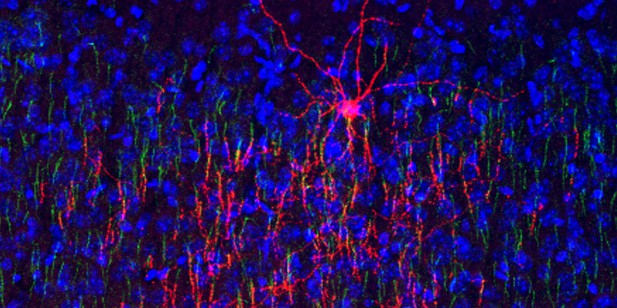
Microscopy image of axo-axonic cells (red) connecting to pyramidal neurons (green) in the motor cortex. Cell nuceli are shown in blue. Image credit: Ricardo Raudales (CC BY 4.0).
Whether we are memorising facts or reacting to a loud noise, nerve cells in different brain areas must be able to communicate with one another through precise, meaningful signals. Specialized nerve cells known as interneurons act as “traffic lights” to precisely regulate when and where this information flows in neural circuits.
Axo-axonic cells are a rare type of inhibitory interneuron that are thought to be particularly important for controlling the passage of information between different groups of excitatory neurons. This is because they only connect to one key part of their target cell – the axon-initial segment – where the electrical signals needed for brain communication (known as action potentials) are initiated. Since axo-axonic cells are inhibitory interneurons, this connection effectively allows them to ‘veto’ the generation of these signals at their source.
Although axo-axonic cells have been identified in three brain regions using traditional anatomical methods, there were no ‘tags’ readily available that can reliably identify them. Therefore, much about these cells remained unknown, including how widespread they are in the mammalian brain. To solve this problem, Raudales et al. investigated which genes are switched on in axo-axonic cells but not in other cells, identifying a unique molecular signature that could be used to mark, record, and manipulate these cells.
Microscopy imaging of brain tissue from mice in which axo-axonic cells had been identified revealed that they are present in many more brain areas than previously thought, including nearly all regions of the broadly defined cerebral cortex and even the hypothalamus, which controls many innate behaviors. Axo-axonic cells were also ‘wired up’ differently, depending on where they were located; for example, those in brain areas associated with memory and emotions had wider-ranging input connections than other areas.
The finding of Raudales et al. provide, for the first time, a method to directly track and manipulate axo-axonic cells in the brain. Since dysfunction in axo-axonic cells is also associated with neurological disorders like epilepsy and schizophrenia, gaining an insight into their distribution and connectivity could help to develop better treatments for these conditions.




