Developmental Neuroscience: Catching a wave
As the brain develops, neurons start to form the sensory networks that enable us to interpret the world around us in terms of light, sound and touch (Huberman et al., 2008). Before these sensory networks are fully functional, sensory structures such as the retina and cochlea create waves of spontaneous neural activity that help to shape the network (Kirkby et al., 2013). At the same time, the visual cortex produces spontaneous oscillations called spindle-bursts that depend on input from the retina (Hanganu et al., 2006). These various forms of spontaneous activity only occur during a short developmental window. In rats, for instance, they are only produced in the retina and visual cortex within the first two weeks after birth, just before the young rat can open its eyes at postnatal day 14.
In the visual system, a temporary circuit in the retina produces spontaneous retinal waves that sweep across its surface, and output neurons transmit these waves through the optic nerve to the visual thalamus (Galli and Maffei, 1988). Thalamic axons then project this information to the visual cortex, completing the basic visual pathway. It has taken over twenty years of research to figure out the details of the temporary circuit that produces retinal waves (Ford and Feller, 2012), but we know relatively little about the circuits that transform retinal waves, which are poorly synchronized, into spindle-bursts, which are highly synchronized, in the thalamus and cortex. Now, in eLife, Yasunobu Murata and Matthew Colonnese of George Washington University have shed new light on this problem (Murata and Colonnese, 2016).
In experiments performed on neonatal rats, Murata and Colonnese mapped the roles of the retina, thalamus and cortex in the creation of spindle-bursts by removing these three regions in the brain's visual pathway one by one and recording any neural activity that remained elsewhere in the pathway. Silencing the retina (by injecting it with activity-blocking drugs) reduced activity in both thalamus and cortex by 90%, showing that retinal waves drive spindle-bursts throughout the visual pathway. By contrast, silencing the thalamus reduced the level of spontaneous activity in the cortex and completely prevented the synchronization of any remaining activity there. It is clear, therefore, that the thalamus is required to convert retinal waves into spindle-bursts in the cortex. Finally, silencing the cortex nearly abolished spontaneous activity in the thalamus, leaving only weak and slow residual oscillations.
Taken together, these results suggest that a pathway that connects the cortex and thalamus both amplifies and synchronizes oscillations generated in the thalamus to produce spindle-bursts in response to retinal waves. However, this synchronizing circuit is active only for a short time: this period, which is called the spindle-burst window, lasts from postnatal day 5 to postnatal day 11.
What circuit changes underlie this transient amplifier? To tackle this question, Murata and Colonnese used optogenetic techniques to stimulate the cortex and mimic spontaneous spindle-bursts in the corticothalamic pathway. They found that, early in the spindle-burst window (postnatal day 5–7), the pathway amplified thalamic activity by a small amount, but did not synchronize it. Later, when the pathway had been strengthened (postnatal day 9–11), repeated stimulation of the cortex led to spindle-burst-like oscillations in the thalamus. Then, after the spindle-burst window had closed (postnatal day 13–14), cortical stimulation excited and then suppressed thalamic output, preventing spindle-burst-like oscillations in thalamus. These findings suggest that, later in development, the cortex inhibits the thalamus and prevents the corticothalamic pathway from amplifying spindle-bursts.
So how does the cortex inhibit the thalamus and shut down the transient amplifier? In adults, the corticothalamic pathway directly excites the sensory thalamus and, at the same time, indirectly inhibits it by activating a feedforward pathway through the thalamic reticular nucleus (Figure 1). Because indirect inhibition outweighs direct excitation, activation of the corticothalamic pathway can truncate the output from the thalamus (Golshani et al., 2001). The late development of this feedforward pathway might explain when the transient amplifier is shut down.
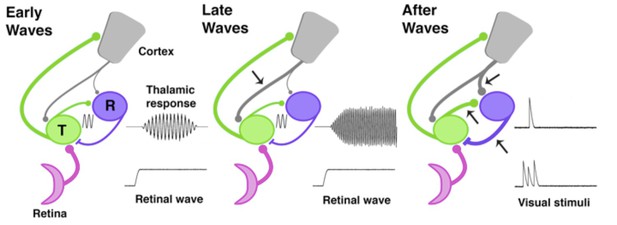
The development of thalamic circuits.
Here, we show how developing thalamic and cortical pathways might temporarily enable spindle-bursts. Pathways linking the retina (pink), thalamus (green, T), reticular thalamic nucleus (purple, R), and cortex (grey) are shown at three different times during development based on data from rats and mice. The thickness of each line represents the strength of the pathway; arrows mark pathways that increase in strength at each developmental timepoint. Transmission speed and the strength of the connection between the thalamus and its synaptic partners help to set the frequency and level of synchronization of oscillations (Bal et al., 1995). During the early and middle stages of the spindle-burst window (left), an ascending pathway transmits retinal waves to thalamus and cortex. Early in the spindle-burst window, thalamic circuitry produces brief, low frequency spindle-bursts (indicated by sine wave), likely through connections to the reticular nucleus, which have just become functional at this time. A modest corticothalamic projection (grey) amplifies this oscillation. Later in the spindle-burst window (middle), a strengthened corticothalamic projection (arrow) amplifies, speeds, and prolongs thalamic spindle-bursts. After the spindle-burst window (right), reciprocal connections between thalamus and the reticular nucleus continue to develop (lower arrows), as may the projection from the cortex to the reticular nucleus (upper arrow). At the same time, both the thalamic and cortical components of spindle-bursts disappear: this enables the thalamus to respond to transient stimulation from the retina, before the thalamic response is quickly suppressed by the cortex.
In addition to spontaneously generated retinal waves, visual stimuli that excite the retina can also evoke a spindle-burst in the thalamus and cortex, but only late during this brief developmental window (postnatal day 9–11). Using light to stimulate the retina, Murata and Colonnese find that visually-evoked spindle-bursts are similarly amplified by the corticothalamic pathway. After the spindle-burst window closes, visually-evoked responses in the thalamus are no longer synchronized, even after the cortex has been inactivated: this shows that the thalamic component of spindle-bursts has also disappeared by this time. Shutting down thalamic spindle-burst responses to visual input is essential for visual processing in adults.
During the spindle-burst window, thalamic neurons are rapidly developing, which may temporarily enable spindle-bursts. Their electrical excitability increases, as does synaptic connectivity with the reticular nucleus (Figure 1), both of which contribute to mature thalamic circuitry (Warren and Jones, 1997). The thalamus can only produce spindle-bursts for a few days during development, and during this time it is only partially wired into oscillatory networks with the reticular nucleus and cortex.
Synchronized neural activity during development can influence the shape of mature neural circuits. During the second postnatal week in mice, synapses in the cortex that fire out of sync with their neighbors become weaker, while synapses that fire in sync persist (Winnubst et al., 2015). Synchronized spindle-bursts, both spontaneous and sensory-evoked, may have a similar effect on synaptic connections because they provide a way to coordinate neuronal firing patterns, which is required to stabilize synapses.
Experiments that distort retinal waves by targeting their circuit generator have shown how they shape connectivity patterns between the retina and thalamus (Kirkby et al., 2013). Now that we have a better understanding of the circuits that connect the retina, the visual thalamus and the visual cortex, experiments that disrupt spindle-bursts could lead to further insights into the development of the visual system.
References
-
Assembly and disassembly of a retinal cholinergic networkVisual Neuroscience 29:61–71.https://doi.org/10.1017/S0952523811000216
-
Retinal waves trigger spindle bursts in the neonatal rat visual cortexJournal of Neuroscience 26:6728–6736.https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0752-06.2006
-
Mechanisms underlying development of visual maps and receptive fieldsAnnual Review of Neuroscience 31:479–509.https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.31.060407.125533
-
Maturation of neuronal form and function in a mouse thalamo-cortical circuitJournal of Neuroscience 17:277–295.
Article and author information
Author details
Publication history
- Version of Record published: October 11, 2016 (version 1)
Copyright
© 2016, Fogerson et al.
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 967
- views
-
- 121
- downloads
-
- 0
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.
Download links
Downloads (link to download the article as PDF)
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools)
Further reading
-
- Neuroscience
Combining information from multiple senses is essential to object recognition, core to the ability to learn concepts, make new inferences, and generalize across distinct entities. Yet how the mind combines sensory input into coherent crossmodal representations - the crossmodal binding problem - remains poorly understood. Here, we applied multi-echo fMRI across a four-day paradigm, in which participants learned 3-dimensional crossmodal representations created from well-characterized unimodal visual shape and sound features. Our novel paradigm decoupled the learned crossmodal object representations from their baseline unimodal shapes and sounds, thus allowing us to track the emergence of crossmodal object representations as they were learned by healthy adults. Critically, we found that two anterior temporal lobe structures - temporal pole and perirhinal cortex - differentiated learned from non-learned crossmodal objects, even when controlling for the unimodal features that composed those objects. These results provide evidence for integrated crossmodal object representations in the anterior temporal lobes that were different from the representations for the unimodal features. Furthermore, we found that perirhinal cortex representations were by default biased towards visual shape, but this initial visual bias was attenuated by crossmodal learning. Thus, crossmodal learning transformed perirhinal representations such that they were no longer predominantly grounded in the visual modality, which may be a mechanism by which object concepts gain their abstraction.
-
- Genetics and Genomics
- Neuroscience
Genome-wide association studies have revealed >270 loci associated with schizophrenia risk, yet these genetic factors do not seem to be sufficient to fully explain the molecular determinants behind this psychiatric condition. Epigenetic marks such as post-translational histone modifications remain largely plastic during development and adulthood, allowing a dynamic impact of environmental factors, including antipsychotic medications, on access to genes and regulatory elements. However, few studies so far have profiled cell-specific genome-wide histone modifications in postmortem brain samples from schizophrenia subjects, or the effect of antipsychotic treatment on such epigenetic marks. Here, we conducted ChIP-seq analyses focusing on histone marks indicative of active enhancers (H3K27ac) and active promoters (H3K4me3), alongside RNA-seq, using frontal cortex samples from antipsychotic-free (AF) and antipsychotic-treated (AT) individuals with schizophrenia, as well as individually matched controls (n=58). Schizophrenia subjects exhibited thousands of neuronal and non-neuronal epigenetic differences at regions that included several susceptibility genetic loci, such as NRG1, DISC1, and DRD3. By analyzing the AF and AT cohorts separately, we identified schizophrenia-associated alterations in specific transcription factors, their regulatees, and epigenomic and transcriptomic features that were reversed by antipsychotic treatment; as well as those that represented a consequence of antipsychotic medication rather than a hallmark of schizophrenia in postmortem human brain samples. Notably, we also found that the effect of age on epigenomic landscapes was more pronounced in frontal cortex of AT-schizophrenics, as compared to AF-schizophrenics and controls. Together, these data provide important evidence of epigenetic alterations in the frontal cortex of individuals with schizophrenia, and remark for the first time on the impact of age and antipsychotic treatment on chromatin organization.






