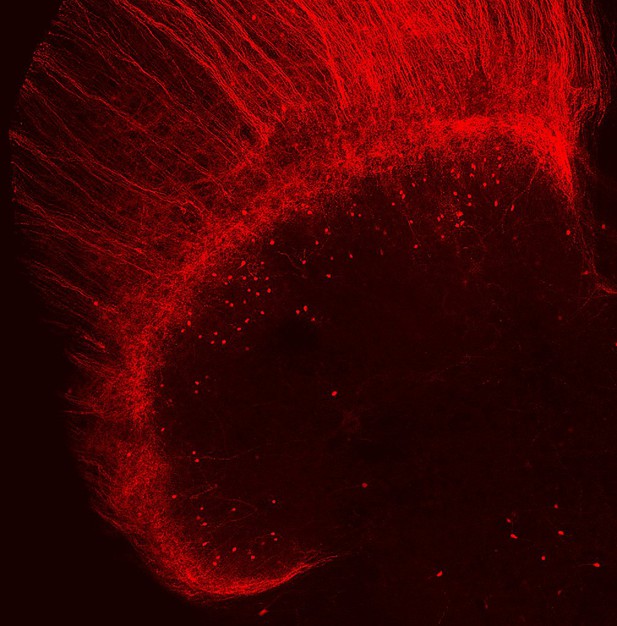
Neurons expressing CGRP (red) in the spinal cord. Image credit: Line Löken (CC BY 4.0)
The ability to sense pain is critical to our survival. Normally, pain is provoked by intense heat or cold temperatures, strong force or a chemical stimulus, for example, capsaicin, the pain-provoking substance in chili peppers. However, if nerve fibers in the arms or legs are damaged, pain can occur in response to touch or pressure stimuli that are normally painless. This hypersensitivity is called mechanical allodynia.
A protein called calcitonin gene-related peptide, or CGRP, has been implicated in mechanical allodynia and other chronic pain conditions, such as migraine. CGRP is found in, and released from, the neurons that receive and transmit pain messages from tissues, such as skin and muscles, to the spinal cord. However, only a few distinct groups of CGRP-expressing neurons have been identified and it is unclear if these nerve cells also contribute to mechanical allodynia.
To investigate this, Löken et al. genetically engineered mice so that all nerve cells containing CGRP produced red fluorescent light when illuminated with a laser. This included a previously unexplored group of CGRP-expressing neurons found in a part of the spinal cord that is known to receive information about non-painful stimuli. Using neuroanatomical methods, Löken et al. monitored the activity of these neurons in response to various stimuli, before and after a partial nerve injury. This partial injury was induced via a surgery that cut off a few, but not all, branches of a key leg nerve.
The experiments showed that in their normal state, the CGRP-expressing neurons hardly responded to mechanical stimulation. In fact, it was difficult to establish what they normally respond to. However, after a nerve injury, brushing the mice’s skin evoked significant activity in these cells. Moreover, when these CGRP cells were artificially stimulated, the stimulation induced hypersensitivity to mechanical stimuli, even when the mice had no nerve damage. These results suggest that this group of neurons, which are normally suppressed, can become hyperexcitable and contribute to the development of mechanical allodynia.
In summary, Löken et al. have identified a group of nerve cells in the spinal cord that process mechanical information and contribute to touch-evoked pain. Future studies will identify the nerve circuits that are targeted by CGRP released from these nerve cells. These circuits represent a new therapeutic target for managing chronic pain conditions related to nerve damage, specifically mechanical allodynia, which is the most common complaint of patients with chronic pain.




