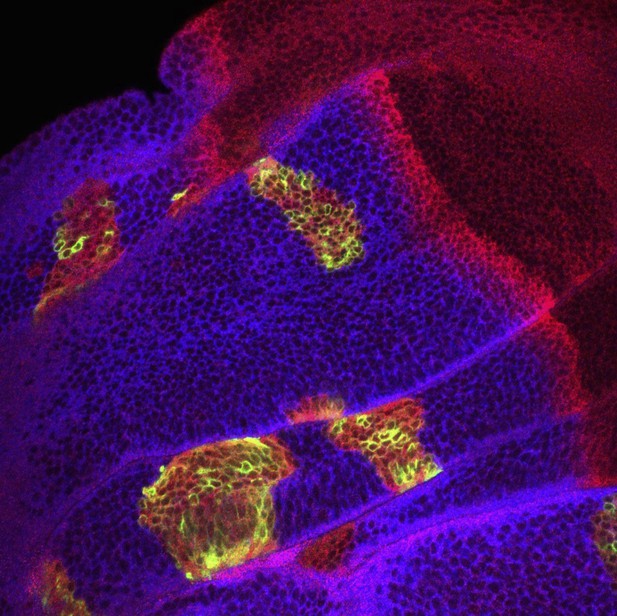
Cells that are unable to process Ci-155 (blue) in the developing wing of a fruit fly only induce hedgehog signaling (red) when Ci-155 is activated by an intermediate gene in the pathway (green cells) or by hedgehog molecules released from nearby cells (top right, no blue). Image credit: Jamie Little (CC BY 4.0)
Morphogens play a crucial role in determining how cells are organized in developing organisms. These chemical signals act over a wide area, and the amount of signal each cell receives typically initiates a sequence of events that spatially pattern the multiple cells of an organ or tissue. One of the most well-studied groups of morphogens are the hedgehog proteins, which are involved in the development of many animals, ranging from flies to humans.
In fruit flies, hedgehog proteins kickstart a cascade of molecular changes that switch on a set of 'target' genes. They do this by ultimately altering the activity of a protein called cubitus interruptus, which comes in two lengths: a long version called Ci-155 and a short version called Ci-75. When hedgehog is absent, Ci-155 is kept in an inactive state in the cytoplasm, where it is slowly converted into its shorter form, Ci-75: this repressor protein is then able to access the nucleus, where it switches ‘off’ the target genes. However, when a hedgehog signal is present, the processing of Ci into its shorter form is inhibited. Instead, Ci-155 becomes activated by a separate mechanism that allows the long form protein to enter the nucleus and switch ‘on’ the target genes. But it was unclear whether hedgehog requires both of these mechanisms in order to act as a morphogen and regulate the activity of developmental genes.
To answer this question, Little et al. mutated the gene for Ci in the embryo of fruit flies, so that the Ci-155 protein could no longer be processed into Ci-75. Examining the developing wings of these flies revealed that the genes targeted by hedgehog are still activated in the correct pattern. In some parts of the wing, Ci-75 is required to switch off specific sets of genes. But when Little et al. blocked these genes, by adding a gene that constantly produces the Ci repressor in the presence or absence of hedgehog, the adult flies still developed normally structured wings. This suggests that hedgehog does not need to regulate the processing of Ci-155 into Ci-75 in order to perform its developmental role.
Previous work showed that when one of the major mechanisms used by hedgehog to activate Ci-155 is blocked, fruit flies are still able to develop normal wings. Taken together with the findings of Little et al., this suggests that the two mechanisms induced by hedgehog can compensate for each other, and independently regulate the development of the fruit fly wing. These mechanisms, which are also found in humans, have been linked to birth defects and several common types of cancer, and understanding how they work could help the development of new treatments.




