Totipotency: A developmental insurance policy
The very first decisions in the life of a mammal are made even before the embryo implants into the womb. During this time, as the number of cells in the embryo increases from one to two to four and so on, the cells start to specialize to form distinct lineages. The first choice a cell faces is whether to join a cell population called the inner cell mass and become part of the embryo, or to join the trophectoderm lineage and become part of the placenta.
The biology of this cell fate decision has been a subject of intrigue and experimental pursuit for over half a century. Building on landmark work by the late Krystof Tarkowski, Martin Johnson and others (Johnson and Ziomek, 1981; Tarkowski and Wróblewska, 1967), recent studies have demonstrated the importance of the Hippo signaling pathway – a pathway well known for regulating cell growth and death – in this process (reviewed in Sasaki, 2017). These studies have established how the polarity and position of a cell either cause activation of the Hippo pathway in the inner cells of the embryo, or inhibit it in the outer cells of the embryo to promote the expression of genes encoding a trophectoderm identity.
Previous attempts to determine the exact timing of when cells commit to either the inner cell mass (ICM) or the trophectoderm (TE) lineage yielded somewhat conflicting results. Now, in eLife, Janet Rossant and colleagues – including Eszter Posfai of the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto as first author – report how they have used the thread and needle of fluorescent reporters and single-cell transcriptomics to stitch together classic and recent findings on this topic (Posfai et al., 2017).
A transcription factor called CDX2 has a central role in triggering the TE transcriptional program. The expression of CDX2 in cells that go on to become part of the TE relies on a complex called TEAD-YAP, which is activated by inhibition of the Hippo pathway in the outer cells of the embryo (Nishioka et al., 2009). Posfai et al. used a CDX2-GFP fusion (McDole and Zheng, 2012) to sort CDX2-positive and CDX2-negative cells, followed by single-cell RNA sequencing, to determine how the TE and ICM transcriptional programs became established as the embryo developed from the 16-cell stage to the 32-cell stage.
These data raise the question of what the progressive stabilization of cell fate might tell us about commitment to either lineage. Could the expression of TE genes restrict cells to a TE fate even when challenged experimentally (i.e., when placed in a new context)? In the assays used to test these questions, either single cells have to be implanted into genetically-distinct host embryos to generate a chimera, or an embryo needs to be rebuilt from isolated cells of one particular type (inner or outer). The contribution of daughter cells to the resulting embryo will reveal details about lineage commitment in the parental cells. With these techniques, the labs of Tarkowski, Johnson and Rossant previously established that both the inner and outer cells remain totipotent – that is, they can give rise to the ICM and TE lineages – until the 16-cell stage, with some inner cells remaining totipotent until the 32-cell stage (Suwińska et al., 2008; Rossant and Vijh, 1980; Ziomek et al., 1982).
Posfai et al. perform a contemporary version of these classic experiments using the CDX2-GFP fluorescent genetic marker, rather than cell position, to discriminate between prospective TE and ICM cells. They were able to precisely match cell fate commitment to the relevant gene expression profile of individual cells for both (GFP-positive and GFP-negative) populations at successive stages of development. This allowed them to confirm previous results and to paint a detailed picture of the molecular players that are potentially involved in stabilizing these two cell fates. For cells expressing CDX2, cell fate is basically sealed soon after blastocyst formation (at the 32-cell stage), and they are unable to give rise to the ICM. ICM cells, on the other hand, delay their commitment by an additional cell cycle, up until some point between the 32- and 64-cell stages (Figure 1). Posfai et al. confirm these results by genetically and pharmacologically modulating the activity of the Hippo pathway, which connects apico-basal cell polarity (or the lack of it in ICM cells) to gene expression.
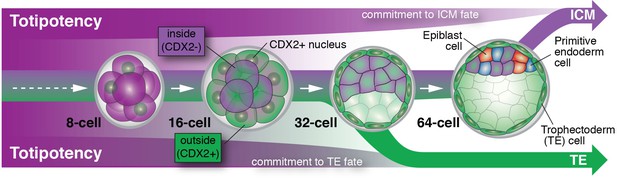
Cell differentiation in mammalian embryos.
Cells that develop into the trophectoderm (TE) express the transcription factor CDX2 (denoted here as CDX2+) and commit to their cell fate at around the 32-cell stage. Cells that will develop into the inner cell mass (ICM) keep their options open and only commit to their cell fate at a time between the 32- and 64-cell stage; these cells do not express CDX2 (denoted here as CDX2-). As embryos grow from the 32- to the 64-cell stage, ICM cells start to differentiate into two new cell lineages: the embryonic epiblast (future fetus) and the extra-embryonic primitive endoderm (future yolk sac).
This raises the question of why commitment to the ICM lineage takes place later during development. Perhaps it is no coincidence that ICM cells gradually begin to make their next cell fate choice during this time window. It is at this time that ICM cells make a decision to become epiblast (future fetus) versus primitive endoderm (future yolk sac). Therefore, the ICM may not be a cell fate per se, but rather a transitory state that lasts only until all the cells in the embryo have been allocated to one of the three lineages that make up the blastocyst. An asynchrony in making these early fate decisions could therefore reflect a developmental insurance policy: a strategy to guarantee that enough cells differentiate for each of the cell types that lay the foundation for all embryonic and extra-embryonic tissues (Saiz et al., 2016).
References
-
Roles and regulations of Hippo signaling during preimplantation mouse developmentDevelopment, Growth & Differentiation 59:12–20.https://doi.org/10.1111/dgd.12335
-
Development of blastomeres of mouse eggs isolated at the 4- and 8-cell stageJournal of Embryology and Experimental Morphology 18:155–180.
-
The developmental potential of mouse 16-cell blastomeresThe Journal of Experimental Zoology 221:345–355.https://doi.org/10.1002/jez.1402210310
Article and author information
Author details
Publication history
- Version of Record published: March 28, 2017 (version 1)
Copyright
© 2017, Saiz et al.
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 938
- views
-
- 165
- downloads
-
- 0
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.
Download links
Downloads (link to download the article as PDF)
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools)
Further reading
-
- Developmental Biology
Inhibitory G alpha (GNAI or Gαi) proteins are critical for the polarized morphogenesis of sensory hair cells and for hearing. The extent and nature of their actual contributions remains unclear, however, as previous studies did not investigate all GNAI proteins and included non-physiological approaches. Pertussis toxin can downregulate functionally redundant GNAI1, GNAI2, GNAI3, and GNAO proteins, but may also induce unrelated defects. Here, we directly and systematically determine the role(s) of each individual GNAI protein in mouse auditory hair cells. GNAI2 and GNAI3 are similarly polarized at the hair cell apex with their binding partner G protein signaling modulator 2 (GPSM2), whereas GNAI1 and GNAO are not detected. In Gnai3 mutants, GNAI2 progressively fails to fully occupy the sub-cellular compartments where GNAI3 is missing. In contrast, GNAI3 can fully compensate for the loss of GNAI2 and is essential for hair bundle morphogenesis and auditory function. Simultaneous inactivation of Gnai2 and Gnai3 recapitulates for the first time two distinct types of defects only observed so far with pertussis toxin: (1) a delay or failure of the basal body to migrate off-center in prospective hair cells, and (2) a reversal in the orientation of some hair cell types. We conclude that GNAI proteins are critical for hair cells to break planar symmetry and to orient properly before GNAI2/3 regulate hair bundle morphogenesis with GPSM2.
-
- Computational and Systems Biology
- Developmental Biology
Organisms utilize gene regulatory networks (GRN) to make fate decisions, but the regulatory mechanisms of transcription factors (TF) in GRNs are exceedingly intricate. A longstanding question in this field is how these tangled interactions synergistically contribute to decision-making procedures. To comprehensively understand the role of regulatory logic in cell fate decisions, we constructed a logic-incorporated GRN model and examined its behavior under two distinct driving forces (noise-driven and signal-driven). Under the noise-driven mode, we distilled the relationship among fate bias, regulatory logic, and noise profile. Under the signal-driven mode, we bridged regulatory logic and progression-accuracy trade-off, and uncovered distinctive trajectories of reprogramming influenced by logic motifs. In differentiation, we characterized a special logic-dependent priming stage by the solution landscape. Finally, we applied our findings to decipher three biological instances: hematopoiesis, embryogenesis, and trans-differentiation. Orthogonal to the classical analysis of expression profile, we harnessed noise patterns to construct the GRN corresponding to fate transition. Our work presents a generalizable framework for top-down fate-decision studies and a practical approach to the taxonomy of cell fate decisions.






