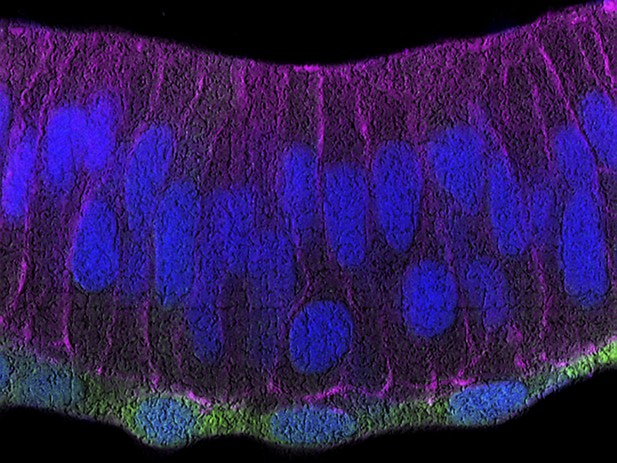
Zebrafish retina, with the RPE in green and the neural retina in purple. Image credit: Moreno-Marmol et al. (CC BY 4.0)
Rounded eyeballs help to optimize vision – but how do they acquire their distinctive shape? In animals with backbones, including humans, the eye begins to form early in development. A single layer of embryonic tissue called the optic vesicle reorganizes itself into a two-layered structure: a thin outer layer of cells, known as the retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE for short), and a thicker inner layer called the neural retina. If this process fails, the animal may be born blind or visually impaired.
How this flat two-layered structure becomes round is still being investigated. In fish, studies have shown that the inner cell layer – the neural retina – generates mechanical forces that cause the developing tissue to curve inwards to form a cup-like shape. But it was unclear whether the outer layer of cells (the RPE) also contributed to this process.
Moreno-Marmol et al. were able to investigate this question by genetically modifying zebrafish to make all new RPE cells fluoresce. Following the early development of the zebrafish eye under a microscope revealed that RPE cells flattened themselves into long thin structures that stretched to cover the entire neural retina. This change was made possible by the cell’s internal skeleton reorganizing. In fact, preventing this reorganization stopped the RPE cells from flattening, and precluded the optic cup from acquiring its curved shape. The results thus confirmed a direct role for the RPE in generating curvature.
The entire process did not require the RPE to produce new cells, allowing the curved shape to emerge in just a few hours. This is a major advantage for fast-developing species such as zebrafish. In species whose embryos develop more slowly, such as mice and humans, the RPE instead grows by producing additional cells – a process that takes many days. The development of the eye thus shows how various species use different evolutionary approaches to achieve a common goal.




