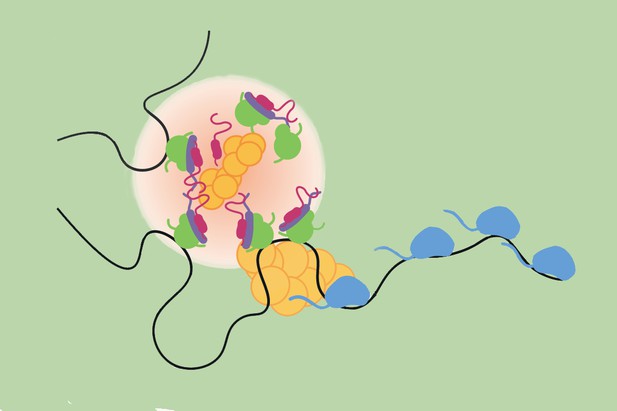
Transcription hubs (light pink) form in response to Notch signalling, bringing together various molecular actors at target genes (black line) in order to activate them. Image credit: deHaro-Arbona et al. (CC BY 4.0)
To correctly give rise to future tissues, cells in an embryo must receive and respond to the right signals, at the right time, in the right way. This involves genes being switched on quickly, with cells often ensuring that a range of molecular actors physically come together at ‘transcription hubs’ in the nucleus – the compartment that houses genetic information. These hubs are thought to foster a microenvironment that facilitates the assembly of the machinery that will activate and copy the required genes into messenger RNA molecules. The resulting ‘mRNAs’ act as templates for producing the corresponding proteins, allowing cells to adequately respond to signals.
For example, the activation at the cell surface of a molecule called Notch triggers a series of events that lead to important developmental genes being transcribed within minutes. This process involves a dedicated group of proteins, known as Notch nuclear complexes, quickly getting together in the nucleus and interacting with the transcriptional machinery. How they do this efficiently at the right gene locations is, however, still poorly understood. In particular, it remained unclear whether Notch nuclear complexes participate in the formation of transcription hubs, as well as how these influence mRNA production and the way cells ‘remember’ having been exposed to Notch activity.
To investigate these questions, DeHaro-Arbona et al. genetically engineered fruit flies so that their Notch nuclear complexes and Notch target genes both carried visible tags that could be tracked in living cells in real time. Microscopy imaging of fly tissues revealed that, due to their characteristics, Notch complexes clustered with the transcription machinery and formed transcription hubs near their target genes.
All cells exposed to Notch exhibited these hubs, but only a third produced the mRNAs associated with Notch target genes; adding a second signal (an insect hormone) significantly increased the proportion. This illustrates how ‘chance’ and collaboration influence the way the organism responds to Notch signalling. Finally, the experiments revealed that the hubs persisted for at least a day after removing the Notch signal. This ‘molecular memory’ led to cells responding faster when presented with Notch activity again.
The work by DeHaro-Arbona sheds light on how individual cells respond to Notch signalling, and the factors that influence the activation of its target genes. This knowledge may prove useful when trying to better understand diseases in which this pathway is implicated, such as cancer.




