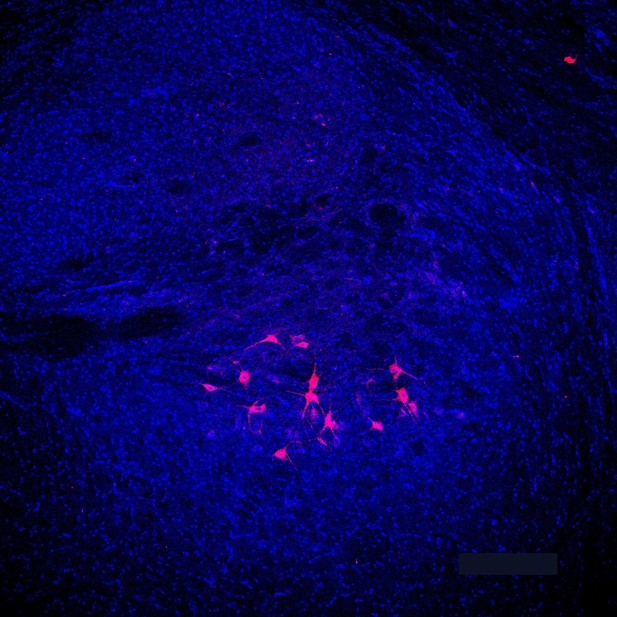
Brain section (blue) from a mouse that had received a neural tracer (pink) through the oral cavity, demonstrating the presence of a neural circuit connecting the oral cavity to the brain. Image credit: Barr et al. (CC BY-NC 2.0)
A lot of cancer survivors experience a decline in mental health, persisting often decades after successful treatment. Many factors contribute to this reduced mental well-being, including the physical, emotional and financial stresses they experience.
Scientists think that the increased prevalence of mental health disorders among cancer patients and survivors may also be linked to the cancer itself. Previous research has shown that most tumors, in particular in melanomas, cervical and ovarian cancers, and head and neck cancers, contain sensory nerves that sense thermal, mechanical and chemical changes and so alert an organism about a potential danger, such as extreme temperature, pressure, changes in pH or inflammation.
To investigate whether these nerves contribute to the worsened mental health of cancer patients, Barr, Walz et al. studied male mice with tumors growing in their mouths, mimicking the disease of patients with head and neck cancers. The mice with tumors exhibited several altered behaviors linked to their well-being, suggesting that they had reduced overall health compared to mice without tumors. For example, they were less inclined to build nests, accept treats or run on a wheel.
Next, Barr, Walz et al. injected a fluorescent dye into the tumors to label the nerves inside the cancerous growths. Fluorescence microscopy and imaging studies revealed that, days later, the dye had traveled to multiple regions of the brain, indicating that the nerves in the tumors had connected to a preexisting nerve circuit that included these brain regions.
Further experiments revealed that the nerve cells in these brain regions were more active in mice with tumors and had different functional properties compared to mice without tumors. Removing the connecting nerves either genetically or with a drug improved all the behaviors of the mice with tumors. Treating the mice with painkillers also improved some but not all of their behaviors, indicating that pain is not the exclusive driver of such behavioral shifts. These two experiments suggest that the nerves from the tumors relay information about pain to the brain and contribute to reduced well-being of the mice.
Further studies will test whether these tumor-brain connections also contribute to behavioral changes in mice with other types of cancer. The data suggest that disrupting the neural connections between a tumor and the brain may improve the mental health of patients with cancer, but more research is needed to establish this link.




