Cancer: How the immune system spots tumors
The immune system is best known for its role in defending the body against microbial infections. People carrying mutations that affect the immune system are, therefore, highly susceptible to infectious diseases and usually require continuous care to avoid infections. However, it has also been proposed that the immune system can eliminate cancer cells. This idea, known as immune surveillance, is several decades old, but there is little experimental evidence to support it. In large part, this is because the mechanisms used by the body to recognize cancer cells remain poorly understood.
A key feature of the immune system is its ability to distinguish between pathogens (‘non-self’) and the body's own cells (‘self’). Immune cells detect certain components that are found in many microorganisms, such as the complex carbohydrates that make up bacterial and fungal cell walls. Because these components are unique to microbes, detecting them allows the innate immune response—the body's first line of defence—to identify the cell they came from as ‘non-self’ and potentially harmful, and then act to neutralize the threat.
The carbohydrates are recognized by the so-called pattern-recognition receptors, such as Toll-like receptors and C-type lectin receptors, which are found in two types of immune cell—dendritic cells and macrophages (Takeuchi and Akira, 2010). Pathogens cannot easily evade detection because the components that are recognized by the receptors are essential for microbial fitness and survival.
This approach cannot be used to detect tumors because they develop from the host's own cells. Rather, in order to perform immune surveillance the immune system has to be able to distinguish tumor cells from normal cells. One way that this would be possible is if cancer cells produce signals that can be detected by the immune system. Clearly, if such signals exist, they would be the first feature to be lost by the cancer cells as they evolve under the selection pressure imposed by immune surveillance. Unless, that is, getting rid of these signals comes with a significant cost to the cancer cell.
Now, in eLife, Tadatsugu Taniguchi of the University of Tokyo and co-workers—including Shiho Chiba, Hiroaki Ikushima and Hiroshi Ueki as joint first authors—report evidence that immune surveillance does indeed rely on this strategy. They report that the pattern-recognition receptor Dectin-1 plays a crucial role in recognizing a process called tumor cell-associated glycosylation and in initiating an anti-tumor innate immune response (Chiba et al., 2014).
Glycosylation is a reaction where a carbohydrate molecule called a glycan is added to a protein. Altered glycosylation is a universal feature of tumor cells (Varki et al., 2009). By increasing where and how much glycosylation occurs on their surface, many tumor cells develop an advantage over other cells when migrating to and spreading through other organs.
Chiba et al. found that two proteins play crucial roles in suppressing the spread of cancer: Dectin-1 and IRF5 (Figure 1). Dectin-1 recognizes molecules called β-glucans that are found on fungal cell walls (Brown, 2006). When Dectin-1 recognizes its target, the transcription factor IRF5 activates innate immunity in response (del Fresno et al., 2013). Chiba et al. now show that Dectin-1 also recognizes particular glycosylation associated structures called N-glycan structures, which are highly expressed in several tumor cell lines—but not in non-cancerous cells. When N-glycan structures are detected, Dectin-1 triggers an anti-tumor immune response.
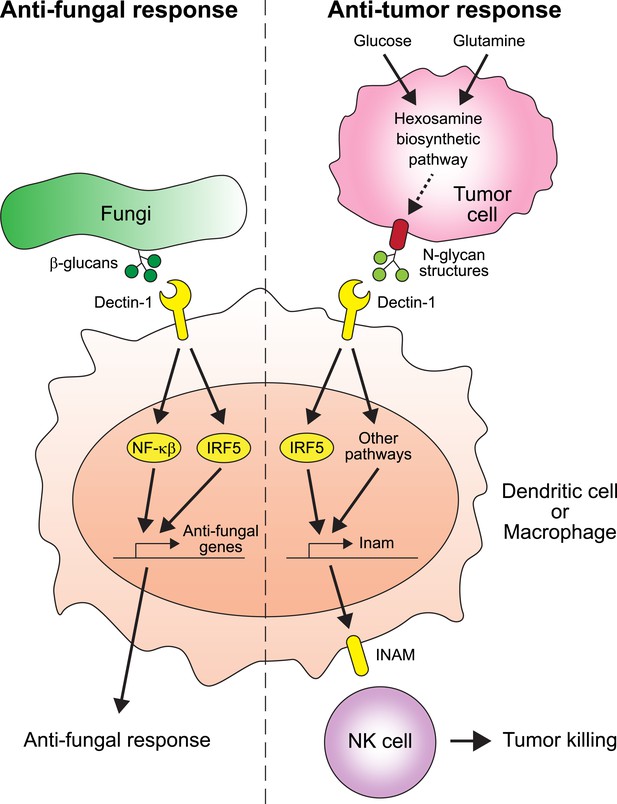
The receptor protein Dectin-1 plays an important role in the anti-fungal and anti-tumor responses of the innate immune system.
Left: Dectin-1 is expressed on dendritic cells and macrophages, and recognizes molecules called β-glucans (dark green circles) on fungal cell walls. This recognition triggers the signaling pathways that activate transcription factors including IRF5 and NF-κβ (del Fresno et al., 2013), which cause anti-fungal genes to be expressed. Right: Chiba et al. found that Dectin-1 can also recognize N-glycan structures expressed on certain tumor cell lines. Recognizing these tumor cell signals activates IRF5 and perhaps other unidentified pathways, which causes tumoricidal action by natural killer (NK) cells. At least part of the mechanism for natural killer cell mediated tumor killing involves increasing the expression of the Inam gene. It would be interesting in the future to determine if Dectin-1 recognizes N-glycan structures as a proxy for the increased activity of the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway in tumor cells.
Natural killer (NK) cells are lymphocytes (or white blood cells) that can kill cancer cells and so could play an important role in immune surveillance (Vivier et al., 2012). Chiba et al. found in their experimental model that natural killer cells are indeed required for the elimination of tumor cells. Furthermore, natural killer cells rely on Dectin-1 expressed on dendritic cells and macrophages in order to kill tumor cells; the findings therefore reveal a new functional link between dendritic cells, macrophages and natural killer cells.
Chiba et al. have taken an important step towards understanding how the anti-tumor immune response works. As is normal for a brand-new finding, this work raises a number of important questions. The level and/or the specific structural patterns of glycosylation on tumor cells appears to be important for the fitness of cancer cells. Therefore, an immune surveillance system based on cell surface glycan recognition may have evolved to prevent cancer cells themselves evolving in a way that enables them to evade the anti-tumor immune response. In this regard, it would be important to know whether Dectin-1 is activated by either an altered structure or increased level of N-glycans on tumor cells.
It is possible that the total level or specific structural variants of cell surface N-glycans may reflect the metabolic state of the cell. For example, the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway—which is used by cells to produce a particular type of sugar—is more active than normal in some cancers and can affect the glycosylation patterns of cell surface proteins (Wellen et al., 2010). It would be very interesting to investigate whether Dectin-1 (and other C-type lectins) evolved to detect the increased activity of the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway through its effect on cell surface N-glycans, as a proxy for cancer cells (Figure 1).
References
-
Dectin-1: a signalling non-TLR pattern-recognition receptorNature Reviews Immunology 6:33–43.https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1745
-
Targeting natural killer cells and natural killer T cells in cancerNature Reviews Immunology 12:239–252.https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3174
Article and author information
Author details
Publication history
- Version of Record published: September 24, 2014 (version 1)
Copyright
© 2014, Okabe and Medzhitov
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 5,229
- views
-
- 413
- downloads
-
- 6
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.
Download links
Downloads (link to download the article as PDF)
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools)
Further reading
-
- Chromosomes and Gene Expression
- Immunology and Inflammation
Ikaros is a transcriptional factor required for conventional T cell development, differentiation, and anergy. While the related factors Helios and Eos have defined roles in regulatory T cells (Treg), a role for Ikaros has not been established. To determine the function of Ikaros in the Treg lineage, we generated mice with Treg-specific deletion of the Ikaros gene (Ikzf1). We find that Ikaros cooperates with Foxp3 to establish a major portion of the Treg epigenome and transcriptome. Ikaros-deficient Treg exhibit Th1-like gene expression with abnormal production of IL-2, IFNg, TNFa, and factors involved in Wnt and Notch signaling. While Ikzf1-Treg-cko mice do not develop spontaneous autoimmunity, Ikaros-deficient Treg are unable to control conventional T cell-mediated immune pathology in response to TCR and inflammatory stimuli in models of IBD and organ transplantation. These studies establish Ikaros as a core factor required in Treg for tolerance and the control of inflammatory immune responses.
-
- Evolutionary Biology
- Immunology and Inflammation
CD4+ T cell activation is driven by five-module receptor complexes. The T cell receptor (TCR) is the receptor module that binds composite surfaces of peptide antigens embedded within MHCII molecules (pMHCII). It associates with three signaling modules (CD3γε, CD3δε, and CD3ζζ) to form TCR-CD3 complexes. CD4 is the coreceptor module. It reciprocally associates with TCR-CD3-pMHCII assemblies on the outside of a CD4+ T cells and with the Src kinase, LCK, on the inside. Previously, we reported that the CD4 transmembrane GGXXG and cytoplasmic juxtamembrane (C/F)CV+C motifs found in eutherian (placental mammal) CD4 have constituent residues that evolved under purifying selection (Lee et al., 2022). Expressing mutants of these motifs together in T cell hybridomas increased CD4-LCK association but reduced CD3ζ, ZAP70, and PLCγ1 phosphorylation levels, as well as IL-2 production, in response to agonist pMHCII. Because these mutants preferentially localized CD4-LCK pairs to non-raft membrane fractions, one explanation for our results was that they impaired proximal signaling by sequestering LCK away from TCR-CD3. An alternative hypothesis is that the mutations directly impacted signaling because the motifs normally play an LCK-independent role in signaling. The goal of this study was to discriminate between these possibilities. Using T cell hybridomas, our results indicate that: intracellular CD4-LCK interactions are not necessary for pMHCII-specific signal initiation; the GGXXG and (C/F)CV+C motifs are key determinants of CD4-mediated pMHCII-specific signal amplification; the GGXXG and (C/F)CV+C motifs exert their functions independently of direct CD4-LCK association. These data provide a mechanistic explanation for why residues within these motifs are under purifying selection in jawed vertebrates. The results are also important to consider for biomimetic engineering of synthetic receptors.





