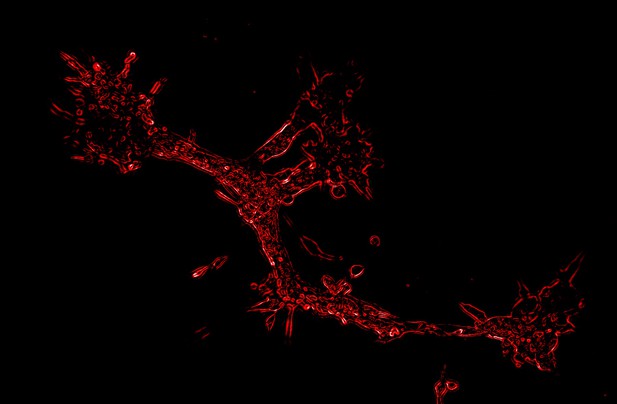
A blood vessel-like structure induced by a modified form of the L1CAM protein produced in mice. Image credit: Angiolini et al. (CC BY 4.0)
Growing tumors stimulate the formation of new blood vessels to supply the oxygen and nutrients the cancerous cells need to stay alive. Stopping tumors from forming the blood vessels could therefore help us to treat cancer. To do so, we need to understand how different proteins control when and how blood vessels develop.
Cells make proteins by first ‘transcribing’ genes to form RNA molecules. In many cases, the RNA then goes through a process called alternative splicing. Proteins known as splicing factors cut out different segments of the RNA molecule and stick together the remaining segments to form templates for protein production. This enables a single gene to produce many different variants of a protein.
Angiolini, Belloni, Giordano et al. have now studied mouse and human versions of the cells that line the blood vessels grown by tumors. This revealed that a splicing factor called NOVA2 targets a protein called L1CAM, which is normally responsible for gluing adjacent cells together. Angiolini et al. found that NOVA2 splices L1CAM into a form not seen before. Instead of remaining anchored to cell surfaces, the newly identified form of L1CAM is released into the blood circulation, where it stimulates new blood vessels to grow.
Samples taken from the blood vessels of human ovarian tumors showed high levels of both NOVA2 and the modified form of L1CAM, while blood vessels in healthy tissue contain no, or very low levels of both proteins. Therefore, if the new form of L1CAM can be detected in the blood, it could be used to help cancer diagnosis, and to indicate which patients would benefit from treatments that restrict the growth of blood vessels in tumors. Further work is now needed to explore these possibilities.




