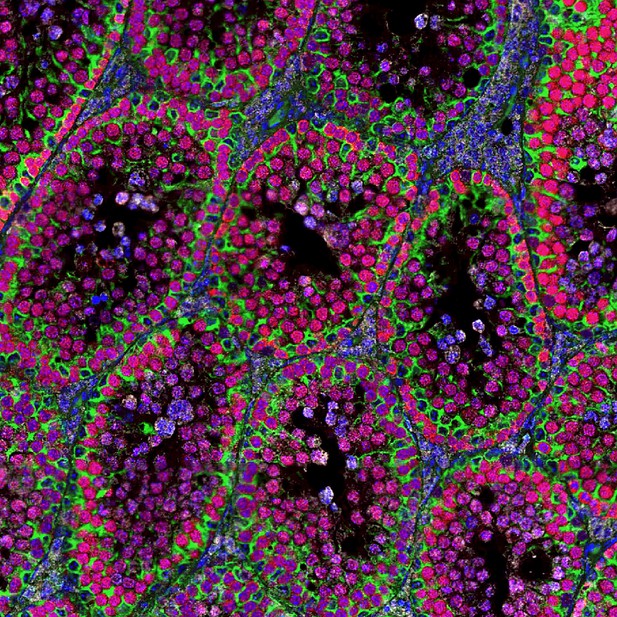
Microscopy image of a section from a mouse testis lacking the enzyme PARL, showing spermatocytes (Red), Sertoli cells (green), and the protein GPX4 (white).
Up to 9% of men are thought to experience infertility. These individuals may not produce enough healthy sperm cells. The root cause of infertility is often not discovered but, in some cases, it is associated with genetic defects in cell compartments known as mitochondria.
Mitochondria are responsible for converting energy from food into a form of chemical energy cells need to power vital processes. However, it remains unclear how defects in mitochondria contribute to male infertility.
Leigh syndrome is one of the most prevalent and severe diseases caused by genetic defects in mitochondria. The condition often develops in childhood and affects the nervous system, muscle and other organs, leading to many symptoms including muscle weakness and neurological regression. A previous study found that mutant mice that lack an enzyme, called PARL, display symptoms that are similar to those observed in humans with Leigh syndrome. PARL is found inside mitochondria where it cuts specific proteins to ensure they are working correctly in the cells.
Radaelli et al. used extensive microscopy and biochemical analyses to study the fertility of male mice lacking PARL. The experiments revealed that the males were infertile due to a failure to produce sperm: spermatocytes, which usually develop into sperm cells, where much more likely to die in mice without PARL (by a process known as ferroptosis).
Further experiments demonstrated that the mitochondria of the mutant mice had a shortage of two crucial molecules, a protein called GPX4 and a lipid called Coenzyme Q, which are required to prevent death by ferroptosis. It appears that this shortage was responsible for the demise of spermatocytes in the male mutant mice affected by infertility.
These findings reveal a new role for PARL in the body and provide evidence that mitochondrial defects in living mammals can trigger ferroptosis, thereby contributing to male infertility. In the future, this research may pave the way for new treatments for male infertility and other diseases associated with defects in mitochondria.




