TRPM5-mediated calcium uptake regulates mucin secretion from human colon goblet cells
Figures
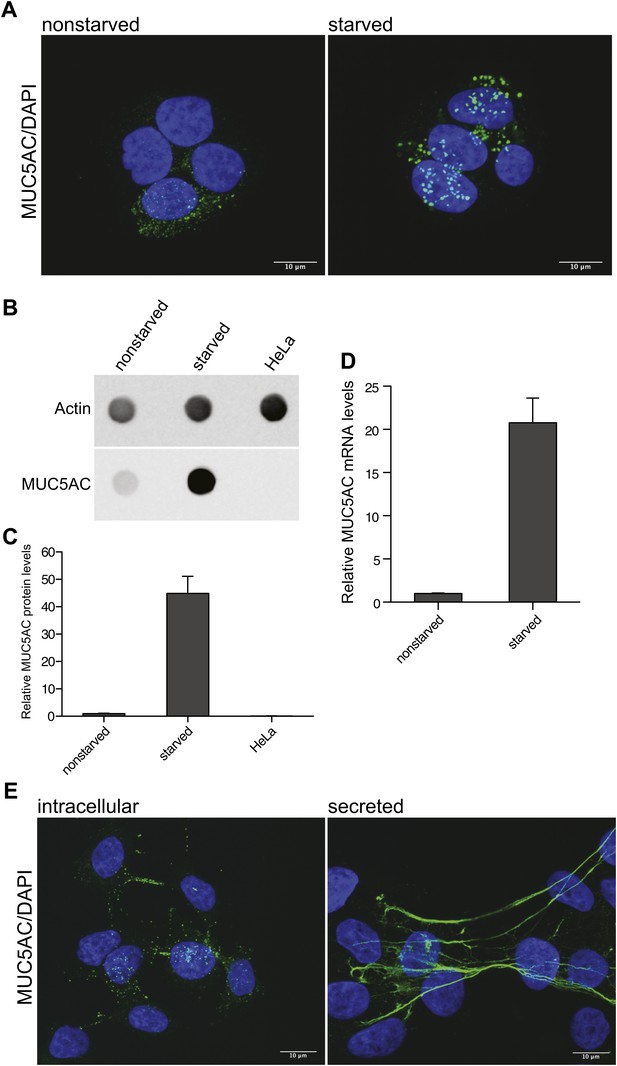
Mucin synthesis and secretion from goblet cells.
(A) Nonstarved and starved N2 cells were fixed and analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy with an anti-MUC5AC antibody (green). The nuclear DNA was stained with DAPI (blue) to localize the position of the nucleus. (B) Dot blot of total lysates of nonstarved, starved N2 and HeLa cells were probed with anti-MUC5AC and anti-actin antibody. (C) The dot blots in (B) were quantified and normalized to actin levels. The y-axis represents relative values with respect to the values of nonstarved N2 cells. Average values ± SEM are plotted as bar graphs (N = 3). (D) Nonstarved and 5 days starved N2 cells were lysed and total RNA was extracted for quantitative real-time PCR analysis. The values for MUC5AC mRNA levels were normalized to the values of the housekeeping gene HPRT1. The y-axis represents relative values with respect to nonstarved N2 cells. Average values ± SEM are plotted as bar graphs (N = 4). (E) Starved N2 cells were treated for 2 hr with 2 μM PMA. To detect the remaining intracellular mucin after PMA release, the secreted mucin was removed by DTT and trypsin treatment of the goblet cells prior to fixation (experimental procedures). After fixation, cells were permeabilized and examined by immunofluorescence microscopy with DAPI and an anti-MUC5AC antibody. Secreted MUC5AC was detected by fixing the secreted mucus directly on the cells after PMA treatment, followed by immunofluorescence microscopy using an anti-MUC5AC specific antibody.
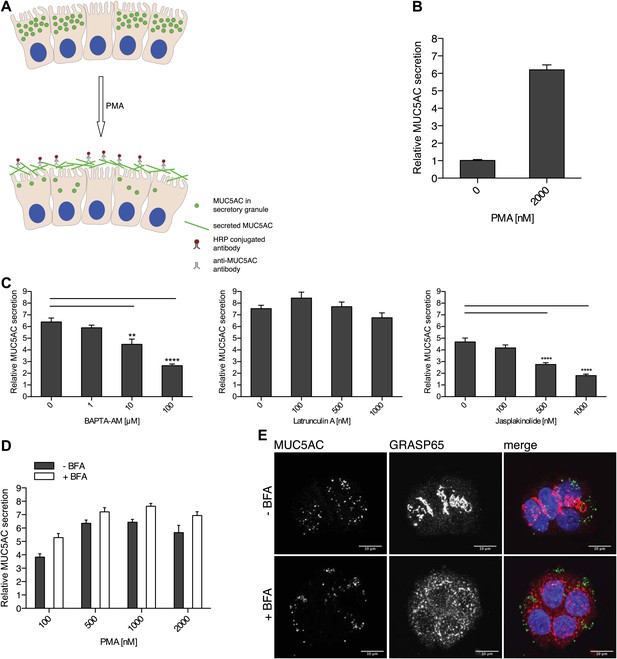
Mucin secretion assay.
(A) Illustration of the mucin secretion assay. Starved N2 cells are treated with PMA. Secreted MUC5AC is fixed on the cell surface and labeled with anti-MUC5AC antibodies followed by quantitative detection using HRP-conjugated secondary antibody. (B) Starved N2 cells were treated for 2 hr ± 2 μM PMA, fixed with formaldehyde and the amount of secreted MUC5AC bound to the cell surface was detected with anti-MUC5AC antibody and measured by chemiluminescence. The values were normalized to values obtained for—PMA treatment. Average values ± SEM are plotted as bar graphs (N = 10). (C) Starved N2 cells were pretreated for 30 min with BAPTA-AM, Latrunculin A or Jasplakinolide and incubated at 37°C. After 30 min, 2 μM PMA was added containing the respective drugs (BAPTA-AM, Latrunculin A or Jasplakinolide) and incubated for 2 hr at 37°C. Cells were fixed and secreted MUC5AC was detected by chemiluminescence. The values were normalized to values obtained for −PMA treatment. Average values ± SEM are plotted as bar graphs (N = 10). Compared datasets were considered as statistically significant when p<0.01 (**) and p<0.0001 (****). (D) Starved N2 cells were preincubated for 15 min with 2 μg/ml (+BFA) and incubated at 37°C. After 30 min, increasing concentrations of PMA were added in the presence or absence of 2 μg/ml BFA (+/− BFA) and incubated for 2 hr at 37°C. Cells were fixed and secreted MUC5AC was detected by chemiluminescence. The values were normalized to values obtained for −PMA treatment. Average values ± SEM are plotted as bar graphs (N = 5). (E) Starved N2 cells were incubated for 45 min with or without 2 μg/ml BFA (+/− BFA) at 37°C. After 45 min cells were fixed, permeabilized and examined by immunofluorescence microscopy with an anti-MUC5AC antibody (green), an anti-GRASP65 antibody (red) and DAPI (blue).
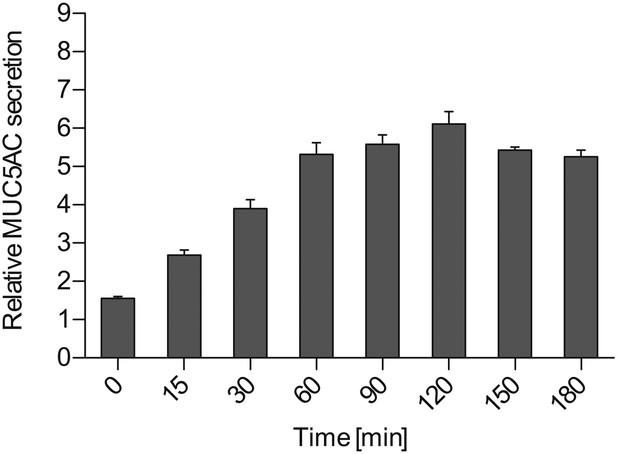
Time course for MUC5AC secretion.
Starved N2 cells were treated for the indicated times with 2 μM PMA, fixed with formaldehyde and the amount of secreted MUC5AC bound to the cell surface was detected with anti-MUC5AC antibody and measured by chemiluminescence. The values were normalized to values obtained for −PMA treatment. Average values ± SEM are plotted as bar graphs (N = 6).
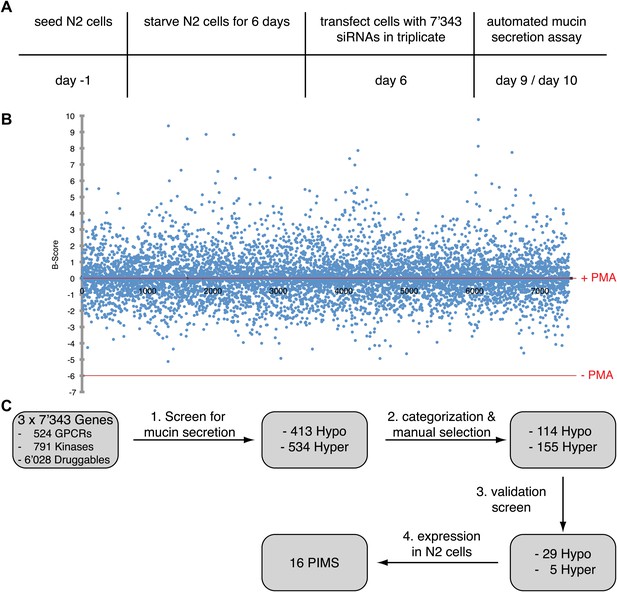
Identification of proteins required for MUC5AC secretion.
(A) Screening procedure. N2 cells were serum starved for 6 days. The cells were then seeded into the wells of 96-well plates and transfected in triplicates on three sets of plates with siRNAs directed against 7343 components. 3 days after transfection, the cells were treated for 2 hr with 2 μM PMA and analyzed by an automated chemiluminescence assay for the detection of secreted MUC5AC. (B) The B-score of each gene product tested was calculated using the triplicate measurements of the chemiluminescence values. All siRNAs that altered secretion with a B-score less than −1.5 (hyposecretory) and higher than 1.5 (hypersecretory) were selected as positive hits for further analysis. −PMA (lower red line) and +PMA (upper red line) indicate mock treated controls without PMA (−PMA) and with 2 μM PMA (+PMA). (C) Flowchart depicting screen for PIMS and validation process. From the initial collection of 7343 siRNAs, 413 were classified as hyposecretory and 534 as hypersecretory hits (Supplementary file 1). From this pool we further selected 114 hyposecretory and 155 hypersecretory components (Supplementary file 1). A second validation screen with siRNAs distinct from the primary screen confirmed 29 proteins that gave a MUC5AC hyposecretory phenotype and 5 with a hypersecretory secretory defect (Table 1).
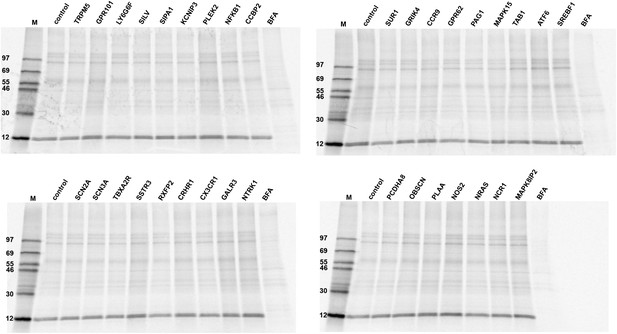
PIMS are not required for constitutive secretion of newly synthesized proteins.
N2 cells were starved for 6 days and transfected with the corresponding siRNA on day 6. The cells were grown for 3 additional days, pulsed with 35S-methionine and chased with cold methionine-containing medium. The medium was collected and analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by autoradiography. Treatment with BFA during the pulse and chase was used as positive control to score effects on the secretion of newly synthesized proteins.
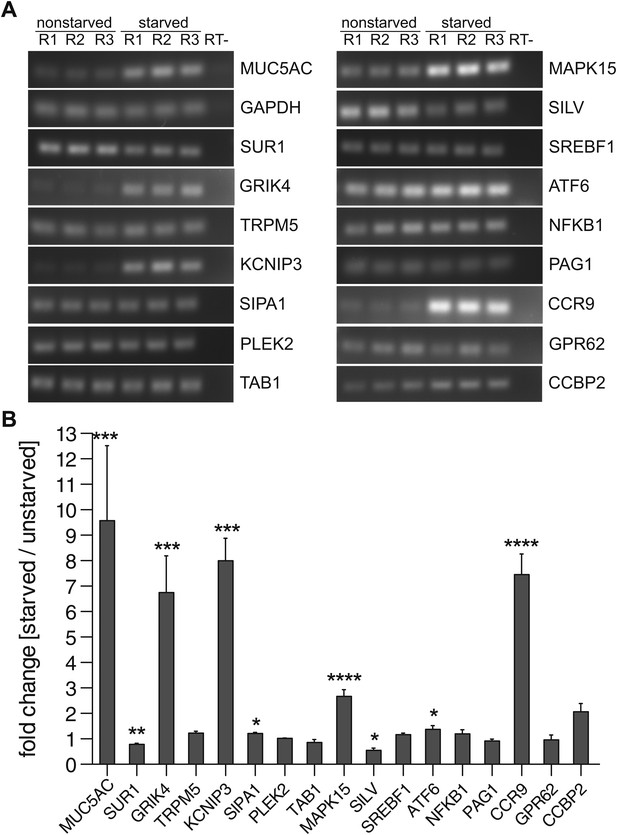
Expression profile of PIMS.
(A) Total RNA was extracted from nonstarved- and 5-day starved N2 cells. 1 μg of total RNA was used to generate cDNA by reverse transcription. PCR was performed on cDNA with primers specific for the indicated genes and PCR products were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. (B) Results in (A) were quantified and values were normalized to the housekeeping gene GAPDH. The y-axis represents relative values of starved compared to nonstarved N2 cells. Average values ± SEM are plotted as bar graphs (N = 3). Compared datasets were considered as statistically significant when p<0.05 (*), p<0.01 (**), p<0.001 (***) and p<0.0001 (****). Abbreviations: R1: replicate 1; R2: replicate 2; R3: replicate 3; RT-: reverse transcription without reverse transcriptase.
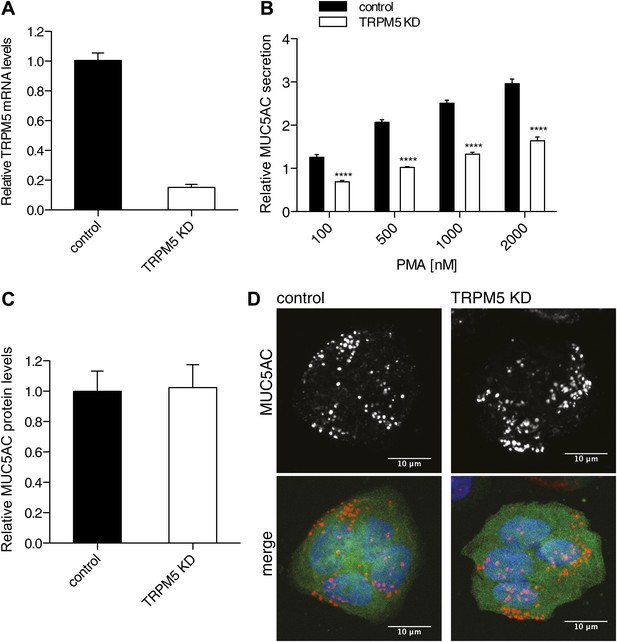
TRPM5 in mucin homeostasis.
(A) Total RNA was extracted from control and TRPM5 stable knockdown (TRPM5 KD) cells and analyzed for knockdown efficiency of TRPM5 on mRNA level by quantitative real-time PCR using primers specific for TRPM5. TRPM5 values were normalized to values of the housekeeping gene GAPDH. The knockdown of TRPM5 is represented as relative value compared to control cells. Results are means ± SEM. (N = 5). (B) Control and TRPM5 stable knockdown cells were starved for 6 days and seeded on 96-well plates. At day 9, cells were treated with increasing concentrations of PMA for 30 min and analyzed by chemiluminescence using anti-MUC5AC antibody. After the mucin secretion assay these cells were stained with DAPI and imaged by fluorescence microscopy. Nuclei were counted using ImageJ and the chemiluminescence value for MUC5AC of each well was normalized to the number of nuclei per well. The y-axis represents relative values with respect to the values of control cells not treated with PMA. Average values ± SEM are plotted as bar graphs (N = 5). Datasets were considered as statistically significant when p<0.0001 (****). (C) N2 cells were starved for 6 days and seeded for dot blot analysis. At day 9 cells were lysed and analyzed by dot blot with an anti-MUC5AC and anti-actin antibody. The intensity of the spots was quantified using ImageJ. Intensities of MUC5AC spots were normalized to the intensity of actin spots. Results are means ± SEM. (N = 6). (D) Control and TRPM5 stable knockdown cells were differentiated by starvation. After starvation cells were fixed, permeabilized and analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy with an anti-MUC5AC antibody (red) and DAPI (blue). Cells shown in green represent expression of GFP, showing that these cells express shRNA specific for TRPM5 and are depleted of TRPM5.
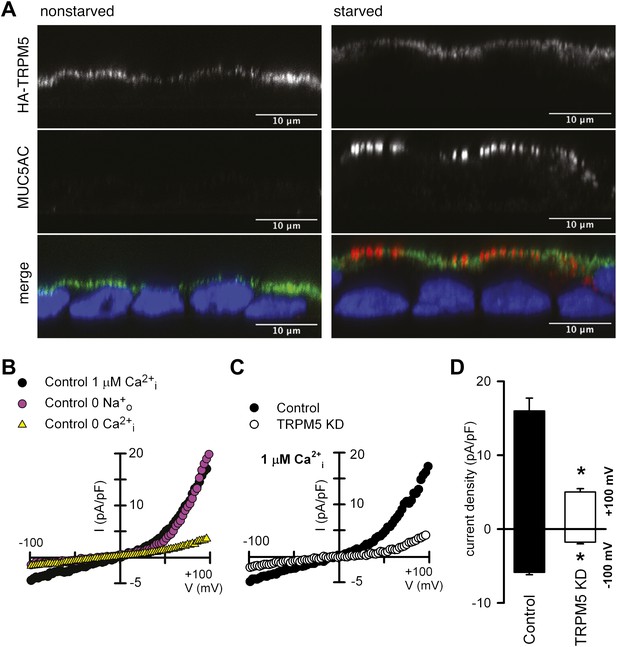
TRPM5 localization and activity.
(A) Nonstarved and starved N2 cells stably transfected with HA-TRPM5 were fixed and analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy with an anti-HA antibody (green) and an anti-MUC5AC antibody (red). The nuclear DNA was stained with DAPI (blue) to localize the position of the nucleus. (B) Ramp current-voltage relations of cationic currents recorded from a starved N2 cell dialyzed with internal solutions containing 1 μM Ca2+ and bathed in Na+-containing or Na+-free solutions. A ramp current obtained in a cell dialyzed with internal solutions containing 0 Ca2+ and bathed in Na+-containing is also shown. (C) Representative ramp current-voltage relations of cationic currents recorded from a control and TRPM5-depleted N2 cells dialyzed with internal solutions containing 1 μM Ca2+ and bathed in Na+-containing solutions. (D) Mean TRPM5-like current density recorded at ±100 mV from control (n = 6) and TRPM5 KD cells (n = 8). * p<0.05.
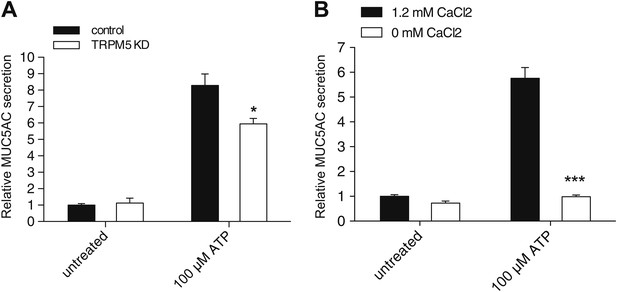
TRPM5 modulates ATP-induced MUC5AC secretion.
(A) Control and TRPM5 stable knockdown cells were starved and incubated for 30 min at 37°C with 100 μM ATP. Secreted MUC5AC was collected and processed for dot blot analysis with an anti-MUC5AC antibody. The dot blots were quantified and normalized to intracellular actin levels. The y-axis represents relative values with respect to the values of untreated control cells. Average values ± SEM are plotted as bar graphs (N = 6). Datasets were considered as statistically significant when p<0.01 (*). (B) Starved N2 cells were incubated for 30 min at 37°C with 100 μM ATP in the presence (1.2 mM CaCl2) or absence (0 mM CaCl2) of extracellular Ca2+. Secreted MUC5AC was collected and analyzed by dot blot with an anti-MUC5AC antibody. The dot blots were quantified and normalized to intracellular actin levels. The y-axis represents relative values with respect to the values of untreated N2 cells in the presence of 1.2 mM CaCl2. Average values ± SEM are plotted as bar graphs (N = 3). Datasets were considered as statistically significant when p<0.001 (***).
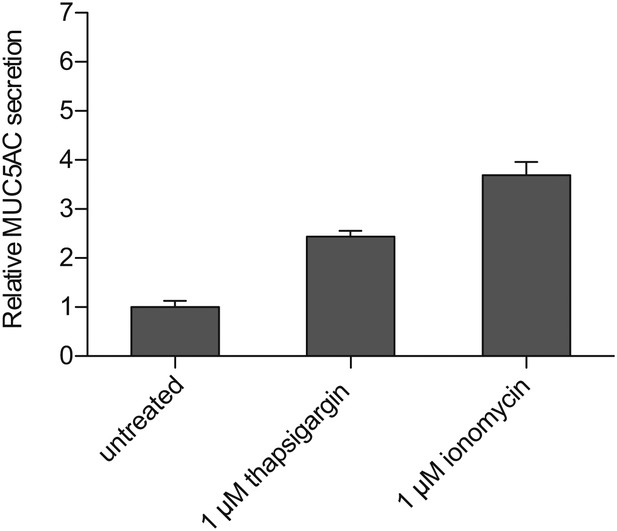
Ca2+ dependent MUC5AC secretion.
Starved N2 cells were treated for 30 min with the indicated concentrations of thapsigargin and ionomycin. Secreted MUC5AC was collected and processed for dot blot analysis with an anti-MUC5AC antibody. The dot blots were quantified and normalized to intracellular β-tubulin levels. The Y-axis represents relative values with respect to the values of untreated cells. Average values ± SEM are plotted as bar graphs (N = 6). Datasets were considered as statistically significant with the following p values: Untreatedt vs 1 μM thapsigargin, p<0.0001 (****); untreated vs 1 μM ionomycin, p<0.0001 (****); thapsigargin vs ionomycin, p<0.01 (**)
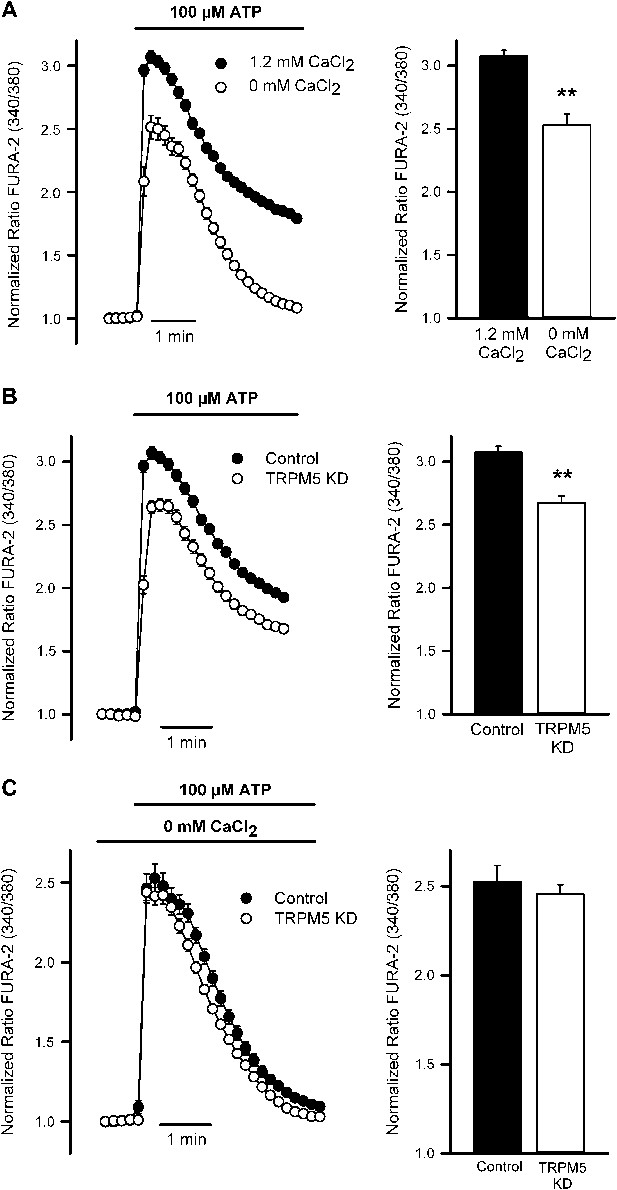
TRPM5 modulates ATP-induced Ca2+ entry.
(A) Time course of mean Ca2+ responses (Fura-2 ratio) obtained in starved N2 cells treated with 100 μM ATP in the presence (n = 138) or absence of 1.2 mM Ca2+ (n = 118) in the extracellular solution. Right panel, average peak [Ca2+] increases obtained from traces shown in the right panel. *p<0.01. (B) Time course of mean Ca2+ responses (Fura-2 ratio) obtained in starved control (n = 179) and TRPM5 KD N2 cells (n = 163) treated with 100 μM ATP. Right panel, average peak [Ca2+] increases obtained from traces shown in the right panel. *p<0.01. (C) Time course of mean Ca2+responses (Fura-2 ratio) obtained in starved control (n = 118) and TRPM5 KD N2 cells (n = 89) treated with 100 μM ATP and bathed in Ca2+-free solutions. Right panel, average peak [Ca2+] increases obtained from traces shown in the right panel. *p<0.01.
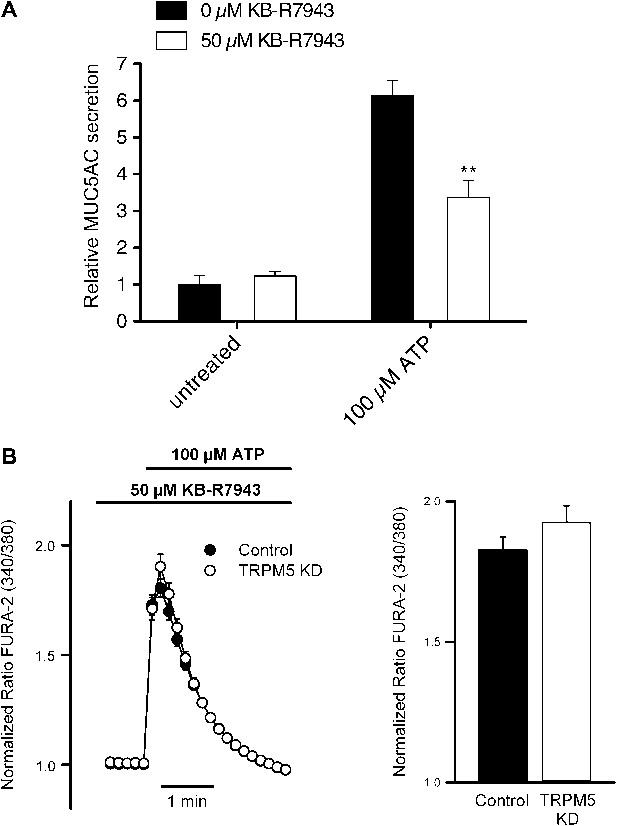
Effect of inhibiting the NCX on MUC5AC secretion and Ca2+ entry.
(A) Starved N2 cells were preincubated for 15 min with or without KB-R7943 (50 μM) followed by incubation with 100 μM ATP in the presence or absence of KB-R7943. Secreted MUC5AC was analyzed by dot blot with an anti-MUC5AC antibody. The dot blot was quantified and normalized to intracellular tubulin amount. The y-axis represents relative values with respect to values of untreated control cells. Average values ± SEM are plotted as bar graphs (N = 6). Datasets were considered as statistically significant when p<0.01 (**). (B) Time course of mean Ca2+ responses (Fura-2 ratio) obtained in starved control (n = 84) and TRPM5 KD N2 cells (n = 83) treated with 100 μM ATP in the presence of 50 μM KB-R7943. Right panel, average peak [Ca2+] increases obtained from traces shown in the right panel.
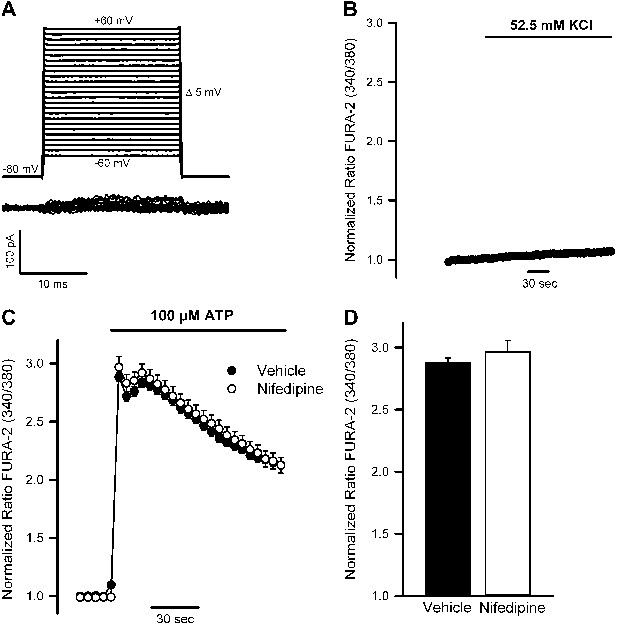
Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels are not expressed or functional in N2 cells.
(A) Current traces (bottom) obtained in a starved N2 cell held at −80 mV and pulsed from −60 mV to +60 mV in 5 mV voltage steps (top). Traces are representative of six cells recorded under identical conditions. None of the recorded cells presented voltage-gated Ca2+ currents. (B) Lack of Ca2+ response (Fura-2 ratio) in starved control N2 cells exposed to high K+ solutions. Mean ± SEM, n = 43. (C) Left, time course of mean Ca2+ responses (Fura-2 ratio) obtained in starved control N2 cells treated with 100 μM ATP in the absence (n = 35) or presence (n = 48) of the voltage-gated Ca2+ channel blocker nifedipine (100 μM). Right panel, peak [Ca2+] increases obtained from traces shown in the right panel.
Tables
Thirty-four proteins involved in MUC5AC secretion
| Gene ID | Symbol | MUC5AC secretion | Type | Known localization | Expression in N2 cells |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6833 | SUR1 | Hyposecretory | Transporter | PM | Detected |
| 2900 | GRIK4 | Hyposecretory | Ion channel | PM | Detected |
| 29,850 | TRPM5 | Hyposecretory | Ion channel | PM | Detected |
| 6326 | SCN2A | Hyposecretory | Ion channel | PM | Not detected |
| 6328 | SCN3A | Hyposecretory | Ion channel | PM | Not detected |
| 6915 | TBXA2R | Hyposecretory | GPCR | PM | Not detected |
| 6753 | SSTR3 | Hyposecretory | GPCR | PM | Not detected |
| 122042 | RXFP2 | Hyposecretory | GPCR | PM | Not detected |
| 1394 | CRHR1 | Hyposecretory | GPCR | PM | Not detected |
| 10,803 | CCR9 | Hyposecretory | GPCR | PM | Detected |
| 524 | CX3CR1 | Hyposecretory | GPCR | PM | Not detected |
| 8484 | GALR3 | Hyposecretory | GPCR | PM | Not detected |
| 83,550 | GPR101 | Hyposecretory | GPCR | PM | Not detected |
| 118442 | GPR62 | Hyposecretory | GPCR | PM | Detected |
| 4914 | NTRK1 | Hyposecretory | TM receptor | PM | Not detected |
| 9437 | NCR1 | Hyposecretory | TM receptor | PM | Not detected |
| 55,824 | PAG1 | Hyposecretory | Other | PM | Detected |
| 259215 | LY6G6F | Hyposecretory | TM receptor | PM | Not detected |
| 56,140 | PCDHA8 | Hyposecretory | Cadherin | PM | Not detected |
| 225689 | MAPK15 | Hyposecretory | Kinase | Cytosol | Detected |
| 23,542 | MAPK8IP2 | Hyposecretory | Other | Cytosol | Not detected |
| 10,454 | TAB1 | Hyposecretory | Scaffold | Cytosol | Detected |
| 6490 | SILV | Hyposecretory | Melanosome biogenesis | Melanosome | Detected |
| 6494 | SIPA1 | Hyposecretory | GTPase activator | Cytosol, nucleus | Detected |
| 30,818 | KCNIP3 | Hyposecretory | Ca2+ binding | Palmitoylated: membrane, cytosol | Detected |
| 22,926 | ATF6 | Hyposecretory | Transcription | ER | Detected |
| 26,499 | PLEK2 | Hyposecretory | Actin binding | Cytoskeleton | Detected |
| 4790 | NFKB1 | Hyposecretory | Transcription | Nucleus, cytosol | Detected |
| 6720 | SREBF1 | Hyposecretory | Transcription | ER | Detected |
| 1238 | CCBP2 | Hypersecretory | GPCR | PM | Detected |
| 84,033 | OBSCN | Hypersecretory | Kinase | Cytosol | NT |
| 9373 | PLAA | Hypersecretory | Other | Cytosol | NT |
| 4843 | NOS2 | Hypersecretory | Other | Cytosol | NT |
| 4893 | NRAS | Hypersecretory | G-protein | Cytosol | NT |
-
ER: endoplasmic reticulum; GPCR: G protein coupled receptor; PM: plasma membrane; TM receptor: transmembrane receptor; NT: not tested.
Identification of proteins involved in MUC5AC secretion (PIMS)
| Gene | PIMS | MUC5AC secretion | Type | Known localization | Expression in starved N2 cells | Disease |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUR1 | 1 | Hyposecretory | Transporter | PM | Unchanged | Diabetes mellitus, insulin secretion (Aittoniemi et al., 2009) |
| GRIK4 | 2 | Hyposecretory | Ion channel | PM | Upregulated | |
| TRPM5 | 3 | Hyposecretory | Ion channel | PM | Unchanged | Insulin secretion (Colsoul et al., 2010) |
| KCNIP3 | 4 | Hyposecretory | Ca2+ binding | Palmitoylated membrane, cytosol | Upregulated | |
| SIPA1 | 5 | Hyposecretory | GTPase activator | Cytosol, nucleus | Unchanged | |
| PLEK2 | 6 | Hyposecretory | Actin binding | Cytoskeleton | Unchanged | |
| TAB1 | 7 | Hyposecretory | Scaffold | Cytosol | Unchanged | |
| MAPK15 | 8 | Hyposecretory | Kinase | Cytosol | Upregulated | |
| SILV | 9 | Hyposecretory | Melanosome biogenesis | Melanosome | Unchanged | |
| SREBF1 | 10 | Hyposecretory | Transcription regulator | ER | Unchanged | |
| ATF6 | 11 | Hyposecretory | Transcription regulator | ER | Unchanged | |
| NFKB1 | 12 | Hyposecretory | Transcription regulator | Cytosol, nucleus | Unchanged | MUC5AC biosynthesis (Fujisawa et al., 2009); asthma (Hart et al., 1998); COPD (di Stefano et al., 2002) |
| PAG1 | 13 | Hyposecretory | Other | PM | Unchanged | |
| CCR9 | 14 | Hyposecretory | GPCR | PM | Upregulated | Inflammatory bowel disease (Nishimura et al., 2009) |
| GPR62 | 15 | Hyposecretory | GPCR | PM | Unchanged | |
| CCBP2 | 16 | Hypersecretory | GPCR | PM | Unchanged |
-
ER: endoplasmic reticulum; GPCR: G protein-coupled receptor; PM: plasma membrane; TM receptor: transmembrane receptor.
Primer sequences used for detecting mRNA for the respective PIMS in N2 cells
| Gene | Forward primer 5′–3′ | Reverse primer 5′–3′ |
|---|---|---|
| TRPM5 | GTGGCCATCTTCCTGTTCAT | CTTCATCATGCGCTCTACCA |
| CCR9 | GCCAGCCTTGGCCCTGTTGT | TCCAGCAAGGCCTGCGCTTC |
| PLEK2 | AGAACAGGCCAGTGGGTGGGT | GCTCGCTCAGCCTTGCTGCT |
| TAB1 | TCAATCATCGCAGCAATCTC | GGCTACACGGACATTGACCT |
| KCNIP3 | CCACCACCTATGCACACTTCC | GTCGTAGAGATTAAAGGCCCAC |
| SILV | GGGCTACAAAAGTACCCAGAAAC | CCTTGAGGGACACTTGACCAC |
| SIPA1 | CTCCTTTCTGCCACGTACCTT | TTTTGGAGTTCCCTTAGGGTCT |
| HPRT1 | TGACACTGGCAAAACAATGCA | GGTCCTTTTCACCAGCAAGCT |
| MUC5AC | CAACCCCTCCTACTGCTACG | CTGGTGCTGAAGAGGGTCAT |
| GPR62 | GGTGGTTTCCGTGGGGGCTC | TGGGCCCAGACCGCAGGATT |
| PAG1 | TGGACGGCAGCCATGCATCC | ACTGTTGGTGTGGGCAGCGG |
| ATF6 | AGGTGGGTAGCGGTTGGGAGG | GCGGCACCTTACAGGCACCC |
| SREBF1 | CCACGGCAGCCCCTGTAACG | GGGACTGAGACCTGCCGCCT |
| MAPK15 | TACAACAGGTCCCTCCCCGGC | CCCAGTGCCGAGTGGCAGAC |
| SUR1 | GCCTTCGCAGACCGCACTGT | CTGCACGGACGAAGGAGGCG |
| NFKB1 | CGCCACCCGGCTTCAGAATGG | GTATGGGCCATCTGCTGTTGGCA |
| CCBP2 | CGGCGGGCATGGGACCATTT | AAGGCCACCACCAAGGCTGC |
| GRIK4 | CGTGGCTCGTGATGGTCGCC | GCCTCTCAGGAGCGCGGTTG |
| GAPDH | TGCACCACCAACTGCTTAGC | GGCATGGACTGTGGTCATGAG |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
List of positive hits from primary screen.
Lists positive hits from the primary screen, their reason for exclusion, the B-score, the ranking product and the E-value.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00658.019





