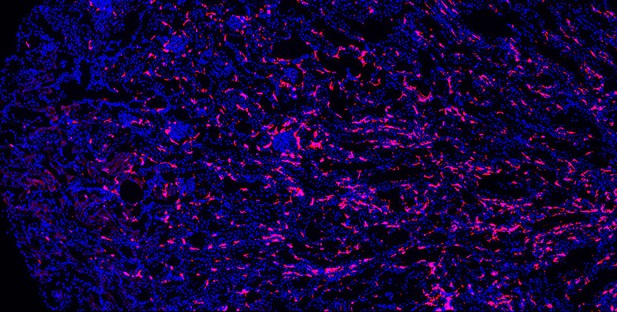
Macrophages (red) in an aged mouse kidney. Image credit: Shintaro Ide (CC BY 4.0)
Older people are more likely to develop kidney disease, which increases their risk of having other conditions such as a heart attack or stroke and, in some cases, can lead to their death. Older kidneys are less able to repair themselves after an injury, which may help explain why aging contributes to kidney disease. Another possibility is that older kidneys are more susceptible to excessive inflammation. Learning more about the processes that lead to kidney inflammation in older people might lead to better ways to prevent or treat their kidney disease.
Immune cells called macrophages help protect the body from injury and disease. They do this by triggering inflammation, which aides healing. Too much inflammation can be harmful though, making macrophages a prime suspect in age-related kidney harm. Studying these immune cells in the kidney and how they change over the lifespan could help scientists to better understand age-related kidney disease.
Now, Ide, Yahara et al. show that one type of macrophage is better at multiplying in older kidneys. In the experiments, mice were genetically engineered to make a fluorescent red protein in one kind of macrophage. This allowed Ide, Yahara et al. to track these immune cells as the mice aged. The experiments showed that this subgroup of cells is first produced when the mice are embryos. They stay in the mouse kidneys into adulthood, and are so prolific that, over time, they eventually become the most common macrophage in older kidneys.
The fact that one type of embryonically derived macrophage takes over with age may explain the increased inflammation and reduced repair capacity seen in aging kidneys. More studies will help scientists to understand how these particular cells contribute to age-related changes in susceptibility to kidney disease.




