Tinnitus and hyperacusis involve hyperactivity and enhanced connectivity in auditory-limbic-arousal-cerebellar network
Figures
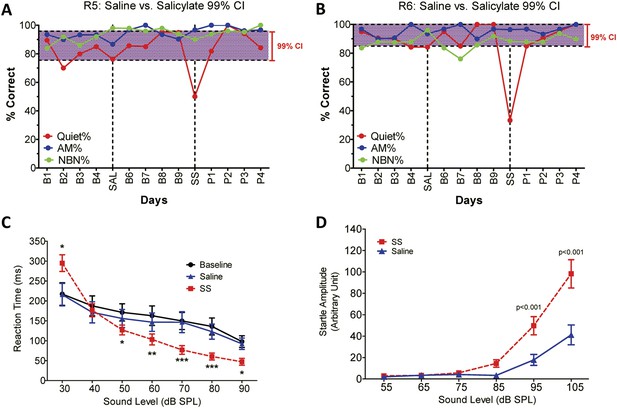
SS-induced tinnitus, hyperacusis, and startle reflex hyperactivity.
(A and B) 2AFC-tinnitus task for two representative rats during baseline days B1–B4, during Saline (SAL) treatment, during baseline days B6–B9, 2 hr post-sodium salicylate (SS), and days P1–P4 post-SS treatment. Percent correct performance shown for NBN, AM, and Quiet trials. Purple-shaded region is the 99% confidence interval for baseline measurements (B1–B4; B6–B9). (C) Mean (+SEM, n = 7) reaction time-intensity functions measured at baseline, after Saline-treatment and after SS-treatment. Reaction times during SS treatment were significantly longer than baseline at 30 dB SPL and significantly shorter than baseline at 50–90 dB SPL (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; and ***p < 0.001). (D) Mean (+SEM, n = 6) startle amplitude-intensify functions after treatment with Saline or SS. Startle amplitudes after SS treatment were significantly larger than after Saline at 95 and 105 dB SPL (p < 0.001).
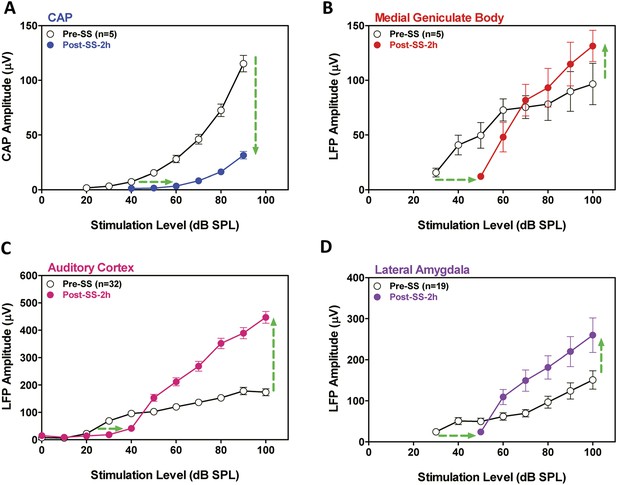
SS depresses cochlear potentials but enhances central auditory evoked responses.
Effects of 300 mg/kg SS on peripheral and central electrophysiological measures. (A) Mean (+SEM, n = 5) compound action potential (CAP) input/output function (average of 6, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 30, and 40 kHz; 10-ms tone burst) recorded from the round window pre- and 2 hr post-SS. Note, 20 dB threshold shift of the function to the right at low intensities (horizontal arrow) and large reduction in CAP amplitude at high intensities (down arrow). (B, C, D) Local field potential input/output functions (50-ms noise bursts) from medial geniculate body, auditory cortex, and lateral amygdala (AMY), respectively, before and 2 hr post-SS. Note, 20 dB threshold shift of the functions to the right at low intensities (horizontal arrows) and large increase in response amplitude (up arrow) at suprathreshold levels (>60 dB SPL).
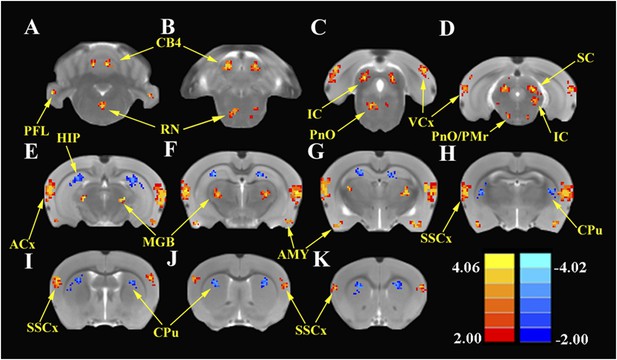
SS enhances and depresses amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations (ALFF) in specific CNS regions.
Panels A (most caudal) through K (most rostral) show MR images of rat brain. Significant differences in ALFF between the SS group vs Saline group 2 hr post-treatment. Thresholds set at a corrected p value of <0.001 determined by Monte Carlo simulation. CB4, lobules 4 of cerebellum; PFL, parafloccular lobe of cerebellum; RN, gigantocellular reticular nucleus; PnO, pontine reticular nucleus oral; PMr, paramedian raphe nucleus; VCx, visual cortex; IC, inferior colliculius; SC, superior colliculius; MGB, medial geniculate body; ACx, auditory cortex; HIP, hippocampus; AMY, amygdala; SSCx, somatosensory cortex; Cpu, caudate putamen. Color heat map scale in lower right shows corrected t-values ranging from +4.06 to −4.02.
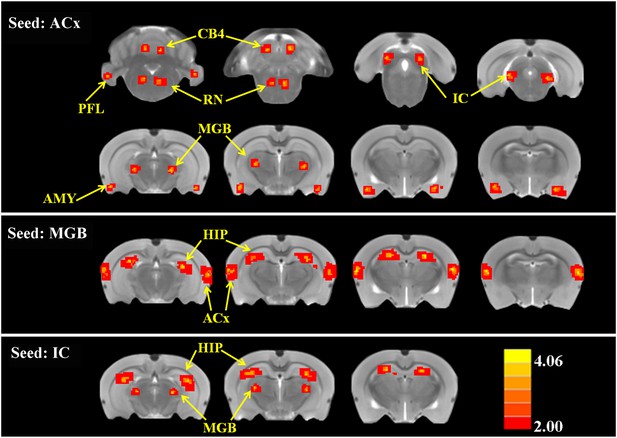
SS alters functional connectivity (FC) in specific brain resions.
ROI FC heat maps showing the regions of the brain where SS induced a statistically significant increase in FC with the ROI placed in the ACx (top row), MGB (middle row), or inferior colliculus (IC) (bottom row). Scale bar shown in lower right; corrected t-values ranged from +4.06 to −2.00. CB4, lobules 4 of cerebellum; PFL, parafloccular lobe of cerebellum; RN, gigantocellular reticular nucleus; IC, inferior colliculius; MGB, medial geniculate body; ACx, auditory cortex; HIP, hippocampus; AMY, amygdala.
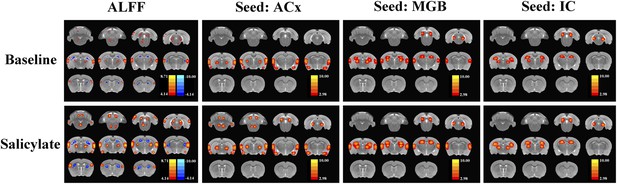
The ALFF and FC data (seeds: ACx, MGB, and IC) for baseline and after SS application separately.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.06576.008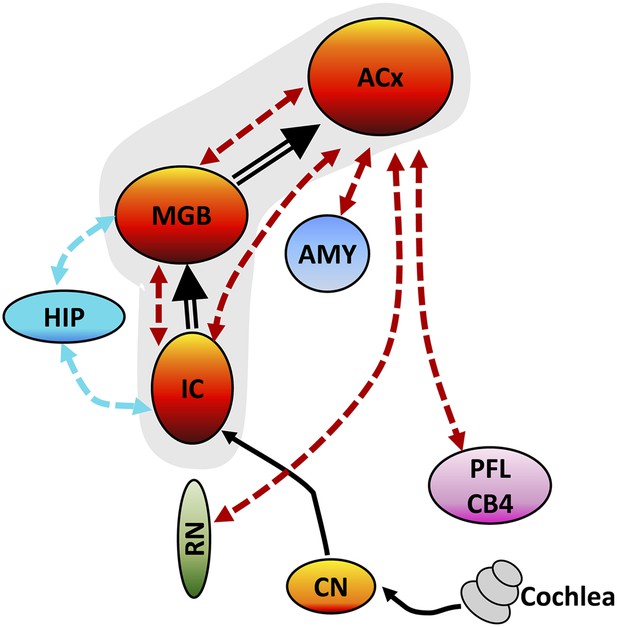
Tinnitus–hyperacusis network model.
Schematic showing some of the major centers in the auditory pathway and areas in the CNS showing increased FC with the auditory cortex (ACx). Black lines show the neural transmission path from the cochlea through the cochlear nucleus (CN), inferior colliculus (IC), medial geniculate body (MGB), and ACx; black double-line reflects SS-induced increases in ALFF and/or increased FC. SS increased ALFF response magnitudes and FC in a central auditory subnetwork (gray shaded area) comprised of the IC, MGB, and AC. The AC serves as a major hub with side branches to the amygdala (AMY), reticular nuclei (RN), and parafloccular lobe (PFL) and cerebellar lobules 4 (CB4); these side branch regions contribute to the emotional, motoric, and conscious awareness of tinnitus and/or hyperacusis. Enhanced activity in the MGB and IC combined with the increased FC of these auditory structures with the hippocampus (HIP) could facilitate tinnitus memory storage or retrieval or assign spatial location to phantom or real sounds.
Tables
SS-induced changes in amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations (ALFF); SS group vs Saline group; p < 0.001 corrected for multiple comparisons
| Brain region | Left | Right | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster size | t-value | Cluster size | t-value | |
| ALFF increased | ||||
| ACx | 167 | 3.812 | 178 | 3.746 |
| IC | 72 | 3.383 | 68 | 3.473 |
| MGB | 52 | 3.432 | 48 | 3.339 |
| SSCx | 37 | 3.383 | 40 | 3.402 |
| VCx | 32 | 3.342 | 39 | 3.312 |
| SC | 40 | 4.123 | 43 | 4.094 |
| AMY | 61 | 4.192 | 60 | 3.923 |
| RN/PnO | 35 | 3.249 | 28 | 3.290 |
| PnO/PMr | 12 | 3.498 | 10 | 3.313 |
| PFL | 38 | 3.349 | 37 | 3.292 |
| CB4 | 38 | 3.349 | 37 | 3.292 |
| ALFF decreased | ||||
| HIP | 108 | −4.087 | 92 | −4.002 |
| CPu | 72 | −3.772 | 71 | −3.741 |
-
Abbreviations: auditory cortex (ACx), inferior colliculus (IC), medial geniculate body (MGB), somatosensory cortex (SSCx), visual cortex (VCx), superior colliculi (SC), amygdala (AMY), gigantocellular reticular nucleus (RN), pontine reticular nucleus oral (PnO), paramedian raphe nucleus (PMr), parafloccular lobe of cerebellum (PFL), cerebellum lobule 4 (CB4), hippocampus (HIP), caudate-putamen (CPu), sodium salicylate (SS).
SS-induced increases in functional connectivity (FC); p < 0.001 corrected for multiple comparisons
| Seed region | Brain region | Left | Right | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster size | t-value | Cluster size | t-value | ||
| ACx | MGB | 62 | 3.900 | 70 | 3.859 |
| IC | 82 | 3.912 | 88 | 3.632 | |
| AMY | 67 | 3.897 | 68 | 3.839 | |
| RN | 52 | 3.983 | 48 | 3.902 | |
| PFL | 39 | 3.992 | 35 | 3.954 | |
| CB4 | 51 | 4.066 | 53 | 4.070 | |
| MGB | ACx | 195 | 4.074 | 210 | 4.084 |
| HIP | 162 | 4.032 | 178 | 4.109 | |
| IC | MGB | 72 | 4.098 | 60 | 4.013 |
| HIP | 140 | 4.064 | 131 | 3.904 | |
-
Abbreviations: medial geniculate body (MGB), inferior colliculus (IC), amygdala (AMY), reticular nucleus (RN), parafloccular lobe of cerebellum (PFL), cerebellum lobule 4 (CB4), auditory cortex (ACx), hippocampus (HIP), sodium salicylate (SS).





