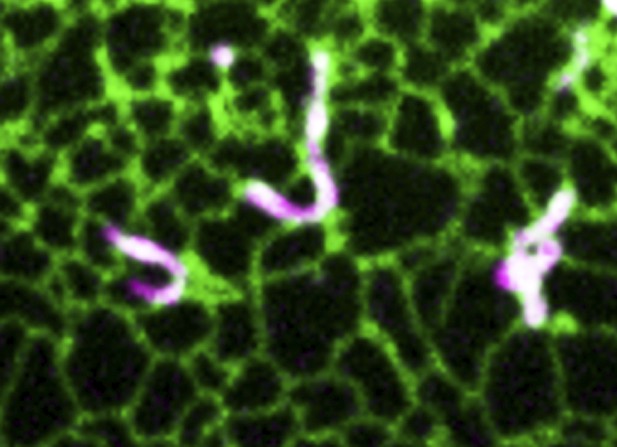
A portion of a cell showing an intracellular organelle called the endoplasmic reticulum (in green) that has been recruited to the surface of other intracellular organelles called mitochondria (in magenta) using the modified Magnet system. Image credit: Benedetti et al. (CC BY 4.0)
The cell relies on direct interactions among proteins and compartments called organelles to stay alive. Manipulating these interactions allows researchers to control a wide variety of cell behaviors. A system called ‘Magnets’ uses light to trigger interactions between proteins. Magnets uses a segment of a protein called Vivid from a common bread mold that responds to light. When light shines on two of these segments, it causes them to bind together, in a process known as dimerization.
In the Magnets system, Vivid segments are attached to specific proteins or organelles. By using light, researchers can force their target molecules to come together and trigger signals that can change cell behavior. However, the Magnets system has limitations: its stability and low efficiency mean that the cells need to be kept at low temperatures and that several copies of Vivid are needed. These conditions can interfere with the activity of the target proteins.
To expand the technique, Benedetti et al. added mutations to make the Vivid protein more similar to proteins found in fungi that thrive at temperatures around 50°C. These changes meant that the enhanced system could work at body temperature in mammals.
Further mutations at the interface between the two Vivid segments improved the efficiency of dimerization. This enhanced version was put to the test in different applications, including delivering proteins to different organelles and bringing organelles together. The enhanced Magnets system should enable researchers to control a greater variety of signaling events in the cell. In addition, the methodology established for improving the efficiency of the Magnets system could be useful to researchers working on other proteins.




