. MYRF-11-700(syb1313) is partially processed in ER, which produces N-MYRF translocating into nucleus, even though a large amount of MYRF-11-700(syb1313) accumulates in ER. MYRF-11-790(syb1333) is not cleaved; they reside in ER and are mostly degraded. MYRF-11-482(syb1491) and MYRF-11-656(syb1468), neither of which contains TMD, are transported into nucleus but fail to regulate gene expression.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | Punc-25-mcherry::rab-3(juIs236) II | Yishi Jin lab | CZ8656 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | Punc-25-mCherry::Rab-3(juIs236)/mT1 II, pan-1(gk142)/mT1 III | this paper | BLW1056 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | +/mT1 II; pan-1(gk142)/mT1 III; Pflp-13-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs46) | this paper | BLW1115 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | Punc-25-GFP(juIs76)/mT1 II, pan-1(gk142)/mT1 III | this paper | BLW1104 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | Punc-25-mCherry::Rab-3(juIs236)/mT1 II, pan-1(gk142)/mT1 III; Punc-25-pan-1b::gfp(ybqIs131) | this paper | BLW1363 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | Punc-25-mCherry::Rab-3(juIs236)/mT1 II, pan-1(gk142)/mT1 III; Punc-25-pan-1a(ybqEx624) | this paper | BLW1319 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | Punc-25-mCherry::Rab-3(juIs236)/mT1 II, pan-1(gk142)/mT1 III; Punc-25-pan-1c(ybqEx626) | this paper | BLW1321 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | Punc-25-mCherry::Rab-3(juIs236)/mT1 II, pan-1(gk142)/mT1 III | BLW1167 | ||
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | pan-1-loxp (syb1217) III; Punc-25-mCherry::Rab-3(juIs236) II | this paper | BLW1646 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | pan-1-loxp (syb1217) III; Punc-25-mCherry::Rab-3(juIs236) III; Punc-25-Cre(tmIs1072) | this paper | BLW1645 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | myrf-1(ju1121) Punc-25-mCherry::Rab-3(juIs236) II; Pmyrf-1-gfp::myrf-1::flag-myrf-1_3'UTR(ybqEx164) | Meng et al., 2017 | BLW314 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | myrf-2(ybq42) X; Pmyrf-2-gfp::myrf-2::HA(ybqIs128) | this paper | BLW1348 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | Ppan-1-NLS::tagRFP(ybqIs138) | this paper | BLW1397 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | Punc-25-mCherry::Rab-3(juIs236)/mT1 II, pan-1(gk142)/mT1 III; Punc-25-pan-1b (delta LRR) (ybqEx642) | this paper | BLW1401 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | Punc-25-mCherry::Rab-3(juIs236)/mT1 II, pan-1(gk142)/mT1 III; Punc-25-pan-1b (delta SP) (ybqEx643) | this paper | BLW1402 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | Punc-25-mCherry::Rab-3(juIs236)/mT1 II, pan-1(gk142)/mT1 III; Punc-25-pan-1b (delta TM) (ybqEx644) | this paper | BLW1403 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | Punc-25-mCherry::Rab-3(juIs236)/mT1 II, pan-1(gk142)/mT1 III; Punc-25-pan-1b (delta Cyto) (ybqEx645) | this paper | BLW1404 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | Punc-25-mCherry::Rab-3(juIs236) II; Punc-25-mig-10(1-40)::myrf-1 (681–931)::Flag(ybqEx752) | this paper | BLW1674 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | Punc-25-mCherry::Rab-3(juIs236) II; Punc-25-nep-2 (1–51)::myrf-1 (681–931)::Flag(ybqEx754) | this paper | BLW1676 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1 (1–700)::3xflag(syb1313)/mIn1 II | this paper | PHX1313 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1 (1–790)::3xflag(syb1333)/mIn1 II | this paper | PHX1333 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1 (1–482)::3xflag(syb1491)/mIn1 II | this paper | PHX1491 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1 (1–656)::3xflag(syb1468)/mIn1 II | this paper | PHX1468 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1(S483A,K488A)::3xflag(syb1313)/mIn1 II | this paper | PHX1487 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-2 (1–728)::3xflag(syb1454) X | this paper | PHX1454 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1 (1–700)::3xflag(syb1313)/mIn1 II; Pflp-13-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47) IV | this paper | BLW1570 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1 (1–790)::3xflag(syb1333)/mIn1 II; Pflp-13-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47) IV | this paper | BLW1571 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1 (1–482)::3xflag(syb1491)/mIn1 II; Pflp-13-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47) IV | this paper | BLW1617 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1 (1–656)::3xflag(syb1468)/mIn1 II; Pflp-13-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47) IV | this paper | BLW1615 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1(S483A,K488A)::3xflag(syb1313)/mIn1 II; Pflp-13-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47) IV | this paper | BLW1616 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1 (1–700)::3xflag(syb1313)/mIn1 II; myrf-2(ybq42) X; Pflp-13-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47) IV | this paper | BLW1756 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1 (1–790)::3xflag(syb1333)/mIn1 II; myrf-2(ybq42) X; Pflp-13-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47) IV | this paper | BLW1779 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1 (1–482)::3xflag(syb1491)/mIn1 II; myrf-2(ybq42) X; Pflp-13-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47) IV | this paper | BLW1760 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1 (1–656)::3xflag(syb1468)/mIn1 II; myrf-2(ybq42) X; Pflp-13-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47) IV | this paper | BLW1758 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1(S483A,K488A)::3xflag(syb1313)/mIn1 II; myrf-2(ybq42) X; Pflp-13-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47) IV | this paper | BLW1759 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1(S483A,K488A)::3xflag(syb1313)/mIn1 II; Pflp-13-mCherry::rab-3(ybqIs1) | this paper | BLW1791 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1 (1–700)::3xflag(syb1313)/mIn1 II; glo-1(zu391) X; Pflp-13-mCherry::rab-3(ybqIs1) | this paper | BLW1833 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1 (1–790)::3xflag(syb1333)/mIn1 II; glo-1(zu391) X; Pflp-13-mCherry::rab-3(ybqIs1) | this paper | BLW1834 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1 (1–482)::3xflag(syb1491)/mIn1 II; glo-1(zu391) X; Pflp-13-mCherry::rab-3(ybqIs1) | this paper | BLW1835 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1 (1–656)::3xflag(syb1468)/mIn1 II; glo-1(zu391) X; Pflp-13-mCherry::rab-3(ybqIs1) | this paper | BLW1836 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | pan-1::gfp(ybq47) III | this paper | BLW1258 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | pan-1::gfp(ybq47) III; glo-1(zu391) X | this paper | BLW1839 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | pan-1::gfp(ybq47) III; glo-1(zu391) X; Pflp-13-mCherry::rab-3(ybqIs1) | this paper | BLW1878 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1::3xflag(ybq14) II; glo-1(zu391) X; Pflp-13-mCherry::rab-3(ybqIs1) | this paper | BLW1854 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1(ybq10) II | Meng et al., 2017 | BLW831 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1::3xFlag(ybq14) II | Meng et al., 2017 | BLW889 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-2(ybq46) X | Meng et al., 2017 | BLW1111 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1(ybq14)/mT1 II; pan-1(gk142)/mT1 III | this paper | BLW1465 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1::3xflag(ybq14)/mT1 II; pan-1(gk142)/mT1 III | this paper | BLW1166 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1::3xflag(ybq14)/mT1 II; pan-1(gk142)/mT1 III; Pscm-pan-1b::mCherry(ybqEx778) | this paper | BLW1731 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | Pflp-13-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47) IV | this paper | BLW1419 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | myrf-1(ju1121)/mIn1 II; pan-1::GFP(ybq47) III | this paper | BLW1654 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1::3xflag(ybq14)/mT1 II; pan-1(gk142)/mT1 III | this paper | BLW1883 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1 (1–700)(syb1313)/mT1 II; pan-1(gk142)/mT1 III | this paper | BLW1805 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1 (1–790)(syb1333)/mT1 II; pan-1(gk142)/mT1 III | this paper | BLW1806 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | Pflp-13-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47) III; Punc-25-pan-1(1-G513)::mCherry::KDEL(ybqEx815) | this paper | BLW1881 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | Pflp-13-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47) III; Punc-25-pan-1(1-G513)::mCherry::KDEL(ybqEx817) | this paper | BLW1890 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1::3xFlag(ybq14) II; Punc-25-pan-1(1-G513)::mCherry::KDEL(ybqEx807) | this paper | BLW1842 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1::3xFlag(ybq14) II; Pscm-Pan-1(1-G513)::mCherry::KDEL(ybqEx820) | this paper | BLW1895 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | Punc-25-mCherry::Rab-3(juIs236)/mT1 II; pan-1(gk142)/mT1 III; Pflp-13-pan-1b:gfp(ybqEx821) | this paper | BLW1900 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | pan-1(loxP)(syb1217) III; Pflp-13-gfp(juIs145)/Punc-25-mCherry::Rab-3(juIs236) II | this paper | BLW1825 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | pan-1(loxP)(syb1217) III; Pflp-13-gfp(juIs145)/Punc-25-mCherry::Rab-3(juIs236) II; Punc-25-Cre(tmIs1072) | this paper | BLW1784 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | Pflp-13-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47) III; Phlh-8-GFP(ayIs6) X | this paper | BLW1874 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | Pflp-13-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47) III; myrf-2(ybq42) Phlh-8-GFP(ayIs6) X | this paper | BLW1875 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1 (1–700)::3xflag(syb1313)/mIn1 II; Pflp-13-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47) III; Phlh-8-GFP(ayIs6) X | this paper | BLW1843 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::myrf-1 (1–700)::3xflag(syb1313)/mIn1 II; Pflp-13-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47) III; myrf-2(ybq42) Phlh-8-GFP(ayIs6) X | this paper | BLW1848 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | myrf-1(ybq6)/mIn1 II; myrf-2(ybq42) X; Pflp-13-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47) III; Punc-47-gfp::myrf-1::flag, cb-unc-119(+)(ybqIs92(Si)) IV | this paper | BLW1781 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | myrf-1(ybq6)/mIn1 II; myrf-2(ybq42) X; Pflp-13-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47) III; Punc-47-gfp::myrf-1 (1–482)::flag, cb-unc-119(+)(ybqIs99(Si)) IV | this paper | BLW1782 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | myrf-1(ybq6)/mIn1 II; myrf-2(ybq42) X; Pflp-13-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47) III | this paper | BLW1008 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | myrf-1(ybq6)/mIn1 II; Pflp-13-GFP::rab-3(ybqIs47) III | Meng et al., 2017 | BLW827 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Complete list for factors interacting with MYRF-1 in IP-MS analysis (in Figure 1A).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67628/elife-67628-supp1-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
Complete list for factors interacting with MYRF-2 in IP-MS analysis (in Figure 1A).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67628/elife-67628-supp2-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 3
Complete list for factors interacting with PAN-1 in IP-MS analysis (in Figure 1A).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67628/elife-67628-supp3-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 4
p-values for comparison between all genotypes in Figure 6.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67628/elife-67628-supp4-v1.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67628/elife-67628-transrepform-v1.docx





