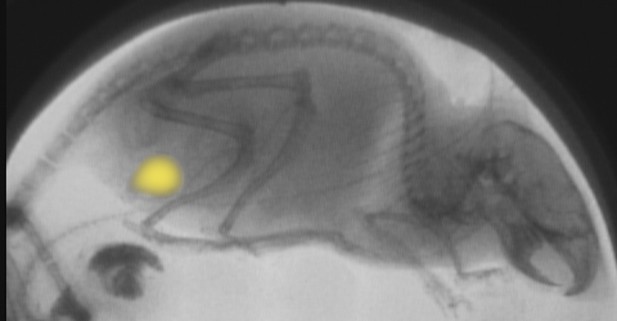
Image of a mouse captured using an X-ray based fluoroscope which has been analyzed using a machine learning algorithm that can identify and quantify the volume of the bladder (yellow). Image credit: Helene De Bruyn (CC BY 4.0)
Healthy adults empty their bladder many times a day with little thought. This seemingly simple process requires communication between the lower urinary tract and the central nervous system. About one in five adults experience conditions like urinary incontinence, urgency, or bladder pain caused by impairments in their lower urinary tract. Despite the harmful effects these conditions have on people’s health and well-being, few good treatments are available.
Mice are often used to study lower urinary tract conditions and treatments. One common technique is to fill a mouse’s bladder using a catheter and measure changes in pressure as the bladder empties and refills. But these procedures and the anesthesia used during them may affect bladder function and skew results.
Here, De Bruyn et al. have developed a new technique that allows scientists to measure bladder function in awake, freely moving mice. The mice’s bladders were photographed using a specialized X-ray based fluoroscope that captured 30 images per second over the course of three hours. A machine learning algorithm was then applied which can automatically detect the circumference of the bladder in each captured image (over 30,000 in total) and quantify its volume. This makes it is possible to measure the bladder as it empties and fills even if the mice move between time frames.
The new approach showed that ‘gold standard’ commonly used methods have a profound effect on the bladder. Surgical implantation of a catheter reduced the bladder to a quarter of its capacity. In addition, one of the most widely used anesthetic drugs in urinary tract research was found to affect the bladder’s ability to drain.
The technique created by De Bruyn et al. provides a new way to study lower urinary tract function and disease in awake, moving animals. This tool would be easy for other academic and pharmaceutical laboratories to implement, and may help scientists discover new therapies for lower urinary tract conditions.




