Microglia: Maestros of anesthesia
Before undergoing a surgical procedure, patients are often given a general anesthetic to put them in a state of unconsciousness. It is widely accepted that anesthetic drugs work by suppressing the activity of neurons. However, more recent studies suggest that non-neuronal cells are also involved, particularly immune cells known as microglia, which monitor the central nervous system to ensure healthy brain function is maintained. Impaired cognition following anesthesia, such as delirium and delayed recovery, have been observed in older patients. Given that microglia are known to play a role in neuroinflammation and age-related neurodegeneration, they may be key to the side effects of general anesthesia (Fan et al., 2020).
Previous studies have shown that microglia are more active and perform more surveillance in anesthetized mice (Stowell et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2019). Furthermore, differences in neuronal activity between awake and anesthetized mice correspond to shifts in both microglial function and calcium signaling (Umpierre et al., 2020). This work revealed how the signaling mechanisms that occur in microglia differ in the awake versus anesthetized state, suggesting that microglia help regulate the general anesthesia response. However, it is still poorly understood how microglia molecularly control anesthesia. Now, in eLife, Yousheng Shu (Fudan University), Bo Peng (Fudan and Nantong Universities) and colleagues – including Yang He, Taohui Liu and Quansheng He as joint first authors – report new observations showing how microglia and neurons interact in specific brain regions during general anesthesia (He et al., 2023).
First, the team investigated how depleting microglia affected the induction of and emergence from general anesthesia. To ablate the microglia, they fed mice a diet containing the compound PLX5622 which inhibits a receptor (known as CSF1R) that microglia need to survive. The PLX5622-fed mice were slower to lose the ability to flip over and stand on their feet (known as the loss of righting reflex) compared to mice given a control diet, suggesting delayed induction of anesthesia. Additionally, the mice also recovered this ability (recovery of righting reflex) faster, indicating earlier emergence from anesthesia. To establish this effect as being microglia-specific, and not due to equivalent cells outside the brain, He et al. fed mice a CSF1R inhibitor that cannot cross the blood-brain-barrier and enter the central nervous system. The rates of induction of and emergence from general anesthesia were similar to those observed in the control group, suggesting that both effects are mediated specifically by microglia. These findings were further validated by recording electrical activity in the brain and muscle, which also indicated a late induction and early emergence from anesthesia in microglia-ablated mice.
Next, He et al. looked at how microglia affect different regions of the brain during general anesthesia using the expression levels of c-Fos as a marker for neuronal activity. This revealed that microglia depletion significantly reduced neuronal activity in the parts of the brain activated by anesthesia, but increased activity in the regions activated during emergence. This region-dependent regulation was also demonstrated through a series of experiments measuring whole-cell recordings of neuronal activity. These findings build upon previous studies showing microglia to modulate neuronal activity in a region-specific manner (Badimon et al., 2020).
Finally, to better understand how microglia affect neuronal function, He et al. knocked out a microglial receptor, known as P2Y12R, that regulates neuronal crosstalk and activity when activated by purines, such as ADP (Yu et al., 2019). P2Y12R knockout was achieved in two different ways: using a selective antagonist to block ligand binding and inhibit downstream signaling, and by inactivating the gene that codes for the receptor in microglial cells through gene editing. Both methods delayed the induction of anesthesia and led to an accelerated right of recovery reflex. To validate this finding, He et al. transplanted the mice with bone marrow cells that mature into P2Y12R-negative microglia and replace the healthy microglia of the central nervous system (Xu et al., 2020). This repopulation led to similar outcomes to those observed in P2Y12R-knockout conditions.
Activation of P2Y12R enhances the level of calcium inside microglia (Jiang et al., 2017). Further experiments increasing or decreasing the amount of intracellular calcium altered how quickly the mice were induced into and emerged from an anesthetic state. These data convincingly show how disruption of purinergic receptor signaling, and consequently microglial calcium signaling, are essential for regulating anesthesia in mice (Figure 1).
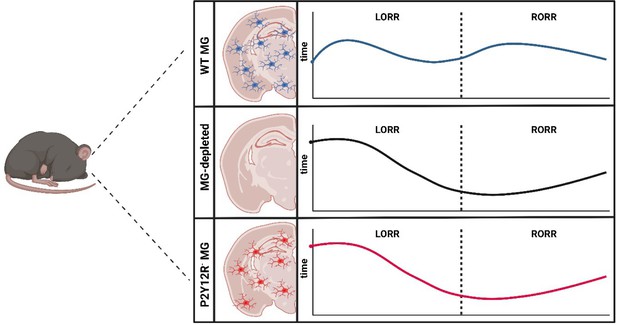
How microglia affect induction of and emergence from anesthetics.
The brains of wild type mice (WT MG; top panel) are populated with immune cells known as microglia (MG; blue). Administration of general anesthetic leads to mice no longer being able to flip over and stand on their feet, known as the loss of righting reflex (LORR). This ability is then restored – known as the recovery of righting reflex (RORR) – as the mice emerge from the anesthesia (dashed line). He et al. found that depleting microglia from the brain (middle panel) caused the loss of righting reflex to occur later, while accelerating the time it took to recover the reflex. This effect was also observed when the brains of the mice were populated with microglia lacking the receptor P2Y12R (red; bottom panel), suggesting that microglia regulate the anesthetic state through this receptor.
Image credit: Figure created using Biorender.com.
The findings of He et al., alongside another recent publication which also revealed microglia regulate general anesthesia through P2Y12R (Cao et al., 2023), provide a new perspective of how immune cells regulate anesthesia. Although previously overlooked, roles for other non-neuronal cells in regulating a state of unconsciousness seem almost inevitable. Surely the vast network of neurons that are suppressed during anesthesia must significantly affect other supporting cells in the brain?
A remaining question, that is also clinically relevant, is how the elevated activity of microglia in older brains affects post-operative delirium in aging populations. A focus on microglia, which are undeniably important for maintaining brain function, may inform better practices in the clinical administration of general anesthesia. This could lead to a more comprehensive understanding of the communication between neurons and microglia within the brain.
References
-
Microglia modulate general anesthesia through P2Y12 receptorCurrent Biology 33:2187–2200.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2023.04.047
-
The role of microglia in perioperative neurocognitive disordersFrontiers in Cellular Neuroscience 14:261.https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2020.00261
Article and author information
Author details
Publication history
- Version of Record published: January 18, 2024 (version 1)
Copyright
© 2024, Khan and Ritzel
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 592
- views
-
- 74
- downloads
-
- 0
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.
Download links
Downloads (link to download the article as PDF)
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools)
Further reading
-
- Neuroscience
The archerfish is unique in its ability to hunt by shooting a jet of water from its mouth that hits insects situated above the water’s surface. To aim accurately, the fish needs to overcome physical factors including changes in light refraction at the air-water interface. Nevertheless, archerfish can still hit the target with a high success rate under changing conditions. One possible explanation for this extraordinary ability is that it is learned by trial and error through a motor adaptation process. We tested this possibility by characterizing the ability of the archerfish to adapt to perturbations in the environment to make appropriate adjustments to its shots. We introduced a perturbing airflow above the water tank of the archerfish trained to shoot at a target. For each trial shot, we measured the error, i.e., the distance between the center of the target and the center of the water jet produced by the fish. Immediately after the airflow perturbation, there was an increase in shot error. Then, over the course of several trials, the error was reduced and eventually plateaued. After the removal of the perturbation, there was an aftereffect, where the error was in the opposite direction but washed out after several trials. These results indicate that archerfish can adapt to the airflow perturbation. Testing the fish with two opposite airflow directions indicated that adaptation took place within an egocentric frame of reference. These results thus suggest that the archerfish is capable of motor adaptation, as indicated by data showing that the fish produced motor commands that anticipated the perturbation.
-
- Neuroscience
Threat-response neural circuits are conserved across species and play roles in normal behavior and psychiatric diseases. Maladaptive changes in these neural circuits contribute to stress, mood, and anxiety disorders. Active coping in response to stressors is a psychosocial factor associated with resilience against stress-induced mood and anxiety disorders. The neural circuitry underlying active coping is poorly understood, but the functioning of these circuits could be key for overcoming anxiety and related disorders. The supramammillary nucleus (SuM) has been suggested to be engaged by threat. SuM has many projections and a poorly understood diversity of neural populations. In studies using mice, we identified a unique population of glutamatergic SuM neurons (SuMVGLUT2+::POA) based on projection to the preoptic area of the hypothalamus (POA) and found SuMVGLUT2+::POA neurons have extensive arborizations. SuMVGLUT2+::POA neurons project to brain areas that mediate features of the stress and threat responses including the paraventricular nucleus thalamus (PVT), periaqueductal gray (PAG), and habenula (Hb). Thus, SuMVGLUT2+::POA neurons are positioned as a hub, connecting to areas implicated in regulating stress responses. Here we report SuMVGLUT2+::POA neurons are recruited by diverse threatening stressors, and recruitment correlated with active coping behaviors. We found that selective photoactivation of the SuMVGLUT2+::POA population drove aversion but not anxiety like behaviors. Activation of SuMVGLUT2+::POA neurons in the absence of acute stressors evoked active coping like behaviors and drove instrumental behavior. Also, activation of SuMVGLUT2+::POA neurons was sufficient to convert passive coping strategies to active behaviors during acute stress. In contrast, we found activation of GABAergic (VGAT+) SuM neurons (SuMVGAT+) neurons did not alter drive aversion or active coping, but termination of photostimulation was followed by increased mobility in the forced swim test. These findings establish a new node in stress response circuitry that has projections to many brain areas and evokes flexible active coping behaviors.






