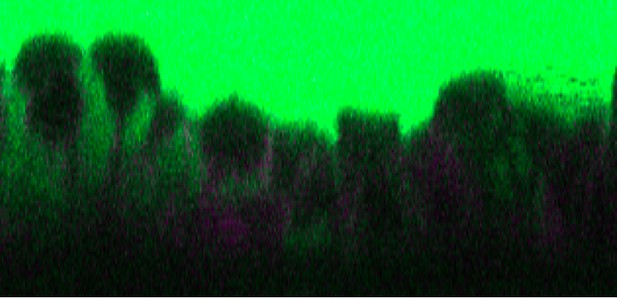
Cross-section of a mouse airway showing secretory cells (in black and magenta) that have sampled small amount of materials from the outside environment (in green). Image credit: Shah, Hou et al. (CC BY 4.0)
Imaging several cell types, at the same time, within a living tissue is no small endeavor. To do so, scientists usually have to perform genetic manipulations that make certain proteins in each cell type fluorescent and therefore easy to track. However, these approaches are cumbersome, limited, and often not applicable to intact human tissues.
A possible alternative would be to make use of autofluorescence – the fact that certain molecules in living cells naturally fluoresce when exposed to a particular wavelength of light. For example, this is the case for NAD(P)H and FAD, two small molecules necessary for life’s biochemical processes, and whose intracellular levels and locations vary depending on cell type.
In response, Shah, Hou et al. developed a new imaging technique that takes advantage of the unique autofluorescence signatures of NAD(P)H and FAD to distinguish between the seven different types of cells that line the surface of the airways of mice.
Using their autofluorescence approach, Shah, Hou et al. were also able to discover a new role for secretory cells, which normally produce fluids, mucus and various proteins necessary for the lungs to work properly. The imaging experiments show that these cells could also sample material from the surface of the airway in a manner similar to how cells in the intestine take up material from the gut and pass their cargo to immune cells that mediate infection control or tolerance. Further studies should uncover more details about this new function of secretory lung cells. Other exciting discoveries may also emerge from researchers adopting the method developed by Shah, Hou et al. to examine a range of organs (both healthy and diseased), and attempting to apply it to human tissues.




