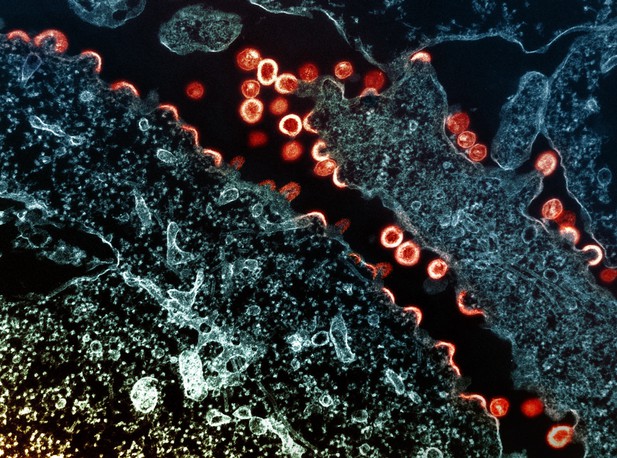
Transmission electron micrograph of HIV-1 virus particles (red/yellow) budding and replicating from a segment of a chronically infected H9 cell (blue/teal). Particles are in various stages of maturity. Image credit: NIAID (CC BY 2.0 DEED)
Approximately 39 million people in the world live with HIV infection. Currently available treatments can reduce the amount of virus to near undetectable levels. But they do not eliminate the virus. A reservoir of HIV-infected cells persists during treatment. If treatment stops, these cells can cause rebounding virus levels and a return of symptoms. As a result, patients living with HIV must remain on treatment their entire lives.
HIV reservoir cells often do not express viral proteins, making them hard for the immune system to find and destroy. Many of these reservoir cells occur in lymph nodes, which makes them difficult for researchers to access for study. Learning more about where these cells hide in the body may enable scientists to develop new treatments to help eliminate them.
Sun et al. show that HIV reservoir cells exist in many body tissues, including the brain. In the experiments, Sun et al. used single HIV genome sequencing to identify HIV genetic sequences in the brain and other body tissues from three recently deceased individuals with HIV. The individuals agreed to donate their tissues for postmortem studies before their deaths. All received antiretroviral therapy until death. The experiments identified functional HIV genetic sequences in lymph nodes and gastrointestinal tissues, known hotspots for HIV-infected cells. Sun et al. also found genetically intact HIV in brain tissue from two of the individuals. The HIV genetic sequences were identical to sequences found in other body tissues. This discovery suggests HIV-infected cells had divided into more HIV-infected cells and spread.
The results suggest that cells harboring intact HIV invade the brain and persist there for extended periods during antiretroviral therapy. To eradicate the virus, interventions targeting HIV reservoir cells must be able to reach the brain. This new information may help researchers developing HIV-reservoir targeting drugs decide which candidates will likely be the most effective. Future studies may also shed light on how HIV reaches the brain and how the infected cells escape destruction by immune cells, which may suggest more treatment strategies.




