Microbial Ecology: How to trigger a fungal weapon
Fungi affect our lives in many different ways, both positive and negative. One of the reasons for this is that most fungi produce a multitude of small organic molecules called secondary metabolites. Different species employ a strikingly diverse arsenal of secondary metabolites, most of which are released into the environment (Sanchez et al., 2012). Secondary metabolites are not directly required to ensure the growth of the organism, but confer an advantage under specific environmental conditions.
Fungi use secondary metabolites to defend against predators and competitors, for chemical communication, or in the case of pathogenic fungi, to manipulate their animal and plant hosts (Brakhage et al., 2013). Secondary metabolism is therefore likely to be shaped to a large extent by interactions with other organisms. For example, fungi secrete enzymes to digest their food, which allows them to grow on virtually any organic matter, but also means that the products of their digestion are in principle a free meal for other organisms. And by secreting secondary metabolites that target these organisms, fungi are able to defend their niche to avoid competitors taking advantage of the available food.
Well-known examples of secondary metabolites produced by fungi are the poisonous food contaminant aflatoxin, the antibiotic penicillin and the anticancer drug taxol. These molecules illustrate the negative and positive effects of secondary metabolites on humans, and underline their outstanding potential for medicinal use. However, it is not known what roles most of these molecules play in the lives of the fungi that produce them. Moreover, most secondary metabolites are not produced when the fungi are grown in the laboratory, which makes it difficult to characterize them. Now in eLife, Matthias Brock and co-workers – including Markus Gressler as first author – report a new role for a major secondary metabolite called terrein, and characterize the environmental stimuli that induce the mold Aspergillus terreus to produce it (Figure 1; Gressler et al., 2015).
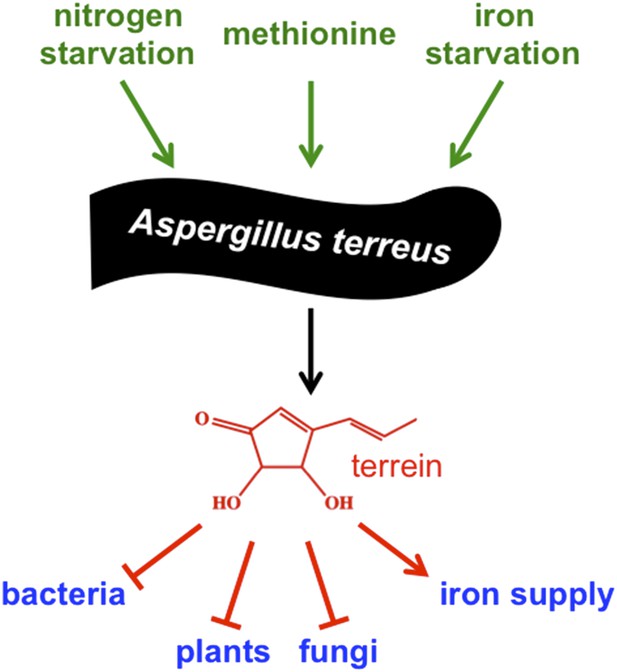
Environmental signals activate production of terrein by the mold Aspergillus terreus to improve its competitiveness.
To adapt to changing environmental conditions and different ecological niches, microorganisms need to be able to sense and respond to environmental signals. Gressler et al. identified three independent signals that stimulate production of the compound terrein by Aspergillus terreus – nitrogen starvation, methionine, and iron starvation. In this mold's natural niche within plants and in the soil surrounding plant roots, terrein is a chemical weapon used to inhibit the growth of bacteria, plants and other fungi, but also helps to improve iron supply to the producer.
A. terreus is a common soil-borne fungus that feeds on dead organic material, but is also able to invade plants and cause life-threatening infections in humans with weakened immune systems. Genome analysis indicated that this fungus might produce more than 68 secondary metabolites, although only 14—including the cholesterol-lowering drug lovastatin—have been identified so far (Guo and Wang, 2014). The compound terrein was first described 80 years ago, but how A. terreus makes terrein was only resolved in 2014 by the Brock group (Zaehle et al., 2014). Terrein was previously shown to be harmful to plant cells as it inhibits the germination of seeds and causes lesions on plant surfaces, and probably helps the fungus to colonize its host.
Based on the observation that potato extract (an ingredient of a standard medium used for culturing fungi) activates the production of terrein, Gressler et al. – who are based at the Hans Knoell Institute, Friedrich Schiller University and Nottingham University – systematically characterized how different conditions impact terrein production. This analysis revealed that the genes that encode the terrein biosynthetic pathway are activated by three independent environmental stimuli: nitrogen starvation, iron starvation, and the presence of the amino acid methionine. These conditions are typically found in the plant and the plant root area, known as the rhizosphere, and are used by the mold to sense these niches.
Next, by genetic engineering of the mold, Gressler et al. identified three transcription factors that activate genes in response to environmental signals. Previous studies have revealed the roles of these regulators in altering the production of primary metabolites – which are required for normal growth and reproduction – in response to stress and the availability of nitrogen and iron (Haas, 2012; Tudzynski, 2014). However, it is not known how the mold perceives the methionine signal. Nitrogen and iron also regulate the production of other secondary metabolites (Tudzynski, 2014; Wiemann et al., 2014), suggesting that these environmental cues are often used to adjust secondary metabolism. The complex environmental control of terrein production revealed by Gressler et al. represents a prime example of how microorganisms adapt their secondary metabolism to the niche they inhabit.
In addition to its ability to inhibit the growth of plants, it has been reported that terrein can inhibit the growth of bacteria, fungi and mammalian cells, and that it can also act as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory (Zaehle et al., 2014). Now, Gressler et al. have discovered that terrein supports iron uptake by the fungus that produces it, but inhibits the growth of even closely related molds. This clearly indicates that terrein improves the competiveness of the producer. It will be exciting to learn how terrein is able to influence many different biological processes in different organisms, and how the producer protects itself against this molecule.
References
-
Regulation of fungal secondary metabolismNature Reviews Microbiology 11:21–32.https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2916
-
Recent advances in genome mining of secondary metabolites in Aspergillus terreusFrontiers in Microbiology 5:717.https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00717
-
Iron—a key nexus in the virulence of Aspergillus fumigatusFrontiers in Microbiology 3:28.https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2012.00028
-
Advances in Aspergillus secondary metabolite research in the post-genomic eraNatural Product Reports 29:351–371.https://doi.org/10.1039/c2np00084a
-
Nitrogen regulation of fungal secondary metabolism in fungiFrontiers in Microbiology 5:656.https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00656
-
Terrein biosynthesis in Aspergillus terreus and its impact on phytotoxicityChemistry & Biology 21:719–731.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2014.03.010
Article and author information
Author details
Publication history
- Version of Record published: September 1, 2015 (version 1)
Copyright
© 2015, Haas
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 1,948
- Page views
-
- 236
- Downloads
-
- 6
- Citations
Article citation count generated by polling the highest count across the following sources: PubMed Central, Crossref, Scopus.
Download links
Downloads (link to download the article as PDF)
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools)
Further reading
-
- Biochemistry and Chemical Biology
- Plant Biology
Metabolism and biological functions of the nitrogen-rich compound guanidine have long been neglected. The discovery of four classes of guanidine-sensing riboswitches and two pathways for guanidine degradation in bacteria hint at widespread sources of unconjugated guanidine in nature. So far, only three enzymes from a narrow range of bacteria and fungi have been shown to produce guanidine, with the ethylene-forming enzyme (EFE) as the most prominent example. Here, we show that a related class of Fe2+- and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases (2-ODD-C23) highly conserved among plants and algae catalyze the hydroxylation of homoarginine at the C6-position. Spontaneous decay of 6-hydroxyhomoarginine yields guanidine and 2-aminoadipate-6-semialdehyde. The latter can be reduced to pipecolate by pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase but more likely is oxidized to aminoadipate by aldehyde dehydrogenase ALDH7B in vivo. Arabidopsis has three 2-ODD-C23 isoforms, among which Din11 is unusual because it also accepted arginine as substrate, which was not the case for the other 2-ODD-C23 isoforms from Arabidopsis or other plants. In contrast to EFE, none of the three Arabidopsis enzymes produced ethylene. Guanidine contents were typically between 10 and 20 nmol*(g fresh weight)-1 in Arabidopsis but increased to 100 or 300 nmol*(g fresh weight)-1 after homoarginine feeding or treatment with Din11-inducing methyljasmonate, respectively. In 2-ODD-C23 triple mutants, the guanidine content was strongly reduced, whereas it increased in overexpression plants. We discuss the implications of the finding of widespread guanidine-producing enzymes in photosynthetic eukaryotes as a so far underestimated branch of the bio-geochemical nitrogen cycle and propose possible functions of natural guanidine production.
-
- Biochemistry and Chemical Biology
- Medicine
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is associated with higher fracture risk, despite normal or high bone mineral density. We reported that bone formation genes (SOST and RUNX2) and advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) were impaired in T2D. We investigated Wnt signaling regulation and its association with AGEs accumulation and bone strength in T2D from bone tissue of 15 T2D and 21 non-diabetic postmenopausal women undergoing hip arthroplasty. Bone histomorphometry revealed a trend of low mineralized volume in T2D (T2D 0.249% [0.156–0.366]) vs non-diabetic subjects 0.352% [0.269–0.454]; p=0.053, as well as reduced bone strength (T2D 21.60 MPa [13.46–30.10] vs non-diabetic subjects 76.24 MPa [26.81–132.9]; p=0.002). We also showed that gene expression of Wnt agonists LEF-1 (p=0.0136) and WNT10B (p=0.0302) were lower in T2D. Conversely, gene expression of WNT5A (p=0.0232), SOST (p<0.0001), and GSK3B (p=0.0456) were higher, while collagen (COL1A1) was lower in T2D (p=0.0482). AGEs content was associated with SOST and WNT5A (r=0.9231, p<0.0001; r=0.6751, p=0.0322), but inversely correlated with LEF-1 and COL1A1 (r=–0.7500, p=0.0255; r=–0.9762, p=0.0004). SOST was associated with glycemic control and disease duration (r=0.4846, p=0.0043; r=0.7107, p=0.00174), whereas WNT5A and GSK3B were only correlated with glycemic control (r=0.5589, p=0.0037; r=0.4901, p=0.0051). Finally, Young’s modulus was negatively correlated with SOST (r=−0.5675, p=0.0011), AXIN2 (r=−0.5523, p=0.0042), and SFRP5 (r=−0.4442, p=0.0437), while positively correlated with LEF-1 (r=0.4116, p=0.0295) and WNT10B (r=0.6697, p=0.0001). These findings suggest that Wnt signaling and AGEs could be the main determinants of bone fragility in T2D.





