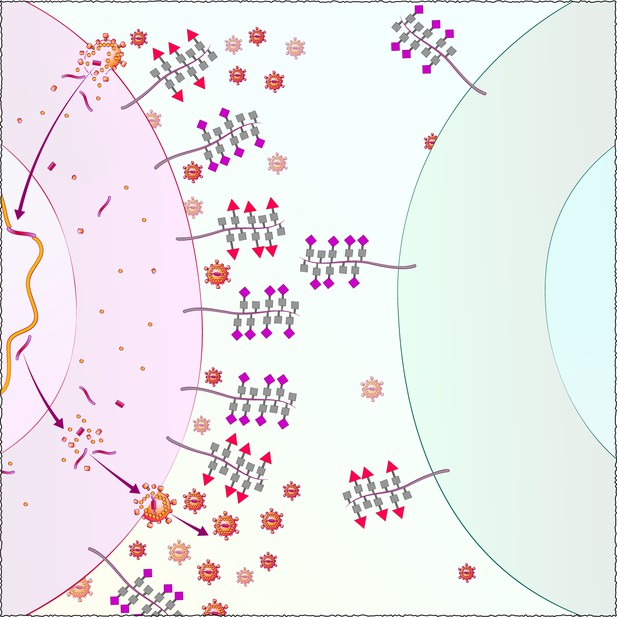
Cells with high levels of sialic acid (purple diamonds) and fucose (red triangles), shown on the left, are more susceptible to HIV infection than cells with low levels of these sugars, shown on the right. Image credit: John Carroll (CC BY 4.0)
Living cells have a sugar coating. These sugars include molecules called glycans, which help cells interact with the outside world. The types of sugars on cells can affect their properties, including potentially their susceptibility to infection by viruses, such as the human immunodeficiency virus, HIV.
To date, most research examining cells susceptible to HIV has focused on cell surface proteins, not sugars. To study these proteins, researchers had previously covered them in metal-studded antibodies (which stick to proteins) and used a technique called cytometry time of flight, or CyTOF for short, to quantify the levels of these proteins on the surface of cells susceptible to HIV. Adapting this tool to investigate sugars could answer questions about HIV infection. For example, does the virus prefer to infect cells coated in certain sugar molecules? And does it change the pattern of sugars on the surface of the cells it infects?
Ma et al. adapted CyTOF to use molecules called lectins (which stick to sugars) in conjunction with the metal-studded antibodies. This made it possible to simultaneously measure the levels of 34 different proteins and 5 different types of sugars on individual cells. The pattern of sugars on the surface of cells from the immune system differed depending on what tissues the cells came from, and what types of cells they were. The results showed that HIV preferred to infect memory CD4 T cells with high levels of two types of sugar: fucose and sialic acid. Furthermore, during infection, the levels of both these sugars increased.
Current treatments for HIV keep virus levels low but do not cure the infection. Further research could determine whether sugars have a role to play in HIV persistence. It is possible that the sugar patterns preferred by the virus help it to avoid detection. A clearer understanding of cell surface sugars could lead to sugar-targeting drugs that kill infected cells.




