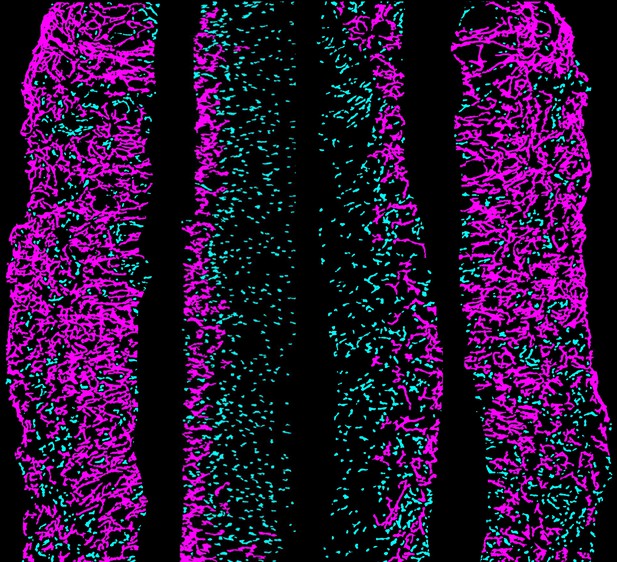
Image showing large (magenta) and small (cyan) groups of Fibronectin proteins assembling along the interface between the neural tube and the surrounding tissue. Image credit: Emilie Guillon (CC BY 4.0)
In embryos, the spinal cord starts out as a flat sheet of cells that curls up to form a closed cylinder called the neural tube. The folding tube is attached to the surrounding tissues through an extracellular matrix of proteins and sugars. Overlapping strands of a protein from the extracellular matrix called Fibronectin connect the neural tube to adjacent tissues, like a kind of biological glue. However, it remained unclear what effect this attachment had on the embryonic development of the spinal cord.
Connecting two overlapping objects with glue to form what is known as an ‘adhesive lap joint’ is common in fields such as woodworking and aeronautical engineering. The glue in these joints comes under shearing stress whenever the two objects it connects try to pull apart. But, thanks to work in engineering, it is possible to predict how different joints will perform under tension. Now, Guillon et al. have deployed these engineering principles to shed light on neural tube development.
Using zebrafish embryos and computational models, Guillon et al. investigated what happens when the strength of the adhesive lap joints in the developing spine changes. This revealed that Fibronectin works like a smart adhesive: rather than staying in one place like a conventional glue, it moves around. As the neural tube closes, cells remodel the Fibronectin, concentrating it on the areas under the highest stress. This seemed to both help and hinder neural tube development. On the one hand, by anchoring the tube equally to the left and right sides of the embryo, the Fibronectin glue helped the spine to develop symmetrically. On the other hand, the strength of the adhesive lap joints made it harder for the neural tube to curl up and close.
If the neural tube fails to close properly, it can lead to birth defects like spina bifida. One of the best-known causes of these birth defects in humans is a lack of a vitamin known as folic acid. Cell culture experiments suggest that this might have something to do with the mechanics of the cells during development. It may be that faulty neural tubes could close more easily if they were able to unglue themselves from the surrounding tissues. Further use of engineering principles could shed more light on this idea in the future.




