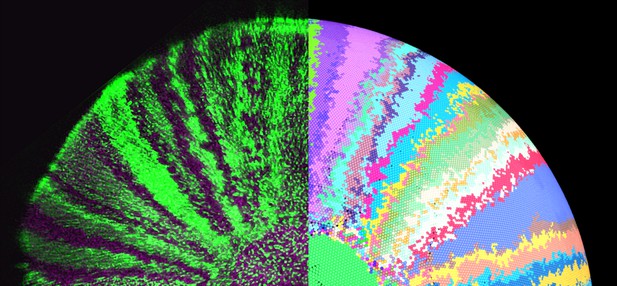
On the left, cells in the neural retina are labeled with a green marker; on the right, a simulation of these data where each ‘cell family’ has been marked with a unique color. Image credit: Tsingos et al. (CC BY 4.0)
By the time babies reach adulthood, they have grown many times larger than they were at birth. This development is driven by an increase in the number and size of cells in the body. In particular, special types of cells, called stem cells, act as a reservoir for tissues: they divide to create new cells that will mature into various specialized structures.
The retina is the light-sensitive part of the eye. It consists of the neural retina, a tissue that contains light-detecting cells, which is supported by the retinal pigment epithelium or RPE. In fish, the RPE and neural retina are replenished by distinct groups of stem cells that do not mix, despite the tissues being close together.
Unlike humans, fish grow throughout adulthood, and their eyes must then keep pace with the body. This means that the different tissues in the retina must somehow coordinate to expand at the same rate: otherwise, the retina would get wrinkled and not work properly. Tsingos et al. therefore wanted to determine how stem cells in the neural retina and RPE co-operated to produce the right number of new cells at the right time.
First, stem cells in the eyes of newly hatched fish were labelled with a visible marker so that their divisions could be tracked over time to build cell family trees. This showed that stem cells behaved differently in the neural retina and the RPE. Computer simulations of the growing retina explained this behavior: stem cells in the neural retina were telling the RPE stem cells when it was time to divide. Combining results from the simulations with data from the experiments revealed that a stem cell decided to keep up dividing partly because of its position in the tissue, and partly because of random chance.
To be healthy, the body needs to fine-tune the number of cells it produces: creating too few cells may make it difficult to heal after injury, but making too many could lead to diseases such as cancer. Understanding how tissues normally agree to grow together could therefore open new avenues of treatment for these conditions.




