Apoptosis: Keeping inflammation at bay
The cells in our bodies are genetically programmed to undergo a natural process of self-destruction called apoptosis, after which the dying cell is removed by cells that have the ability to engulf them (‘phagocytes’). The membrane of the dying cell is still intact as it is engulfed by the phagocyte, so its contents do not come into contact with other nearby cells. Apoptosis does not trigger inflammation, whereas another form of cell death called necrosis—in which the cell membrane is ruptured—is often associated with inflammation (Kerr et al., 1972).
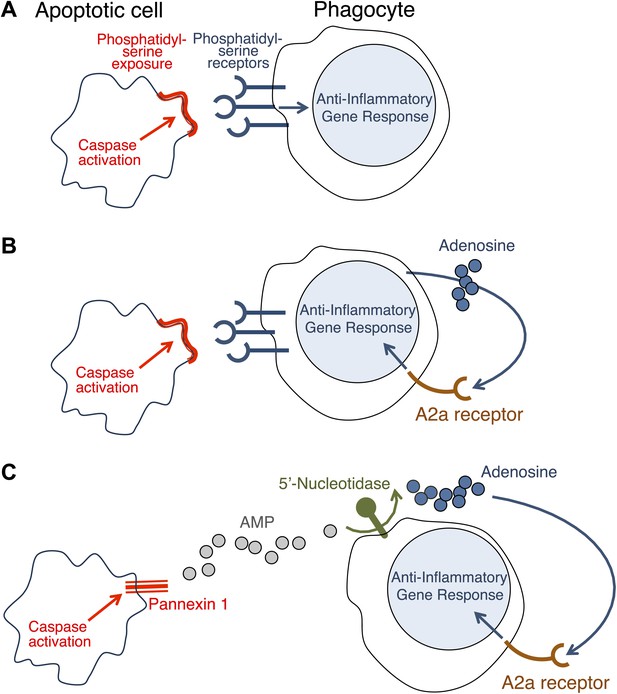
Necrosis causes inflammation because some components of the dying cell that are capable of triggering inflammation come into contact with healthy cells nearby (Rock and Kono, 2008). At first it was assumed that the only reason why apoptosis did not cause inflammation was that all the contents of the dying cell remained inside the membrane and the phagocyte. However, it was later discovered that apoptosis can actually block inflammation (Voll et al., 1997; Fadok et al., 1998). Initial observations suggested that this anti-inflammatory effect is triggered when the phagocytes are exposed to phosphatidylserine—a molecule on the surface of apoptotic cells that has a central role in phagocytosis (Huynh et al., 2002). It seemed, therefore, that these anti-inflammatory changes could be induced only in cells intimately associated with the dying cell (Figure 1A).
How do apoptotic cells trigger an anti-inflammatory response in phagocytes?
(A) Phosphatidylserine molecules on the surface of an apoptotic cell can bind to phosphatidylserine receptors on the surface of a phagocyte and previously it was suggested that this triggered an anti-inflammatory gene response. (B) It was also suggested that the direct apoptotic cell–phagocyte interaction shown in A also results in the release of adenosine by the phagocyte: this adenosine can bind to A2a receptors on the surface of the phagocyte and trigger an anti-inflammatory gene response. (C) Yamaguchi et al. found that the apoptotic cell releases a molecule called adenosine monophosphate (AMP) that is converted to adenosine by a 5′-nucleotidase on the surface of the phagocyte. The adenosine can then trigger an anti-inflammatory gene response by binding to A2a receptors. Enzymes called caspases play a central role in apoptosis in a variety of ways. The action of these caspases is required for the exposure of phosphatidylserine on the surface of the apoptotic cells (A and B); they also activate a channel protein called pannexin-1 to allow the release of AMP (C).
Now, in eLife, Shigekazu Nagata and co-workers at Kyoto University and the Osaka Bioscience Institute—including Hiroshi Yamaguchi as first author—report that apoptotic cells release a molecule called adenosine that can activate an anti-inflammatory gene response in phagocytes (Yamaguchi et al., 2014). They have also shown that adenosine activates this response by stimulating the A2a adenosine receptor in phagocytes.
Similar results have been reported before (Sitkovsky and Ohta, 2005; Köröskényi et al., 2011), but it had been thought that the adenosine was generated by the phagocytes as a consequence of their uptake of the apoptotic cells (Figure 1B). Yamaguchi et al. now show that the adenosine comes from the apoptotic cells themselves, with the phagocytes having only a secondary role in its production. The first step involves enzymes called caspases—which have a central role in apoptosis—cleaving a membrane channel protein called pannexin-1 in the dying cells, and thereby activating it. This results in the release of adenosine monophosphate (AMP) from the dying cells. A 5′-nucleotidase expressed by the phagocytes then removes a phosphate group from the AMP to yield adenosine. The adenosine then binds to the A2a receptor on the phagocytes to trigger an anti-inflammatory gene response (Figure 1C).
Adenosine is not the only soluble molecule released by apoptotic cells to perform a specific role. For example, various other molecules—including lysophosphatidylcholine and the nucleotides ATP and UTP—act as ‘find me’ signals that attract phagocytes towards apoptotic cells (Hochreiter-Hufford and Ravichandran, 2013). Another example is an iron-binding glycoprotein called lactoferrin that inhibits the translocation of certain white blood cells, thereby apparently contributing to the anti-inflammatory effect of apoptosis (Bournazou et al., 2009).
To what extent do the soluble molecules released by apoptotic cells have an effect on cells remote from the site of death? And how does the contribution of these molecules to the anti-inflammatory consequences of apoptosis compare with the contribution that results from direct contact between the dying cell and the cell engulfing it? Nagata and co-workers report that in a mouse model of inflammation (zymosan-induced peritonitis), deletion of either the Pannexin-1 gene or the A2a gene prolongs the inflammation. These findings support the notion that (in this experimental model) adenosine derived from apoptotic cells contributes significantly to the restriction of inflammation. More precise cell-type-specific targeting of these molecules (and other molecules that have anti-inflammatory effects) should lead to an improved understanding of their relative contributions to immune regulation in specific pathological situations.
References
-
Apoptotic human cells inhibit migration of granulocytes via release of lactoferrinJournal of Clinical Investigation 119:20–32.https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI36226
-
Clearing the dead: apoptotic cell sensing, recognition, engulfment, and digestionCold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology 5:a008748.https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a008748
-
Phosphatidylserine-dependent ingestion of apoptotic cells promotes TGF-beta1 secretion and the resolution of inflammationJournal of Clinical Investigation 109:41–50.https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI11638
-
Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kineticsBritish Journal of Cancer 26:239–257.https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1972.33
-
The inflammatory response to cell deathAnnual Reviews of Pathology 3:99–126.https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pathmechdis.3.121806.151456
-
The ‘danger’ sensors that STOP the immune response: the A2 adenosine receptors?Trends in Immunology 26:299–304.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2005.04.004
Article and author information
Author details
Publication history
- Version of Record published: March 25, 2014 (version 1)
Copyright
© 2014, Wallach and Kovalenko
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 5,019
- views
-
- 211
- downloads
-
- 20
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.
Download links
Downloads (link to download the article as PDF)
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools)
Further reading
-
- Cell Biology
Here, we investigated the mechanisms by which aging-related reductions of the levels of Numb in skeletal muscle fibers contribute to loss of muscle strength and power, two critical features of sarcopenia. Numb is an adaptor protein best known for its critical roles in development, including asymmetric cell division, cell-type specification, and termination of intracellular signaling. Numb expression is reduced in old humans and mice. We previously showed that, in mouse skeletal muscle fibers, Numb is localized to sarcomeres where it is concentrated near triads; conditional inactivation of Numb and a closely related protein Numb-like (Numbl) in mouse myofibers caused weakness, disorganization of sarcomeres, and smaller mitochondria with impaired function. Here, we found that a single knockout of Numb in myofibers causes reduction in tetanic force comparable to a double Numb, Numbl knockout. We found by proteomics analysis of protein complexes isolated from C2C12 myotubes by immunoprecipitation using antibodies against Numb that Septin 7 is a potential Numb-binding partner. Septin 7 is a member of the family of GTP-binding proteins that organize into filaments, sheets, and rings, and is considered part of the cytoskeleton. Immunofluorescence evaluation revealed a partial overlap of staining for Numb and Septin 7 in myofibers. Conditional, inducible knockouts of Numb led to disorganization of Septin 7 staining in myofibers. These findings indicate that Septin 7 is a Numb-binding partner and suggest that interactions between Numb and Septin 7 are critical for structural organization of the sarcomere and muscle contractile function.
-
- Cell Biology
Elastic cartilage constitutes a major component of the external ear, which functions to guide sound to the middle and inner ears. Defects in auricle development cause congenital microtia, which affects hearing and appearance in patients. Mutations in several genes have been implicated in microtia development, yet, the pathogenesis of this disorder remains incompletely understood. Here, we show that Prrx1 genetically marks auricular chondrocytes in adult mice. Interestingly, BMP-Smad1/5/9 signaling in chondrocytes is increasingly activated from the proximal to distal segments of the ear, which is associated with a decrease in chondrocyte regenerative activity. Ablation of Bmpr1a in auricular chondrocytes led to chondrocyte atrophy and microtia development at the distal part. Transcriptome analysis revealed that Bmpr1a deficiency caused a switch from the chondrogenic program to the osteogenic program, accompanied by enhanced protein kinase A activation, likely through increased expression of Adcy5/8. Inhibition of PKA blocked chondrocyte-to-osteoblast transformation and microtia development. Moreover, analysis of single-cell RNA-seq of human microtia samples uncovered enriched gene expression in the PKA pathway and chondrocyte-to-osteoblast transformation process. These findings suggest that auricle cartilage is actively maintained by BMP signaling, which maintains chondrocyte identity by suppressing osteogenic differentiation.





