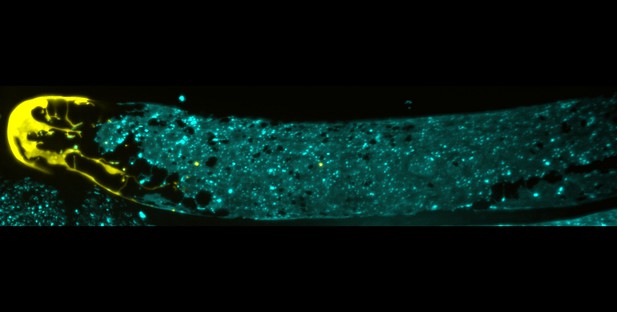
Adult C. elegans gonad; in yellow the distal tip cell, in cyan, the Sh1 cells. Image credit: Gordon et al. (CC BY 4.0).
Stem cells have the rare ability to divide and specialize into the many different types of cells necessary for an organism to survive. For instance, germ stem cells can multiply to produce precursor cells that go on to become eggs or sperm needed for reproduction.
When a stem cell divides, the daughter cells can either remain ‘naïve’, or start to specialize into a given cell type. In many cases, this decision is strongly influenced by the properties of the environment that surrounds the stem cell. However, in the microscopic worm Caenorhabditis elegans, how the daughters of germ stem cells specialize was thought to be a random process, with nearby cells equally likely to specialize or remain naïve.
In this animal, germ stem cells reside in tube-shaped structures called gonads, which are enclosed by a large ‘distal tip’ cell. In addition, cells known as Sh1 surround the gonad. Here, Gordon et al. tracked dividing germ stem cells in the gonads of live worms. This revealed that both the distal tip cell and Sh1 cells have finger-like extensions that form contacts with the germ stem cells. The fate of dividing germ stem cells is shaped by these interactions. If they touch only the distal tip cell, they remain in a naïve state. However, if they contact both the distal tip cell and an Sh1 cell, one daughter of the stem cell becomes an egg precursor – with the daughter closest to the distal tip cell staying naïve. In fact, germ stem cells that are prevented from contacting Sh1 cells divide less often.
Many other types of stem cells, for example in human skin, are believed to make the decision to remain naïve or undergo specialization randomly. The results from Gordon et al. could provide a roadmap to discover hidden layers of control in other organisms, some of which may be potentially relevant in health and disease.




