Scientists have identified a key step in the process that leads to leaky vessels and harmful swelling in eye diseases, according to a new study published today in eLife.
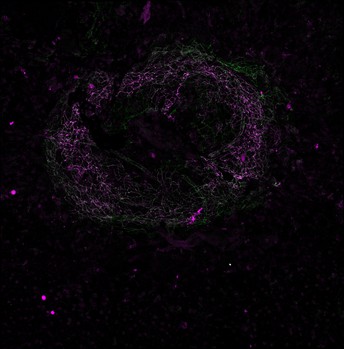
Image of a vascular lesion in a mouse model of eye disease, with leaky blood vessels marked by immunofluorescent staining for vascular endothelial-cadherin phosphorylation at the amino acid Y685 in endothelial cell-cell junctions. Credit: Ross et al. (CC BY 4.0)
The discovery could lead to improved treatments for diseases such as age-related macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy. These diseases cause leaky blood vessels to grow in the eyes, leading to harmful swelling and progressive vision loss.
Currently available treatments block a molecule called VEGF that contributes to both leaking vessels and the growth of new blood vessels in the eye. This dual role of VEGF means that these treatments can prevent harmful swelling but cause adverse side effects such as the death of nerve and blood-vessel cells.
“In this study, we explored whether it would be possible to block the effect of VEGF on blood-vessel leakiness only, while leaving nerve and blood-vessel cells unharmed,” says lead author Ross Smith, a postdoctoral fellow at the Department of Immunology, Genetics and Pathology, Uppsala University, Sweden.
To do this, Smith and his team examined step by step how VEGF causes eye leakiness in mice with diseases that mimic age-related macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy. The animals were engineered to have mutations in proteins in their eyes that are affected by VEGF.
By studying different mutant mice with eye diseases mimicking human conditions, the team identified exactly how VEGF causes vessels to leak. “We applied fluorescent particles to the bloodstream and used microscopy to find these particles outside the blood vessels, or not, depending on whether the leakiness had been stopped by a mutation,” Smith explains. The experiments showed that the effect of VEGF on leakiness could be distinguished from the effect on new blood-vessel formation.
“Our findings provide an answer to the questions on how blood vessels leak and show that leakage can be stopped without killing the blood vessels,” concludes senior author Lena Claesson-Welsh, Professor at the Department of Immunology, Genetics and Pathology, Uppsala University. “Using this insight, we’ve begun testing drugs that could selectively block this leak-inducing step in the process. If this approach is effective, it could lead to new treatments that stop leaking without the harmful side effects of existing drugs.”
Media contacts
Emily Packer
eLife
e.packer@elifesciences.org
+441223855373
About
eLife is a non-profit organisation created by funders and led by researchers. Our mission is to accelerate discovery by operating a platform for research communication that encourages and recognises the most responsible behaviours. We work across three major areas: publishing, technology and research culture. We aim to publish work of the highest standards and importance in all areas of biology and medicine, including Cell Biology, and Human Biology and Medicine, while exploring creative new ways to improve how research is assessed and published. We also invest in open-source technology innovation to modernise the infrastructure for science publishing and improve online tools for sharing, using and interacting with new results. eLife receives financial support and strategic guidance from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, the Max Planck Society and Wellcome. Learn more at https://elifesciences.org/about.
To read the latest Cell Biology research published in eLife, visit https://elifesciences.org/subjects/cell-biology.
And for the latest in Human Biology and Medicine, see https://elifesciences.org/subjects/human-biology-medicine.




