Broad and direct interaction between TLR and Siglec families of pattern recognition receptors and its regulation by Neu1
Figures
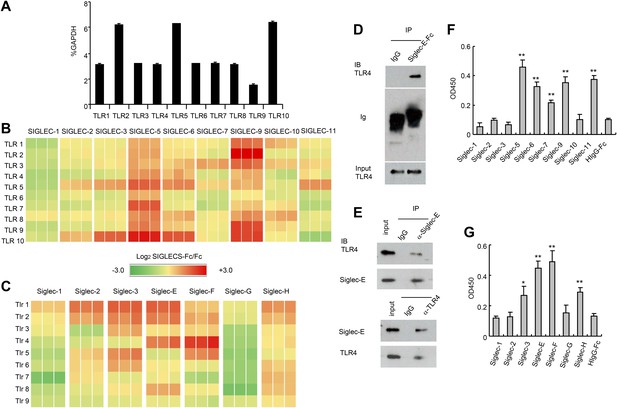
Extensive direct interactions between Siglecs and TLRs.
(A) Evaluation of TLR expression using TLR-primer set. Data shown are means and SEM of triplicate % of GAPDH levels. (B) and (C) Interactions between human (B) or mouse (C) SIGLEC-Fc fusion proteins and TLRs from THP-1 cells (B) or murine splenocyte lysates (C). Recombinant SIGLEC-Fc or control IgG Fc were coated on 96 well plates to capture TLR in the cell lysates. The associated TLRs were detected with biotinylated anti-TLR antibodies that cross-react with both mouse and human TLR. Data shown are the log2 ratios between Siglec-Fc and IgG Fc in triplicate and were repeated three times. (D) Recombinant Siglec-E binds to endogenous Tlr4. Lysates from C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were incubated with either Fc control or SIglec E-Fc. After precipitation with protein A beads, the precipitates were analyzed by Western blot, using antibodies against Siglec-E, Tlr4, and Fc. (E) Interaction between endogenous Tlr4 and Siglec-E in D2SC dendritic cells. Lysates from D2SC cells were immunoprecipitated with either anti-Siglec-E (top) or Tlr4 (bottom) antibodies. The precipitates were analyzed by Western blot, using antibodies against Siglec-E or Tlr4. Similar results were obtained when performed with WT mouse splenocyte lysates (data not shown). (F) Direct interaction between human Siglecs and ectodomain of TLR4. As in (A), except the cell lysates were replaced with recombinant TLR4. (G) Direct interaction between mouse Siglecs and ectodomain of TLR4. As in (B), except the cell lysates were replaced with recombinant TLR4. Data presented in this figure have been reproduced at least three times.
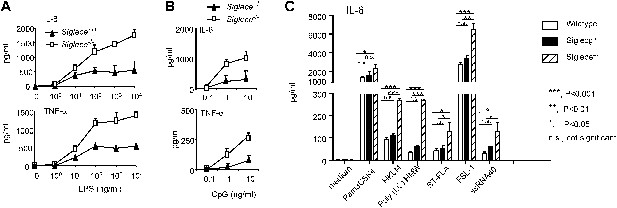
Siglec-E negatively regulates production of inflammatory cytokines by DC in response to TLR ligands.
(A) and (B) Siglec-E inhibits production of IL-6 and TNFα by bone marrow derived DC. DC cultured from WT or Siglece−/− bone marrow were stimulated with indicated concentrations of LPS (A), or poly(I:C) (B) for 16 hr, and supernatant cytokine concentrations were analyzed with cytokine bead array. (C). Targeted mutation of Siglec-E, but not Siglec-G, enhances production of IL-6 to multiple TLR ligands. The TLR agonists used are: synthetic triacylated lipoprotein Pam3CSK4 (TLR1/2 agonist), heat-killed Listeria monocytogenes (HKLM, Tlr2 agonist), poly(I:C), (TLR3 agonist), Salmonella typhimurium flagellin (ST-FLA, TLR5 agonist), synthetic lipoprotein derived from Mycoplasma salivarium (FSL-1, TLR2/6 agonist) and ssRNA40, a 20-mer phosphorothioate-protected single-stranded RNA oligonucleotide containing a GU-rich sequence (TLR8 agonist). All agonist were used at 100 ng/ml. Data represent the mean ± SD for three independent cultures of DCs in each genotype and were repeated at least three times.
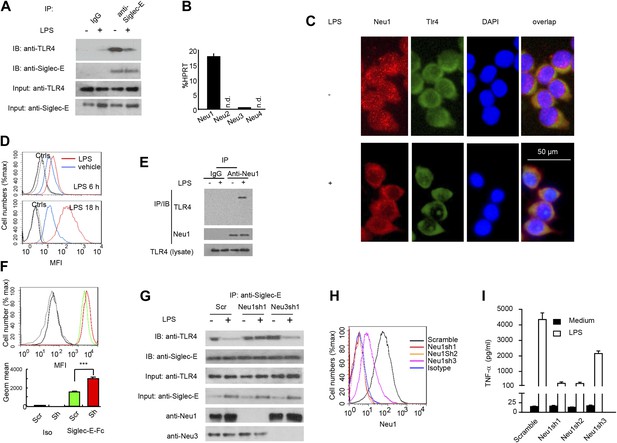
A critical role for Neu1 in Tlr4 activation.
(A) Siglec-E-Tlr4 association is disrupted by LPS stimulation. D2SC cells were cultured in the presence or absence of LPS overnight. Immunoprecipitation was used to test Siglec-E-Tlr4 association as detailed in the Figure 1D legend. (B) Expression of Neu1-4 mRNA in D2SC dendritic cells was determined by RT-PCR. Data shown are mean ± SD transcript levels, expressed as % of the housekeeping gene HPRT. (C) Translocation of Neu1 and its co-localization with TLR4 in D2SC cells. D2SC were cultured in the presence or absence of LPS (100 ng/ml) for 18 hr and co-stained with anti-TLR4 and anti-Neu1 antibodies. (D) Increased cell surface expression of Neu1 on D2SC cells after stimulation with LPS as revealed by flow cytometry. D2SC cells were treated with LPS (100 ng/ml) or vehicle for 6 hr (upper panel) or 18 hr (lower panel). The expression of cell-surface Neu1 was determined by FACS. (E) Physical association between Neu1 and TLR4. D2SC 2 cell lines were stimulated with 2 μg/ml LPS or vehicle for 16 hr were crossed linked with 1 mM DSP at room temperature for 30 min. The lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Neu1 and then probed with anti-Neu1 or anti-TLR4. (F) Silencing Neu1 by lentivirus shRNA increased the cell surface Siglec-E ligands. Histograms shown on top panels are FACS profiles. The bar graphs in the bottom panels represent geometric means ± SD of fluorescence intensity (n = 3). (G) Neu1 disrupts Tlr4-Siglec-E association in DC. D2SC dendritic cells were transduced with lentiviral vector carrying scrambled shRNA, three independent Neu1 shRNAs or Neu3 shRNA. After LPS stimulation for 24 hr, the lysates were used for immunoprecipitation. (H) ShRNA silencing of Neu1 affect cell surface Neu1 levels. Data shown are histogram of flow cytometry data depicting cell surface expression of Neu1 in LPS-stimulated D2SC clones. (I) An essential role for Neu1 in production of TNFα by D2SC cells. Aliquots of 2 × 105 D2SC transfectants were stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 12 hr. The culture supernatants were subsequently collected and analyzed for TNF-α. Scramble, Neu1sh1, 2, 3 represent stable clones expressing three independent Neu1 ShRNAs. Experiments depicted in this figure have been reproduced two to three times.
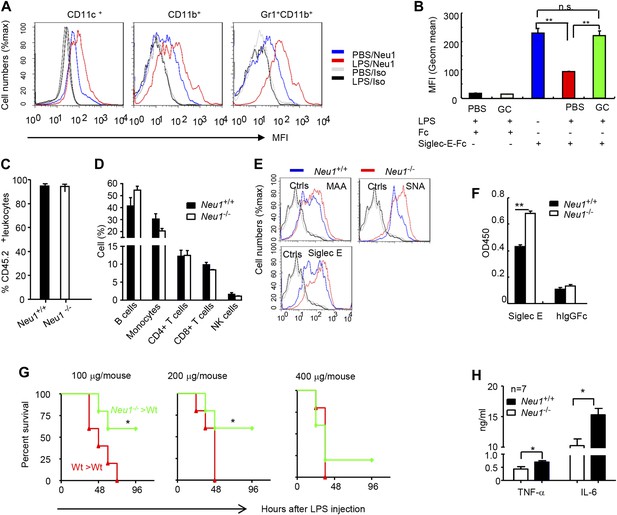
A critical role for hematopoietic cell-expressed Neu1 in endotoxic shock.
(A) LPS stimulation in vivo increased cell surface Neu1 on DC, macrophage, and neutrophil. Data are representative of those from two independent experiments involving two mice per group. Splenocytes were collected from mice 16 hr after they received an injection of LPS (i. p. 200 μg/mouse). (B) The cell surface Siglec-E ligands are down-regulated on DC following LPS stimulation. Data shown are means ± SD (n = 3) and have been reproduced twice. (C–H) Lethally irradiated CD45.1 congenic B6 mice were transplanted with WT or Neu1−/− BM (5 × 106 cells/mouse). 21 weeks later, the mice were bled to analyze hematopoiesis. (C) Comparable reconstitution of donor-derived hematopoietic cells, based on the frequencies of donor-derived CD45.2+ cells. (n = 5). (D) Normal CD45.2+ leukocyte composition of PBL as determined by flow cytometry. Populations were defined as: B cells, B220+; monocytes, NK1.1−CD11b+; CD4+ T cells, CD4+CD3+; CD8+ T cells, CD3+CD8+; NK cells, NK1.1+. (E) Increase of α2,3 and α2,6 sialylation and Siglec-E ligand on Neu1−/− DC. (Gated CD11c+ as DCs). Splenocytes from Neu1+/+ and Neu1−/− mice were stained with FITC-conjugated SNA, MAA, or unconjugated Siglec-E-Fc (detected with PE-anti-mouse IgG Fc) in conjunction with APC-conjugated anti-CD11c mAb. Data shown are histrograms depicting the binding of SNA, MAA and Siglec-E-Fc respectively. (F) Siglec-E-Tlr4 association is increased on Neu1−/− splenocytes, as measured by captured Tlr4 in plates coated with Siglec-E-Fc. (G) Neu1 deficiency increases resistance to LPS challenge. Data shown are Kaplan Meier survival curves of mice that received the indicated doses of LPS (i.p., n = 5 in all groups). The mice were observed for 2 weeks, though all death occurred within 72 hr. (H) Cytokine production in blood measured 16 hr after LPS treatment. Data represent the mean ± SD. All data in this figure are representative of two to three independent experiments.
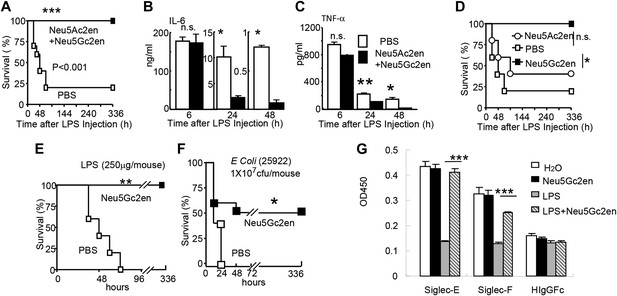
Sialidase inhibitors protect mice against endotoxic shock and preserve Siglec-TLR interactions.
(A) and (D) Survival analyses of mice that were treated with 450 µg/mouse of LPS (i.p., Escherichia coli 0111:B4). The mice received NeuAc2en and/or NeuGc2en (100 µg/mouse/injection) immediately after LPS administration and every 24 hr thereafter. (n = 8–10 for a and n = 5–6 mice for (D), 6–8 week old male mice were used). (B) and (C) Sialidase inhibitors reduce the levels of IL-6 (B) and TNF-α (C), measured at indicated time after LPS treatment. Data shown are means ± SD. (n = 8–10, 6–8 week old male mice). (E) Therapeutic effect of sialidase inhibitors. C57BL/6 mice received 250 µg/mouse of LPS (i.p., E. coli 0111:B4). The mice received NeuGc2en (100 µg/mouse/injection) 6 hr after LPS administration and every 24 hr thereafter. (n = 8–10, 6–8 week old male mice). (F) Neu5Gc2en protects mice against lethal E. coli (strain 25,922, 107 CFU) infection. (G) Sialidase inhibitor prevents LPS-induced disruption of the Siglec-TLR4 interaction. 1 × 107 splenocytes were cultured in RPMI supplemented with 10% FBS, stimulated with or without 2 μg/ml LPS in the presence of 100 μg/ml NeuGc2en or vehicle for 16 hr, and then the cells were lysed. The lysates were added to wells precoated with Siglece-Fc, Siglecf-Fc or hIgG-fc. The amounts of TLR4 captured were measured using anti-TLR4 mAb. All data in this figure are representative of two to three independent experiments.
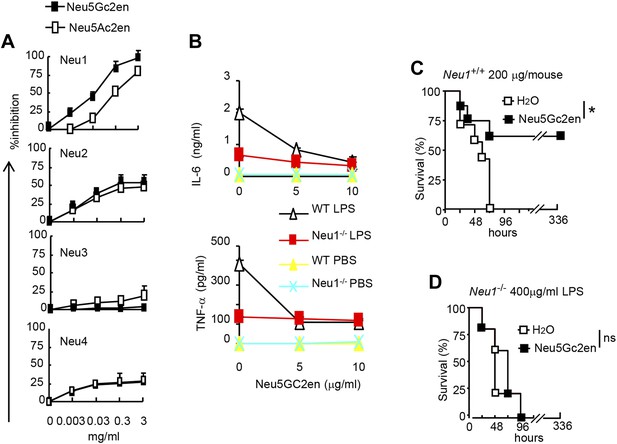
NeuGc2en targets Neu1 to inhibit inflammation and confer protection against endotoxemia.
(A) Comparison of Neu5Ac2en and Neu5Gc2en for inhibitory activity against mouse Neu1-4. Lysates from 293T cells transiently transfected with murine Neu1-4 cDNA were assayed for sialidase activity in the presence of indicated concentrations of inhibitors. Data shown are means ± SD of % inhibition of the activity of each sialidase by indicated concentration of inhibitors. (B) Neu5Gc2en targets Neu1 to inhibit production of inflammatory cytokine by DC in response to LPS. TNFα (upper panel) and IL-6 (lower panel) production by DC cultured from Neu1+/+ or Neu1−/− bone marrow. The DC were stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of indicated doses of Neu5Gc2en. Data shown are means ± SD (n = 3) and have been reproduced twice. (C) and (D) Chimeras consisting of either WT or Neu1−/− bone marrow were challenged with lethal doses of LPS (200 μg/mouse) for WT (C), and 400 μg/mouse for mutant chimeras (D). Sialidase inhibitor was injected at 6 hr after LPS challenge. Data shown are Kaplan–Meier survival curves. Data are representative of those obtained from two to four independent experiments. Statistical significance of survival analysis was determined using log-rank tests, while the pairwise comparison was performed with Student's t tests.
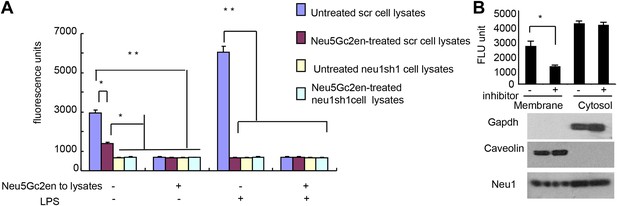
Exogenously added Neu5Gc2en inhibits cell surface but not intracellular Neu1.
(A) LPS stimulation increased sensitivity of Neu1 to exogenously added Neu5Gc2en. D2SC were transduced with lentiviral vectors encoding either scrambled or Neu1 shRNA and incubated with or without 1 µg/ml Neu5Gc2en for 30 min. After washing away the inhibitors, the lysates were analyzed for residual sialidase activity. Sialidase activity in the lysates was detected with 4-MU-NANA. To confirm that remaining activity is susceptible to Neu5Gc2en, the lysates were also assayed in the presence or absence of 1 µg/ml Neu5Gc2en. (B) When added to intact cells, Neu5Gc2en inhibits cell surface but not intracellular Neu1. D2SC cells were incubated with 1 μg/ml of Neu5Gc2en for 1 hr. The plasma membrane and cytoplasmic membranes were prepared as described (Liu and Fagotto, 2011) and measured for sialidase activity. The top panel shows Neu1 activity in cell membrane and cytosolic fractions of the D2SC cells (triplicate data, and mean ± SEM), while the lower panel shows commonly used marker proteins to show the purities of the plasma membrane (caveolin) or GAPDH (cytoplasm). Data are representative of those obtained from two independent experiments. Pairwise comparison was performed with Student's t tests.
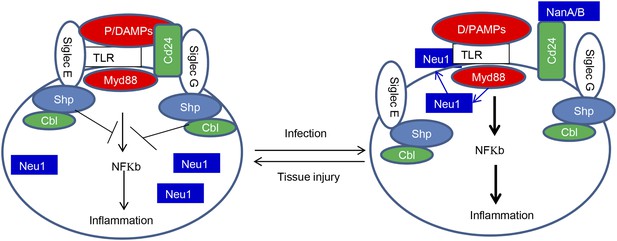
Sialoside-based pattern recognition and self-nonself discrimination by the innate immune system.
TLR signaling is restrained by Siglecs that are either directly (such as Siglec-E) or indirectly through Cd24 (such Siglec-G) in the case of tissue injuries. Infections cause a positive feedback in TLR signaling. Infections cause translocation of Neu1 to cell surface and/or to production of bacterial/viral sialidases. Both host and cellular to desialylate TLR and/or CD24. The Siglecs are dissociated from TLR to allow a more robust inflammation.





