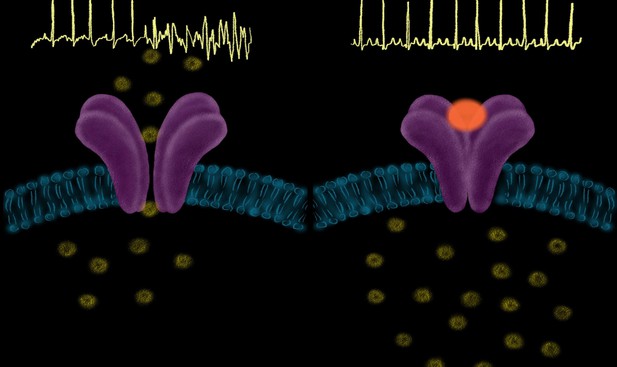
Blocking an ion channel called ryanodine receptor 2 reduces abnormal calcium leaks in the hearts of guinea pigs. Image credit: Joshi et al. (CC BY 4.0)
Each year, more than 300,000 people experience cardiac arrest or sudden cardiac death. Sudden cardiac death is caused by irregular heartbeats known as ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation, which prevent the heart from pumping blood.
During a regular heart rhythm, the heart muscles contract and relax, regulated by a coordinated rise and fall of calcium ions within heart cells. In the cells of diseased hearts, on the other hand, calcium leaks out of a compartment known as the sarcoplasmic reticulum in an uncontrolled manner. This happens because an ion channel in the membrane of the sarcoplasmic reticulum known as ryanodine receptor 2 becomes hyperactive and releases calcium in an uncontrolled manner. This abnormal calcium release leads to irregular calcium waves, which can make the heart’s electrical properties unstable, causing ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation and sudden cardiac death.
Joshi et al. tested whether dantrolene, a molecule that blocks ryanodine receptor 2, can stop calcium leaks from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and prevent lethal arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death in failing hearts. To investigate this, Joshi et al. induced heart failure in guinea pigs that have abnormal heart calcium signalling similar to human heart failure, and then treated the animals with either dantrolene or a placebo.
The results indicate that blocking ryanodine receptor 2 hyperactivity with dantrolene prevents lethal arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death by blocking calcium leaks and by preventing the instability of the electrical properties of the heart. Additionally, Joshi et al. found that dantrolene also improved the diseased heart’s ability to pump adequate amounts of blood, allowing failing hearts to meet increased cardiovascular demands, and thereby improving the heart’s overall function.
The proposed studies come from a strong clinical need to improve bad outcomes in people who keep having fatal heart rhythm episodes despite getting the best medical care. Many heart failure patients are plagued by recurrent defibrillator shocks to abort sudden cardiac death from relentless lethal heart rhythms. These shocks are painful, injure the heart, and worsen the quality of life. Unfortunately, management options are extremely limited for these patients.
The findings of Joshi et al. indicate that dantrolene may be a potential treatment for people with fatal heart rhythms who are at risk of sudden cardiac death and could have a positive impact on these people’s quality of life. However, before this can happen, dantrolene will first have to be thoroughly tested to ensure effectivity and safety in humans. In any case, Joshi et al. have opened a new avenue in the search for medications to treat deadly arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death.




