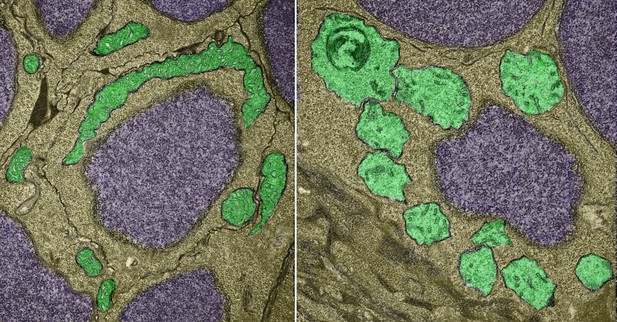
Mitochondria (in green) in a neuron from a transgenic zebrafish treated with MG2I and exposed to red light: these structures showed catastrophic damage compared with a normal neuron from a control zebrafish (left panel). Image credit: Xie, Jiao, Bai, Ilin et al. (CC BY 4.0)
Most life processes require the energy produced by small cellular compartments called mitochondria. Many internal and external factors can harm these miniature powerhouses, potentially leading to cell death. For instance, in patients with Parkinson’s or Alzheimer’s disease, dying neurons often show mitochondrial damage. However, it is unclear exactly how injured mitochondria trigger the demise of these cells. Gaining a better understanding of this process requires studying the impact of mitochondrial damage in live neurons, something that is still difficult to do.
As a response to this challenge, Xie, Jiao, Bai, Ilin et al. designed a new tool that can specifically injure mitochondria in the neurons of live zebrafish larvae at will, and fine-tune the amount of damage inflicted. The zebrafish are genetically engineered so that the mitochondria in their neurons carry a protein which can bind to a chemical compound called MG2I. When attached to each other, MG2I and the protein respond to far-red light by locally creating highly damaging chemicals. This means that whenever far-red light is shone onto the larvae, mitochondria in their neurons are harmed – the brighter the light, the stronger the damage.
Zebrafish larvae exposed to these conditions immediately stopped swimming: mitochondria in their neurons could not produce enough energy and these cells could therefore no longer communicate properly. The neurons then started to die about 24 hours after exposure to the light, suggesting that the mitochondrial damage triggered other downstream processes that culminated in cell death.
This new light-controlled tool could help to understand the consequences of mitochondrial damage, potentially revealing new ways to rescue impaired neurons in patients with Parkinson’s or Alzheimer’s disease. In the future, the method could be adapted to work in any type of cell and deactivate other cell compartments, so that it can be used to study many types of diseases.




