dPob/EMC is essential for biosynthesis of rhodopsin and other multi-pass membrane proteins in Drosophila photoreceptors
Figures
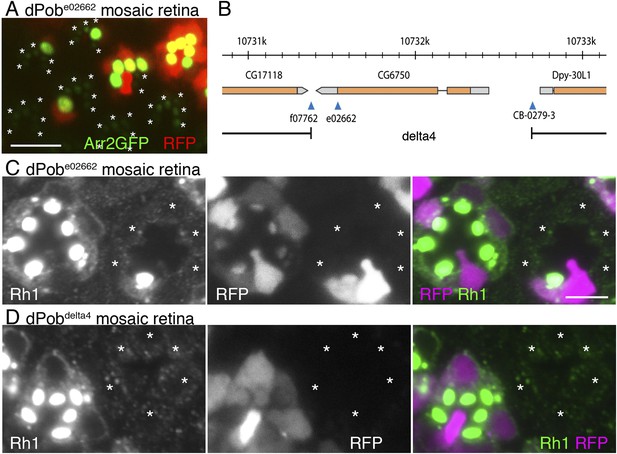
Identification of CG6750 as an essential gene for rhodopsin 1 (Rh1) biosynthesis.
(A) Observation of fluorescent protein localizations in CG6750e02662 mosaic retinas by the water immersion technique. RFP (red) indicates wild-type photoreceptors (R1–R8). Arrestin2::GFP (green) shows endogenous Rh1 localization in R1–R6 peripheral photoreceptors. (B) Schematic drawing of CG6750 and insertion/deletion mutants. The dPob-null mutant allele, dPob∆4, was created by the recombination of two FRTs on dPobf07762 and dPobCB−0279−3 using an FRT/FLP-based deletion method. (C, D) Immunostaining of dPobe02662 (C) and dPob∆4 (D) retinas expressing RFP as a wild-type cell marker (magenta) by anti-Rh1 antibody (green). Asterisks show mutant cells. Scale bar: 5 μm (A, C, D).
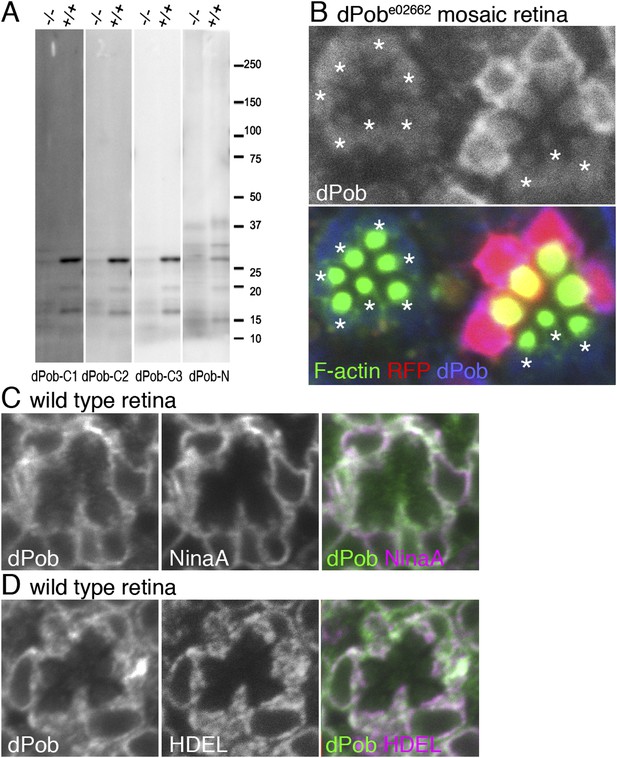
Construction of antisera against dPob.
(A) Immunoblotting of wild-type (+/+) and dPobe02662 homozygous (−/−) extracts from whole larvae using antiserum against dPob N- and C-terminal polypeptides. (B) Immunostaining of a dPobe02662 mosaic retina expressing RFP (red) as a wild-type cell marker (not shown) by rat anti-dPob-C1 antiserum (blue) and phalloidin (green). Asterisks show dPobe02662 homozygous photoreceptors. (C, D) Immunostaining of wild-type retinas by anti-dPob (green) and anti-NinaA (C) or anti-HDEL (D) antisera. Scale bar: 5 μm (B–D).
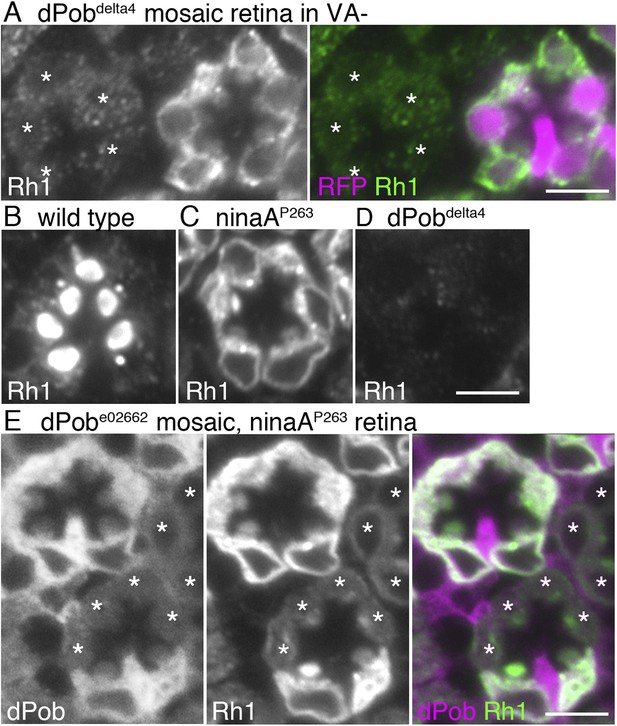
dPob stabilizes rhodopsin 1 (Rh1) apoprotein.
(A) Immunostaining of a dPob∆4 mosaic retina from a fly reared in vitamin A (VA)-deficient medium by anti-Rh1 antibody. Asterisks show dPob∆4 homozygous photoreceptors. (B–D) Immunostaining of a wild-type (B), ninaAp263(C), or dPob∆4 (D) ommatidium of flies reared in normal vitamin A-containing medium. (E) Immunostaining of a dPobe02662 mosaic retina in ninaAp263 homozygous mutant background from a fly reared in normal medium. Asterisks show dPob∆4 homozygous photoreceptors. Scale bar: 5 μm (A–E).
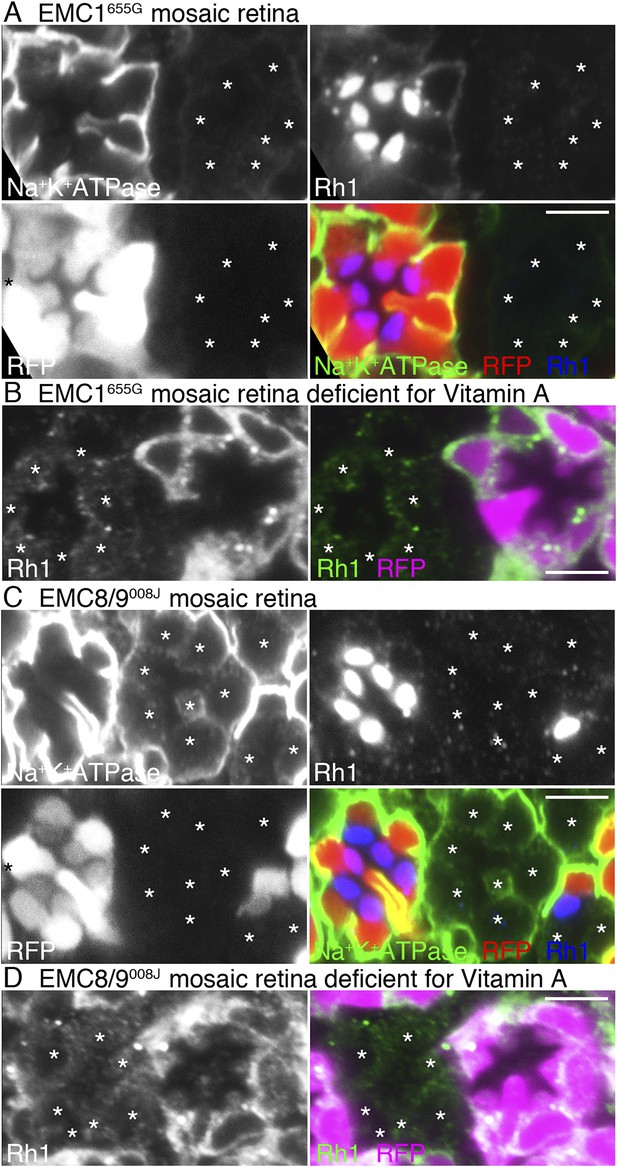
Loss of rhodopsin 1 (Rh1) apoprotein in EMC1 and EMC8/9 deficiency.
Immunostaining of a EMC1655G mosaic retina (A, B) or a EMC8/9008J mosaic retina (C, D) reared in normal (A, C) and vitamin A-deficient media (B, D). Asterisks show EMC1655G or EMC8/9008J homozygous photoreceptors. RFP (red) indicates wild-type photoreceptors (R1–R8). (A, C) Na+K+-ATPase, green; Rh1, blue; RFP, red. (B, D) Rh1, green; RFP, magenta. Scale bar: 5 μm (A–D).
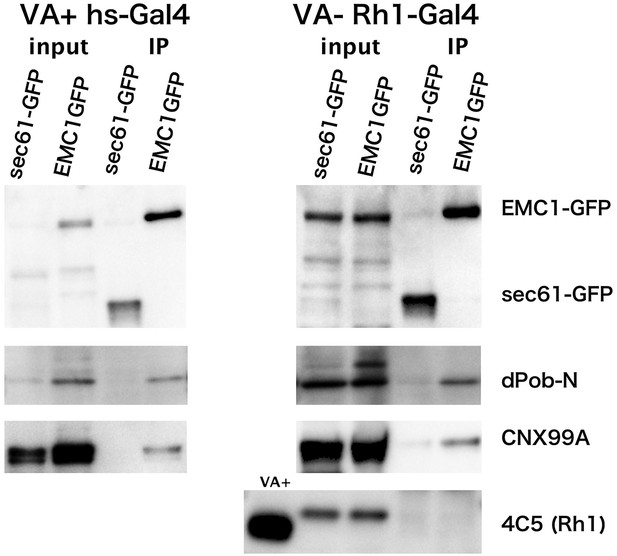
Co-immunoprecipitation of EMC1::GFP with dPob and calnexin (Cnx).
Immunoblotting of precipitates with anti-GFP antibody from the head extract was prepared from Rh1-Gal4/UAS-EMC1::GFP or sec61::GFP flies reared in a vitamin A (VA)-deficient medium (left) or heat shock (hs)-Gal4/UAS-EMC1::GFP or sec61::GFP flies reared in a vitamin A-containing normal medium (right). The mature form of rhodopsin 1 (Rh1) is accumulated in the rhabdomeres in normal medium but not in vitamin A-deficient medium. Instead of the mature form, an N-glycosylated immature form of Rh1 with a larger molecular weight accumulated in the endoplasmic reticulum of flies reared in the vitamin A-deficient medium. In both input extracts prepared from Rh1-Gal4/UAS-EMC1::GFP or sec61::GFP flies there is a band with the same position as EMC1GFP; this band will be the protein cross-reacting to anti-GFP antibody.
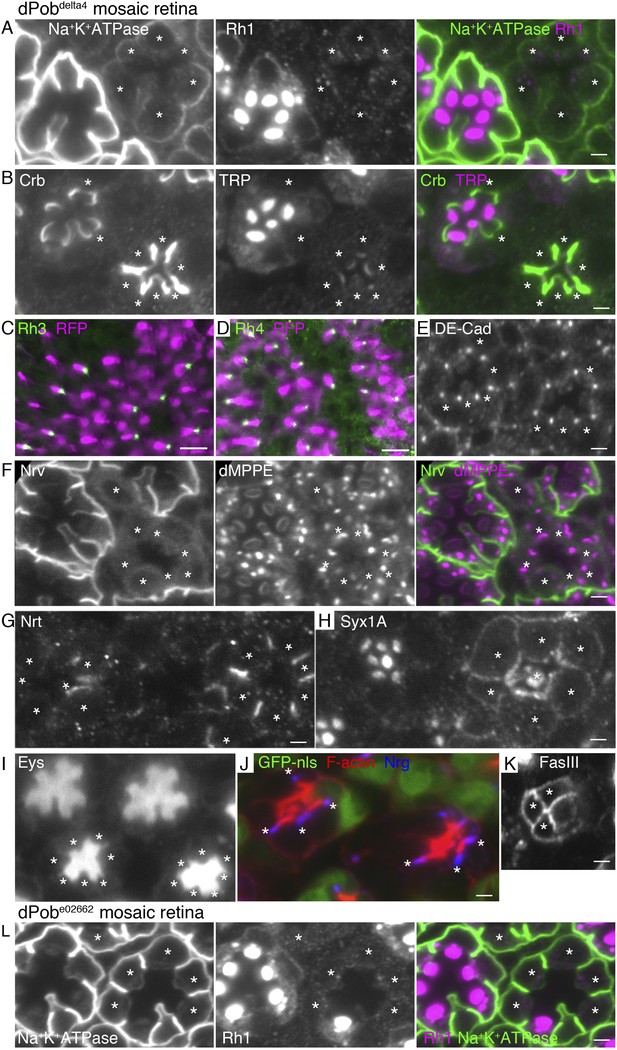
Essential role of dPob in the biosynthesis of multi-pass transmembrane proteins.
Immunostaining of a dPob∆4 mosaic retina (A–H) or a dPobe02662 mosaic retina (I). Asterisks show dPob homozygous photoreceptors. (A) Na+K+-ATPase, green; Rh1, magenta. (B) Crb, green; TRP1, magenta. (C, D) Rh3 (C) and Rh4 (D), green; RFP (wild-type cell marker), magenta. Although the boundary between dPob∆4 and wild-type cells is unclear, all green signals are attached to RFP-expressing cell bodies, indicating that mutant R7 cells do not express Rh3 (C) or Rh4 (D). (E) DE-Cad staining. (F) Nrv, the beta subunit of Na+K+-ATPase, green; dMPPE, magenta. (G) Nrt staining. (H) Syx1A staining. (I) Eys staining. (J) Nrg, blue; F-actin, red; GFP-nls (wild-type cell marker), green. (K) FasIII staining. (L) Na+K+-ATPase, green; Rh1, magenta. Scale bar: 2 μm (A, B), 10 μm (C, D), 2 μm (E–I).
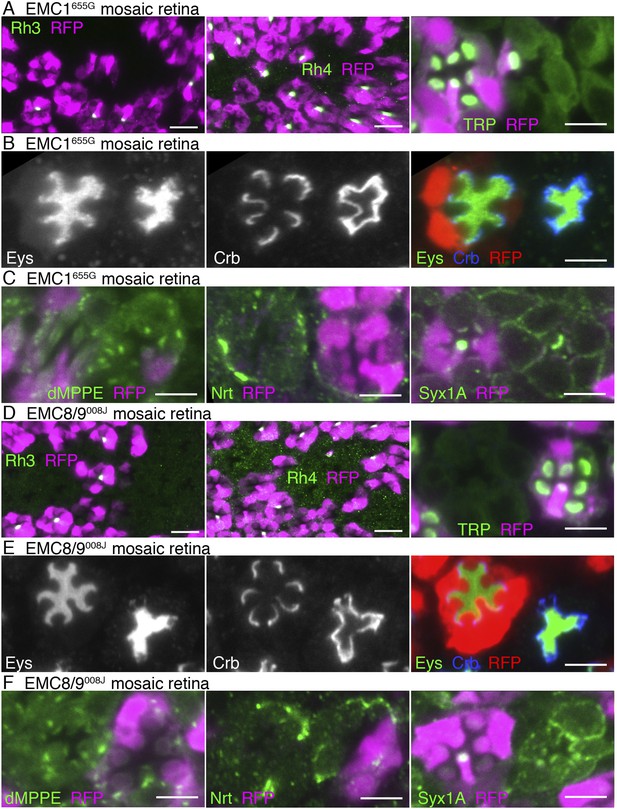
Essential role of EMC1 and EMC8/9 in the biosynthesis of multi-pass transmembrane proteins.
Immunostaining of a EMC1655G mosaic retina (A, B, C) or a EMC8/9008J mosaic retina (D, E, F). (A, D) Left: Rh3, middle: Rh4, right: TRP in green, RFP in magenda. (B, E) Eys in green, Crb in blue, and RFP, wild-type cell marker in red. (C, F) Left: dMPPE, middle: Nrt, right: Syx1A in green, RFP in magenda. Scale bar: 10 μm (left and middle in A, D), 5 μm (right in A, D), 5 μm (B, C, E, F).
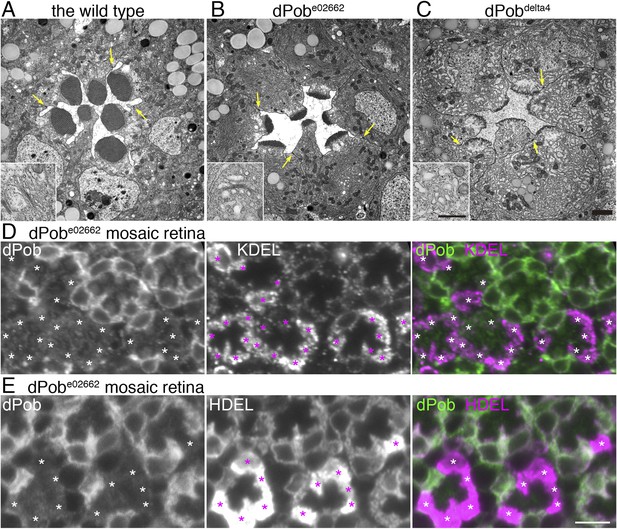
Endoplasmic reticulum membrane amplification and unfolded protein response (UPR) induced in dPob∆4 photoreceptor.
(A–C) Electron microscopy of late pupal photoreceptors: wild-type (A), dPobe02662 (B), and dPob∆4 photoreceptors (C). Arrow indicate adherens junctions. Insets show Golgi bodies. (D, E) Immunostaining of a dPobe02662 mosaic retina. dPob is shown in green and KDEL (D) or HDEL (E) are shown in magenta. Asterisks show dPob∆4 homozygous photoreceptors. Scale bar: 1 μm (A–C), 5 μm (D, E).
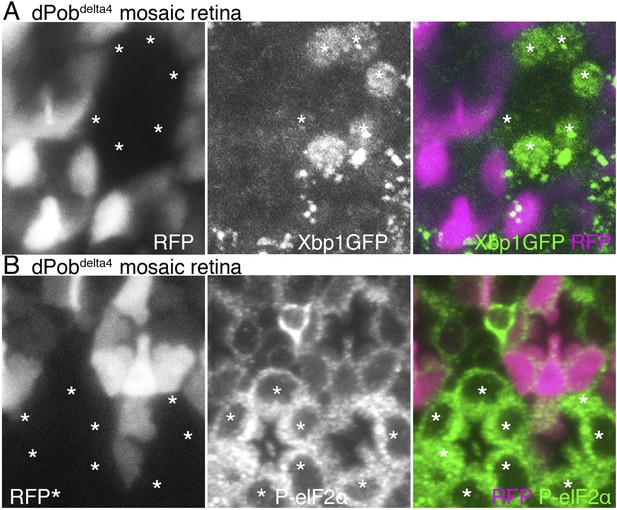
Unfolded protein response (UPR) induced in dPob∆4 photoreceptor.
(A) Projection image from the Z-series section with a 1 μm interval of dPob∆4 mosaic retina expressing RFP (magenta) as a wild-type cell marker and Xbp1:GFP as a UPR sensor. The Xbp1:GFP signal (green) is enhanced by immunostaining using anti-GFP antibody. Asterisks show dPob∆4 homozygous photoreceptors. (B) Immunostaining of a dPob∆4 mosaic retina expressing RFP (magenta) as a wild-type cell marker. Phosphorylated eukaryotic translation Initiation Factor 2α is shown in green. Asterisks show dPob∆4 homozygous photoreceptors.
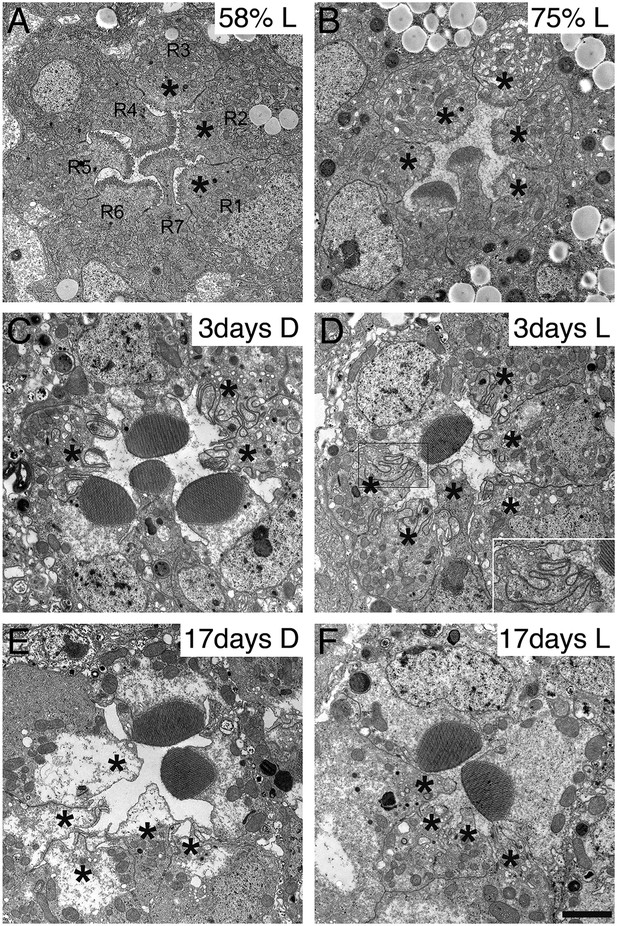
Development and degeneration of dPob∆4 photoreceptor rhabdomeres.
Electron microscopy of pupal and adult dPob∆4 mosaic retinas. Asterisks show dPob∆4 homozygous photoreceptors. Scale bar: 1 μm. (A, B) dPob∆4 mosaic ommatidia from 58% pupal development (A) and 73% pupal development (B) under constant light (L) condition. (C–F) dPob∆4 mosaic ommatidia from flies reared in complete darkness (D) (C, E) or under 12 hr light/12 hr dark conditions (D, F). Ommatidia from 3-day-old (C, D) and 17-day-old (E, F) flies. (D, inset) dPob∆4 R5 photoreceptor rhabdomere at higher magnification.





