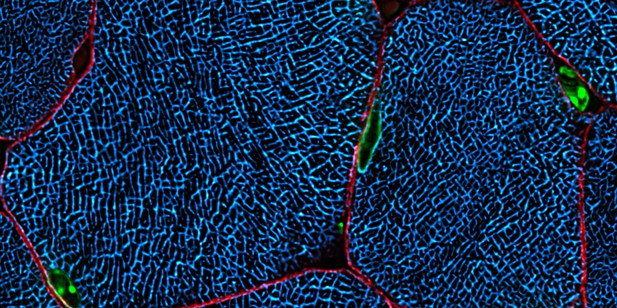
Cross section of skeletal muscle that was subjected to FIM-ID. Nuclei are shown in green. Dystrophin is shown in red and highlights the periphery of the muscle fibers. SERCA1 is shown in cyan and highlights the periphery of the myofibrils. Image credit: Kent W. Jorgenson (CC BY 4.0).
Approximately 45% of human body mass is made of skeletal muscle. These muscles contract and relax to provide the mechanical forces needed for breathing, moving, keeping warm and performing many other essential processes. Both sedentary and active adults lose approximately 30-40% of this muscle mass by the age of 80, increasing their risk of disease, disability and death. As a result, there is much interest in developing therapies that can restore, maintain and increase muscle mass in older individuals.
Muscles are made of multiple fibers that are in turn largely composed of smaller units known as myofibrils. Previous studies have shown that performing resistance training or other exercise that increases the mechanical loads placed on muscles stimulates muscle growth. This growth is largely due to increased girth of the existing muscle fibers. However, it remained unclear whether this was due to myofibrils growing in size, increasing in number, or a combination of both.
To address this question, Jorgenson et al. developed a fluorescence imaging method called FIM-ID to count the number and measure the size of myofibrils within cross-sections of skeletal muscle. Using FIM-ID to study samples of mouse and human muscle fibers then revealed that increasing mechanical loads on muscles increased the number of myofibrils and this was largely responsible for muscle fiber growth.
FIM-ID mostly relies on common laboratory instruments and free open-source software is used to count and measure the myofibrils. Jorgenson et al. hope that this will allow as many other researchers as possible to use FIM-ID to study myofibrils in the future. A better understanding of how the body controls the number of myofibrils may lead to the development of therapies that can mimic the effects of exercise on muscles to maintain or even increase muscle mass in human patients.




