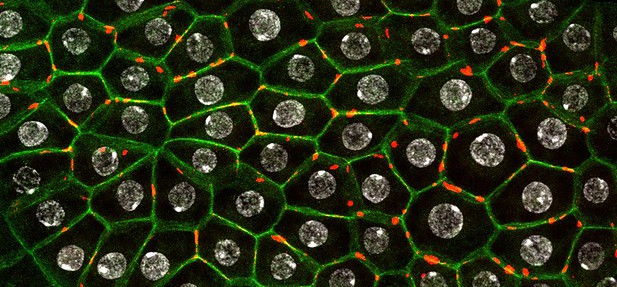
Microscopy image of cytoophidia proteins (CTPS, in red) in the fat body cells of a fly (outlined in green, cell nuclei in grey). Image credit: Liu et al. (CC BY 4.0)
The high rate of obesity has created a global health burden by leading to increased rates of chronic diseases like diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Tackling this issue is complicated as it is influenced by many factors, including genetics, behaviour and environment. To better understand the biochemical changes that underly metabolic issues in a simpler setting, scientists can study fruit flies in the laboratory. These insects share many genes with humans and have similar responses to a high-fat diet.
Previous research identified an enzyme, called CTP synthase (CTPS), which is produced in large amounts by the liver and fat tissue in mammals, and the equivalent in fruit flies, known as the fat body. Multiple CTPS molecules can combine to form long strands of protein called cytoophidia, which have been seen in organisms ranging from humans to bacteria. Recent results showed that the fruit fly equivalent of CTPS drives fat cells to stick together, which is necessary to maintain and form fat tissue. However, it is not clear if altering the levels of CTPS can affect the response to a high-fat diet.
To address this, Liu, Zhang, Wang et al. studied fruit flies on a high-fat diet, showing that this increased the production of CTPS. When the flies were treated to deplete levels of CTPS in the fat body, they had less body weight gain, smaller fat cells and lower amounts of fats in the body. Genetically modified flies with a version of CTPS that was unable to form cytoophidia also showed fewer signs of obesity, indicating how the enzyme might influence the response to dietary fats.
These findings further implicate CTPS in the cause of obesity and help to understand its role. However, it remains to be seen if this also applies to humans. If this is the case, drugs that block the activity of CTPS could help to reduce the impact of a high-fat diet on public health.




