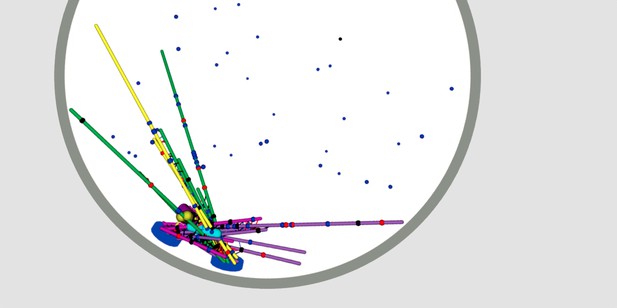
Mitotic spindle and chromosomes rendered from the three-dimensional simulation after running for 60 seconds. Microtubules are shown in green and purple when unattached to kinetochores, yellow and magenta when attached. Image credit: Edelmaier et al. (CC BY 4.0)
Before a cell divides, it must make a copy of its genetic material and then promptly split in two. This process, called mitosis, is coordinated by many different molecular machines. The DNA is copied, then the duplicated chromosomes line up at the middle of the cell. Next, an apparatus called the mitotic spindle latches onto the chromosomes before pulling them apart. The mitotic spindle is a bundle of long, thin filaments called microtubules. It attaches to chromosomes at the kinetochore, the point where two copied chromosomes are cinched together in their middle.
Proper cell division is vital for the healthy growth of all organisms, big and small, and yet some parts of the process remain poorly understood despite extensive study. Specifically, there is more to learn about how the mitotic spindle self-assembles, and how microtubules and kinetochores work together to correctly orient and segregate chromosomes into two sister cells. These nanoscale processes are happening a hundred times a minute, so computer simulations are a good way to test what we know.
Edelmaier et al. developed a computer model to simulate cell division in fission yeast, a species of yeast often used to study fundamental processes in the cell. The model simulates how the mitotic spindle assembles, how its microtubules attach to the kinetochore and the force required to pull two sister chromosomes apart. Building the simulation involved modelling interactions between the mitotic spindle and kinetochore, their movement and forces applied. To test its accuracy, model simulations were compared to recordings of the mitotic spindle – including its length, structure and position – imaged from dividing yeast cells.
Running the simulation, Edelmaier et al. found that several key effects are essential for the proper movement of chromosomes in mitosis. This includes holding chromosomes in the correct orientation as the mitotic spindle assembles and controlling the relative position of microtubules as they attach to the kinetochore. Misaligned attachments must also be readily deconstructed and corrected to prevent any errors. The simulations also showed that kinetochores must begin to exert more force (to separate the chromosomes) once the mitotic spindle is attached correctly.
Altogether, these findings improve the current understanding of how the mitotic spindle and its counterparts control cell division. Errors in chromosome segregation are associated with birth defects and cancer in humans, and this new simulation could potentially now be used to help make predictions about how to correct mistakes in the process.




