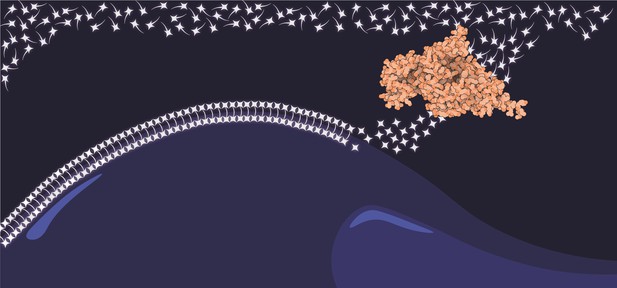
Schematic showing the GDPD enzyme (orange) breaking down lysoPC (stars with tails) in to the nutrient choline (stars) so it can be used to construct important building blocks in the parasite’s membrane (connected string of stars). Image credit: Abhinay Ramaprasad (CC BY 4.0)
Malaria kills over half a million people every year worldwide. A single-celled parasite called Plasmodium falciparum is responsible for the most lethal form of the disease. This malaria-causing agent is carried by mosquitos which transmit the parasite to humans through their bite. Once in the bloodstream, the parasite enters red blood cells and starts to replicate so it can go on to infect other cells.
Like our cells, P. falciparum is surrounded by a membrane, and further membranes surround a number of its internal compartments. To make these protective coats, the parasite has to gather a nutrient called choline to form an important building block in the membrane.
The parasite gets most of its choline by absorbing and digesting a molecule known as lysoPC found in the bloodstream of its host. However, it was unclear precisely how the parasite achieves this. To address this question, Ramaprasad, Burda et al. used genetic and metabolomic approaches to study how P. falciparum breaks down lysoPC.
The experiments found that mutant parasites that are unable to make an enzyme called GDPD were able to infect red blood cells, but failed to grow properly once inside the cells. The mutant parasites took up less choline and, as a result, also made fewer membrane building blocks. The team were able to rescue the mutant parasites by supplying them with large quantities of choline, which allowed them to resume growing. Taken together, the findings of Ramaprasad, Burda et al. suggest that P. falciparum uses GDPD to extract choline from lysoPC when it is living in red blood cells.
More and more P. falciparum parasites are becoming resistant to many of the drugs currently being used to treat malaria. One solution is to develop new therapies that target different molecules in the parasite. Since it performs such a vital role, GDPD may have the potential to be a future drug target.




