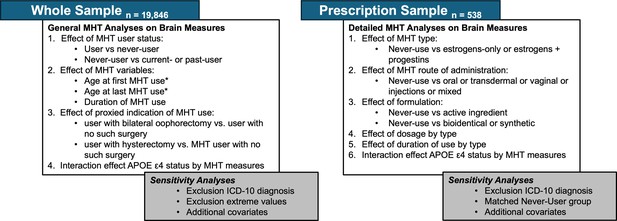
Menopausal hormone therapy and the female brain: Leveraging neuroimaging and prescription registry data from the UK Biobank cohort
Figures
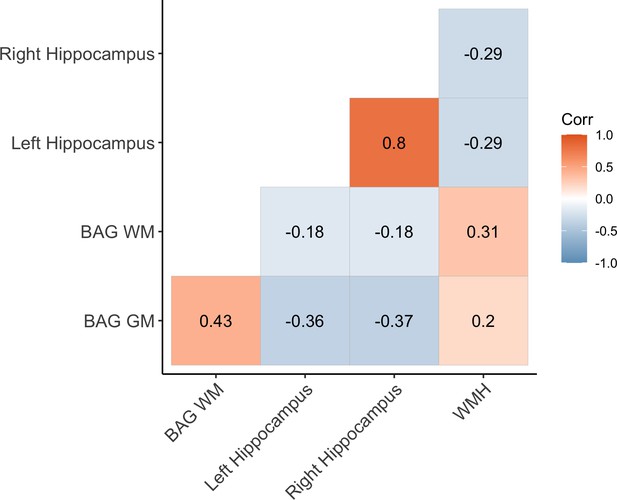
Correlations (Pearson’s r) between white matter (WM) and gray matter (GM) brain age gap (BAG) as well as left and right hippocampal volumes and total white matter hyperintensity (WMH) volume.
BAG measures are adjusted for age (Seripa et al., 2007). WM BAG, GM BAG, and hippocampal volumes were available for 20,360 individuals, and 19,538 had data on WMH volume.
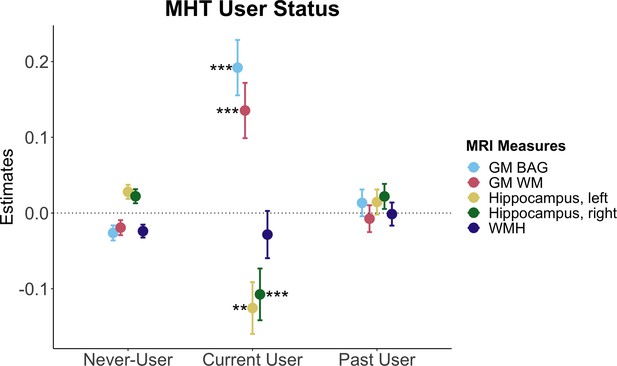
Associations between brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) measures and menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) user status.
Point plot of estimated marginal means with standard errors from separate regression models with brain measure as dependent variable and MHT user status as independent (categorical) variable, with never-users as a reference group. Brain measures include white matter (WM) and gray matter (GM) brain age gap (BAG) as well as left and right hippocampal volumes and total white matter hyperintensity (WMH) volume. Sample sizes per user group, excluding participants with a history of hysterectomy and/or bilateral oophorectomy, were as follows: never-users (n = 10,934), current user (n = 802), past user (n = 3,658). The models were adjusted for age, education, body mass index, lifestyle score, and menopausal status. All variables were standardized prior to performing the regression analysis (subtracting the mean and dividing by the standard deviation). Stars indicate significant associations. Significance codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’.

Associations between brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) measures and history of hysterectomy and/or bilateral oophorectomy in menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) users.
Point plot of estimated marginal means with standard errors from separate regression analysis with MRI measure as dependent variable and history of hysterectomy and/or bilateral oophorectomy as independent (categorical) variable. MHT users without such surgical history served as a reference group. Brain measures include white matter (WM) and gray matter (GM) brain age gap (BAG) as well as left and right hippocampal volumes and total white matter hyperintensity (WMH) volume. Sample sizes were as follows: hysterectomy only (no, n = 5522; yes, n = 546) and bilateral oophorectomy +/- hysterectomy (no, n = 6513; yes, n = 1412). The models were adjusted for age, education, body mass index, lifestyle score, and menopausal status. All variables were standardized prior to performing the regression analysis (subtracting the mean and dividing by the standard deviation). Stars indicate significant associations. Significance codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’.
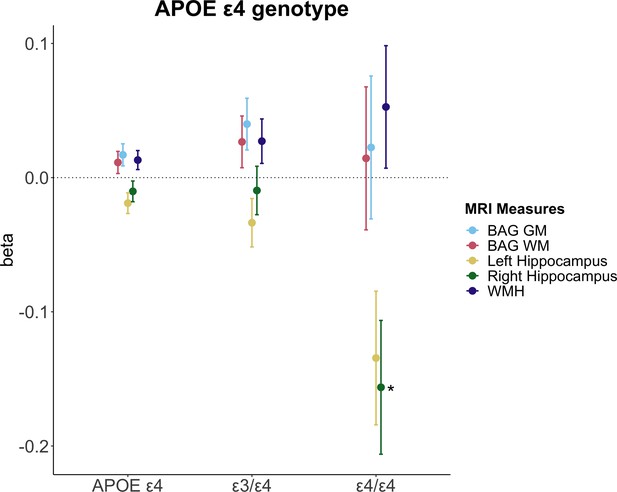
Associations between apolipoprotein ε type 4 (APOE ε4) genotype and brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) measures.
Point plot of standardized beta-values with standard errors from separate multiple regression analysis with MRI measure as dependent variable and APOE ε4 genotype as independent variable. Non-carrier served as a reference group (n=10,787). APOE ε4 (all, n=3935) represents the ε3/ε4 (n=3572) and ε4/ε4 carriers (n=363) grouped together. For WMH, the sample sizes were as follows: non-carrier (n=10,377), APOE ε4 (all, n=3410), ε3/ε4 (n=3410), and ε4/ε4 carriers (n=349). Brain measures include white matter (WM) and gray matter (GM) brain age gap (BAG) as well as left and right hippocampal volumes and total white matter hyperintensity (WMH) volume. The models were adjusted for age, education, body mass index, lifestyle score, and menopausal status. All variables were standardized prior to performing the regression analysis (subtracting the mean and dividing by the standard deviation). Stars indicate significant associations. Significance codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’.
Tables
Sample demographics of menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) never-, current, and past- users in the whole sample.
| MHT User Status | p-value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Never | Current | Past | Never vs | Never vs | Current vs | |
| N | 12,012 | 1153 | 6681 | Current | Past | Past |
| Age* | 61.6±7.1 | 60.1±6.8 | 67.5±6.2 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Ethnic Background, N (%) | 0.084 | <0.001 | 0.824 | |||
| White | 11,590 (96.6) | 1128 (98.0) | 6555 (98.2) | |||
| Asian | 103 (0.9) | 5 (0.4) | 27 (0.4) | |||
| Black | 96 (0.8) | 4 (0.3) | 23 (0.3) | |||
| Chinese | 54 (0.5) | 1 (0.1) | 12 (0.2) | |||
| Mixed | 81 (0.7) | 5 (0.4) | 27 (0.4) | |||
| Other ethnic group | 73 (0.6) | 8 (0.7) | 28 (0.4) | |||
| Education, N (%) | 0.260 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| College/University degree | 6,123 (51.0) | 606 (52.6) | 2,813 (42.1) | |||
| O levels/GCSEs or equivalent | 2,234 (18.6) | 203 (17.6) | 1,447 (21.7) | |||
| A levels/AS levels or equivalent | 1,656 (13.8) | 135 (11.7) | 758 (11.3) | |||
| CSEs or equivalent | 471 (3.9) | 52 (4.5) | 247 (3.7) | |||
| NVQ/HND/HNC or equivalent | 414 (3.4) | 38 (3.3) | 279 (4.2) | |||
| Other professional qualifications | 602 (5.0) | 70 (6.1) | 523 (7.8) | |||
| None of the above | 512 (4.3) | 49 (4.2) | 613 (9.2) | |||
| Lifestyle score | 1.7±1.2 | 1.8±1.3 | 1.7±1.2 | 0.009 | 0.076 | 0.089 |
| BMI* (m2/kg) | 26.0±4.8 | 25.5±4.4 | 26.2±4.6 | 0.003 | 0.003 | <0.001 |
| Menopausal Status, N (%) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| No | 962 (8.0) | 45 (3.9) | 37 (0.6) | |||
| Yes | 9,905 (82.5) | 769 (66.7) | 5,528 (82.8) | |||
| Not sure – had a hysterectomy | 545 (4.5) | 247 (21.4) | 1,057 (15.8) | |||
| Not sure – other reason | 600 (5.0) | 92 (8.0) | 58 (0.9) | |||
| Oophorectomy, yes, N (%) | 443 (3.7) | 224 (19.4) | 1172 (17.7) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.159 |
| Hysterectomy, yes, N (%) | 518 (4.5) | 117 (12.5) | 1083 (18.8) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| APOE ε4 status, carrier, N (%) | 3134 (27.5) | 284 (26.2) | 1557 (24.7) | 0.398 | <0.001 | 0.278 |
| APOE ε4, allele, N (%) | 0.649 | <0.001 | 0.460 | |||
| non-carrier | 8264 (72.5) | 798 (73.8) | 4759 (75.3) | |||
| ε3/ε4 | 2853 (25.0) | 257 (23.8) | 1424 (22.5) | |||
| ε4/ ε4 | 281 (2.5) | 27 (2.5) | 133 (2.1) | |||
| Age started MHT* | 49.8±6.5 | 47.9±5.6 | <0.001 | |||
| Age last used MHT* | 60.1±6.8 | 53.9±6.1 | <0.001 | |||
| Duration of MHT use* | 10.3±8.6 | 6.0±5.6 | <0.001 | |||
-
*
Mean ± Standard Deviation. Age is given in years. Abbreviations: N, sample size; GCSE, General Certificate of Secondary Education; CSE, Certificate of Secondary Education; NVQ, National Vocational Qualification; BMI, body mass index; APOE, apolipoprotein. Significant differences between groups based on t/χ2 tests are highlighted in bold.
Sample demographics of menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) users with and without a history of hysterectomy +/-bilateral oophorectomy in the whole sample.
| MHT Users | p-value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Surgery | Hysterectomy | Oophorectomy | No vs | No vs | Hyster vs | ||
| N | 5,510 | 544 | 1,407 | Hyster | Oopho | Oopho | |
| Age* | 66.1±6.9 | 69.0±5.6 | 66.7±6.7 | <0.001 | 0.003 | <0.001 | |
| Ethnic Background, N (%) | 0.710 | 0.272 | 0.569 | ||||
| White | 5408 (98.3) | 535 (98.5) | 1370 (97.4) | ||||
| Asian | 24 (0.4) | 2 (0.4) | 8 (0.6) | ||||
| Black | 15 (0.3) | 3 (0.6) | 8 (0.6) | ||||
| Chinese | 9 (0.2) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (0.3) | ||||
| Mixed | 22 (0.4) | 2 (0.4) | 6 (0.4) | ||||
| Other ethnic group | 23 (0.4) | 1 (0.2) | 10 (0.7) | ||||
| Education, N (%) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.197 | ||||
| College/University degree | 2559 (46.4) | 184 (33.8) | 557 (39.6) | ||||
| O levels/GCSEs or equivalent | 1,099 (19.9) | 132 (24.3) | 323 (23.0) | ||||
| A levels/AS levels or equivalent | 631 (11.5) | 66 (12.1) | 156 (11.1) | ||||
| CSEs or equivalent | 206 (3.7) | 18 (3.3) | 54 (3.8) | ||||
| NVQ/HND/HNC or equivalent | 209 (3.8) | 24 (4.4) | 63 (4.5) | ||||
| Other professional qualifications | 387 (7.0) | 60 (11.0) | 114 (8.1) | ||||
| None of the above | 419 (7.6) | 60 (11.0) | 140 (10.0) | ||||
| Lifestyle score* | 1.7±1.2 | 1.6±1.2 | 1.8±1.2 | 0.323 | 0.066 | 0.044 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) * | 25.9±4.50 | 26.1±4.2 | 26.7±4.7 | 0.260 | <0.001 | 0.011 | |
| Menopausal Status, N (%) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| No | 81 (1.5) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.1) | ||||
| Yes | 5,290 (96.0) | 444 (81.6) | 615 (43.7) | ||||
| Not sure – had a hysterectomy | 0 (0.0) | 99 (18.2) | 781 (55.5) | ||||
| Not sure – other reason | 139 (2.5) | 1 (0.2) | 10 (0.7) | ||||
| Hysterectomy, yes, N (%) | 666 (89.4) | ||||||
| APOE ε4 status, carrier, N (%) | 1317 (25.3) | 113 (21.9) | 345 (25.9) | 0.100 | 0.678 | 0.085 | |
| APOE ε4, allele, N (%) | 0.095 | 0.427 | 0.161 | ||||
| non-carrier | 3881 (74.7) | 402 (78.1) | 985 (74.1) | ||||
| ε3/ε4 | 1194 (23.0) | 107 (20.8) | 320 (24.1) | ||||
| ε4/ ε4 | 123 (2.4) | 6 (1.2) | 25 (1.9) | ||||
| Age at menopause* | 50.0±5.1 | 43.1±6.8 | 46.9±6.3 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Age started MHT* | 49.2±5.3 | 46.9±5.7 | 45.6±6.1 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Age last used MHT* | 54.7±6.1 | 55.0±7.4 | 55.2±7.4 | 0.312 | 0.014 | 0.646 | |
| Duration of MHT use* | 5.5±5.4 | 8.1±6.6 | 9.6±7.8 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Age MHT rel Age Menopause | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| Same age | 1177 (24.7) | 89 (19.7) | 303 (46.2) | ||||
| After | 1659 (34.8) | 283 (62.7) | 170 (25.9) | ||||
| Before | 1931 (40.5) | 79 (17.5) | 183 (27.9) | ||||
| Age at oophorectomy* | 47.7±8.2 | ||||||
| Age at hysterectomy* | 44.5±10.0 | 46.9±7.9 | <0.001 | ||||
| Age Oopho rel Age Menopause | |||||||
| Same age | 301 (47.8) | ||||||
| After | 271 (43.0) | ||||||
| Before | 58 (9.2) | ||||||
| Age Oopho rel Age MHT | |||||||
| Same age | 740 (59.0) | ||||||
| After | 367 (29.2) | ||||||
| Before | 148 (11.8) | ||||||
| Age Hyster rel Age Menopause | <0.001 | ||||||
| Same age | 278 (61.6) | 324 (54.8) | |||||
| After | 110 (24.4) | 214 (36.2) | |||||
| Before | 63 (14.0) | 53 (9.0) | |||||
| Age Hyster rel Age MHT | <0.001 | ||||||
| Same age | 80 (17.2) | 746 (61.2) | |||||
| After | 111 (23.9) | 296 (24.3) | |||||
| Before | 274 (58.9) | 177 (14.5) | |||||
-
*
Mean ± Standard Deviation. Age is given in years. Hysterectomy/hyster included females without bilateral oophorectomy; Oophorectomy/Oopho constitutes bilateral oophorectomy (+/-hysterectomy; no hysterectomy n=X, with hysterectomy n=Y). Abbreviation: N, sample size; GCSE, General Certificate of Secondary Education; CSE, Certificate of Secondary Education; NVQ, National Vocational Qualification; BMI, body mass index; APOE, apolipoprotein. Significant differences between groups based on t/χ2 tests are highlighted in bold.
Sample demographics of menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) users with prescription data, stratified by estrogen-only MHT or combined MHT use.
| Estrogens-only | Combined | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 224 | 314 | |
| Age (years)* | 66.1±6.6 | 65.5±6.7 | 0.318 |
| Education N (%) | 0.286 | ||
| College/University degree | 104 (46.4) | 158 (50.3) | |
| A levels/AS levels or equivalent | 21 (9.4) | 29 (9.2) | |
| O levels/GCSEs or equivalent | 45 (20.1) | 70 (22.3) | |
| CSEs or equivalent | 9 (4.0) | 14 (4.5) | |
| NVQ/HND/HNC or equivalent | 5 (2.2) | 11 (3.5) | |
| Other professional qualifications | 18 (8.0) | 16 (5.1) | |
| None of the above | 22 (9.8) | 16 (5.1) | |
| Lifestyle score* | 1.7±1.2 | 1.8±1.3 | 0.212 |
| BMI (kg/m2)* | 26.1±4.1 | 26.1±4.8 | 0.959 |
| Menopausal Status (%) | <0.001 | ||
| No | 2 (0.9) | 3 (1.0) | |
| Yes | 140 (62.5) | 285 (90.8) | |
| Not sure – had a hysterectomy | 77 (34.4) | 21 (6.7) | |
| Not sure – other reason | 5 (2.2) | 5 (1.6) | |
| APOE ε4 status, carrier, N (%) | 64 (29.4) | 75 (24.8) | 0.284 |
| APOE ε4, allele, N (%) | |||
| non-carrier | 154 (70.6) | 228 (75.2) | 0.486 |
| ε3/ ε4 | 59 (27.1) | 70 (23.1) | |
| ε4/ ε4 | 5 (2.3) | 5 (1.7) | |
| Hyster-/Oophorectomy, yes (%) | 79 (41.1) | 34 (11.2) | <0.001 |
| Number of drug regimes | 1.39 (0.99) | 2.68 (1.83) | <0.001 |
| Drug dosage, estrogens (mg) | 0.3±0.4 | 1.0±0.7 | <0.001 |
| Drug dosage, progestin (mg) | 5.4±20.6 | ||
| Duration of use, estrogens (weeks) | 202.4±197.7 | 244.8±202.2 | 0.031 |
| Duration of use, progestin (weeks) | 195.2±174.7 | ||
| Route of administration, N (%) | <0.001 | ||
| oral | 40 (17.9) | 193 (61.5) | |
| transdermal | 50 (22.3) | 14 (4.5) | |
| vaginal | 109 (48.7) | 0 (0.0) | |
| injectionꞋ | 4 (1.8) | 5 (1.6) | |
| mixed | 21 (9.4) | 102 (32.5) | |
| Estrogens, active ingredient, N (%) | |||
| estradiol hemihydrate° | 141 (62.9) | ||
| CEE | 18 (8.0) | ||
| estradiol° | 34 (15.2) | ||
| estradiol valerate° | 4 (1.8) | ||
| tibolone | 0 (0.0) | ||
| mixed | 27 (12.1) | ||
| Estrogens + Progestins, active ingredient, N (%) | |||
| estradiol hemihydrate & norethisterone acetate 1 | 51 (16.2) | ||
| estradiol hemihydrate & dydrogesterone° 2 | 14 (4.5) | ||
| estradiol hemihydrate & norethisterone 1 | 13 (4.1) | ||
| estradiol hemihydrate & levonorgestre 2 | 2 (0.6) | ||
| estradiol hemihydrate & drospirenone 3 | 1 (0.3) | ||
| CEE & norgestrel 2 | 19 (6.1) | ||
| CEE & medroxyprogesterone acetate 1 | 10 (3.2) | ||
| CEE & norethisterone1 | 2 (0.6) | ||
| estradiol valerate & norethisterone 1 | 8 (2.5) | ||
| estradiol valerate & levonorgestrel 2 | 3 (1.0) | ||
| estradiol valerate & medroxyprogesterone acetate 1 | 3 (1.0) | ||
| estradiol & norethisterone acetate 1 | 7 (2.2) | ||
| estradiol & norethisterone 1 | 3 (1.0) | ||
| estradiol & progesterone° 1 | 2 (0.6) | ||
| tibolone | 13 (4.1) | ||
| mixed | 163 (51.9) |
-
*
Mean ±Standard Deviation. °Bioidentical form (no circle indicates synthetic form); 1-3=progestin generations; Ꞌincl. subcutaneous and intravenous infections. Abbreviations: N, sample size; GCSE, General Certificate of Secondary Education; CSE, Certificate of Secondary Education; NVQ, National Vocational Qualification; BMI, body mass index; APOE, apolipoprotein; CEE, conjugated equine estrogen. Significant differences between groups based on t/χ2 tests are highlighted in bold.
Gray matter brain age gap model selection based on corrected Akaike Information Criterion (AICc).
| Model name | Age ^(2) | K | AICc | /_\AICc | ModelLik | AICcWt | LL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MHT never-user/user | Yes | 8 | 12347.35 | 0.00 | 1 | 1 | -6165.66 |
| No | 8 | 43951.59 | 31604.24 | 0 | 0 | -21967.79 | |
| MHT never-/current-/past-user | Yes | 10 | 40976.73 | 0.00 | 1 | 1 | -20478.36 |
| No | 9 | 41194.26 | 217.53 | 0 | 0 | -20588.12 | |
| Age at first MHT use | Yes | 9 | 12297.05 | 0.00 | 1 | 1 | -6139.50 |
| No | 8 | 12347.35 | 50.30 | 0 | 0 | -6165.66 | |
| Age at first MHT use rel. menopause | Yes | 8 | 11023.87 | 0.00 | 1 | 1 | -5503.91 |
| No | 7 | 11061.39 | 37.53 | 0 | 0 | -5523.68 | |
| Age at last MHT use | Yes | 9 | 9908.18 | 0.00 | 1 | 1 | -4945.06 |
| No | 8 | 9937.17 | 28.99 | 0 | 0 | -4960.56 | |
| Age at last MHT use rel. menopause | Yes | 8 | 9144.83 | 0.00 | 1 | 1 | -4564.39 |
| No | 7 | 9160.71 | 15.88 | 0 | 0 | -4573.34 | |
| Duration of MHT use | Yes | 9 | 11736.31 | 0.00 | 1 | 1 | -5859.13 |
| No | 8 | 11788.00 | 51.69 | 0 | 0 | -5885.98 | |
| Oophorectomy | Yes | 9 | 21082.53 | 0.00 | 1 | 1 | -10532.25 |
| No | 8 | 21154.50 | 71.97 | 0 | 0 | -10569.24 | |
| Hysterectomy | Yes | 9 | 16161.19 | 0.00 | 1 | 1 | -8071.58 |
| No | 8 | 16220.38 | 59.19 | 0 | 0 | -8102.18 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Assessment of menopausal hormone therapy (MHT)-related variables in the UK Biobank (UKB).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/99538/elife-99538-supp1-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Lifestyle factors, constituting the lifestyle score, in menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) never-, current, and past- users in the whole sample.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/99538/elife-99538-supp2-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 3
Age prediction accuracy for the global gray and white matter models.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/99538/elife-99538-supp3-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 4
Associations between menopausal hormone therapy (MHT)-related variables and brain measures in the whole sample.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/99538/elife-99538-supp4-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 5
Associations between menopausal hormone therapy (MHT)-related variables and brain measures in the prescription MHT sample.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/99538/elife-99538-supp5-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 6
Associations between apolipoprotein ε type 4 (APOE ε4) genotype and brain measures in the whole sample.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/99538/elife-99538-supp6-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 7
Interactions between apolipoprotein ε type 4 (APOE ε4) genotype and menopausal hormone therapy (MHT)-related variables on brain measures in the entire sample.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/99538/elife-99538-supp7-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 8
Interactions between apolipoprotein ε type 4 (APOE ε4) genotype and menopausal hormone therapy (MHT)-related variables on brain measures in the prescription sample.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/99538/elife-99538-supp8-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 9
Associations between menopausal hormone therapy (MHT)-related variables and brain measures in the whole sample, excluding participants with ICD-10 diagnosis known to impact the brain.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/99538/elife-99538-supp9-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 10
Associations between menopausal hormone therapy (MHT)-related variables and brain measures in the prescription MHT sample, excluding participants with ICD-10 diagnosis known to impact the brain.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/99538/elife-99538-supp10-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 11
Associations between menopausal hormone therapy (MHT)-related variables and brain measures in the whole sample, also adjusting for age (Ding et al., 2013).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/99538/elife-99538-supp11-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 12
Associations between menopausal hormone therapy (MHT)-related variables and brain measures in the whole sample, after removal of extreme values.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/99538/elife-99538-supp12-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 13
Detected extreme values of continuous menopausal hormone therapy (MHT)-related variables using the median absolute deviation method.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/99538/elife-99538-supp13-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 14
Associations between menopausal hormone therapy (MHT)-related variables and brain measures in the prescription MHT sample, adjusting for additional covariates.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/99538/elife-99538-supp14-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 15
Associations between menopausal hormone therapy (MHT)-related variables and brain measures in the prescription MHT sample, with age, education, and menopause-status matched never-users.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/99538/elife-99538-supp15-v1.docx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/99538/elife-99538-mdarchecklist1-v1.docx