Wild worm embryogenesis harbors ubiquitous polygenic modifier variation
Figures
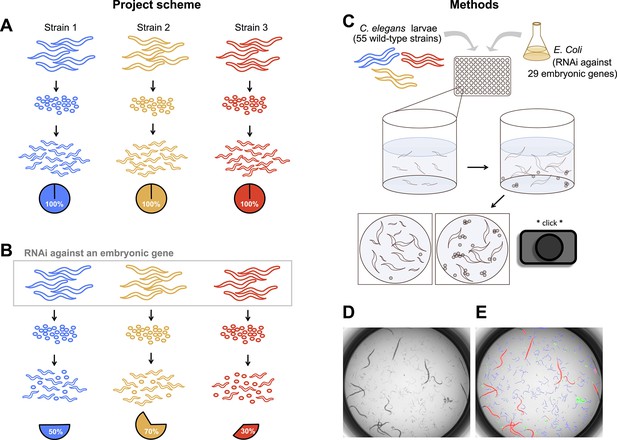
Experimental scheme and methods.
(A) Under ordinary conditions, wild-type Caenorhabditis elegans embryos hatch into larvae. (B) We targeted maternally-expressed genes by RNAi to induce embryonic lethality that varied in penetrance across strains. (C) L1 larvae in the parental generation were fed Escherichia coli expressing dsRNA against target genes, in 96-well plates in liquid media. 5 days later, wells were imaged to capture the penetrance of embryonic lethality in the next generation. (D, E) Raw images were evaluated using DevStaR (White et al., 2013), which identified objects as larvae (blue), dead embryos (green), or adults (red).
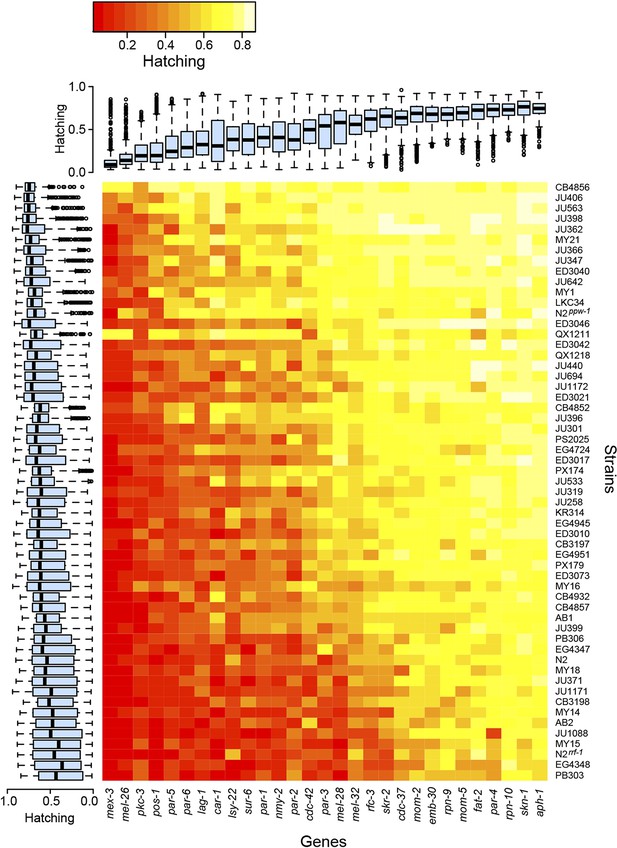
Variability in embryonic lethality.
Each cell represents the embryonic hatching success for a strain and targeted gene, averaged from at least eight replicate wells. The rows and columns are ordered by average hatching, and boxplots illustrate hatching phenotypes for each strain (across all targeted genes) and for each gene (across all strains).
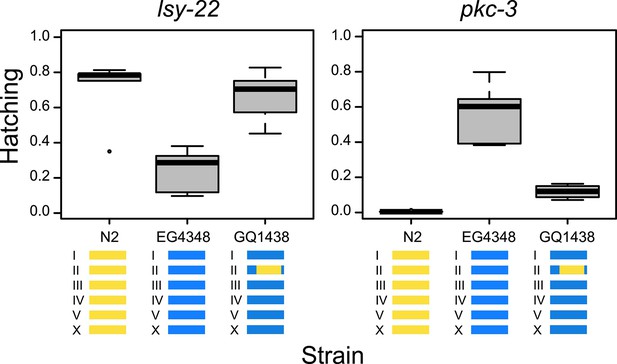
Tests for gene-specific modifiers.
Introgression of part of chromosome II from strain N2 (yellow) into strain EG4348 (blue) rescues the N2 phenotype on lsy-22 (F = 12.15, DF = 2, p = 0.001) and pkc-3 (F = 55.87, DF = 2, p < 0.001); genome-wide analyses found associations between this region and hatching phenotypes for both lsy-22 and pkc-3.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
This file provides source data for Figure 3, which reports hatching for three different strains targeted by RNAi against genes lsy-22 and pkc-3.
It provides counts of dead embryos (emb) or hatched larvae (larv) on individual agarose-media plates seeded with bacteria expressing dsRNA for the target genes. In the data file, the strain QG611 has the N2 genetic background.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.09178.008
Tables
Factorial analysis of deviance of lethality phenotypes for 55 wild-type strains in 29 perturbations of germline-expressed genes
| DF | Deviance | Resid. DF | Resid. Dev | F | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NULL | – | – | 17,855 | 2,201,873 | – | – |
| Strain | 54 | 338,618 | 17,801 | 1,863,255 | 334.697 | <10−15 |
| Targeted gene | 28 | 1,152,310 | 17,773 | 710,945 | 2196.584 | <10−15 |
| Adults per well | 1 | 35,318 | 17,772 | 675,627 | 1885.113 | <10−15 |
| Date | 1 | 2406 | 17,771 | 673,221 | 128.416 | <10−15 |
| Strain × gene | 1512 | 349,415 | 16,259 | 323,806 | 12.334 | <10−15 |
| Strain × adults per well | 54 | 6715 | 16,205 | 317,091 | 6.637 | <10−15 |
| Gene × adults per well | 28 | 7358 | 16,177 | 309,732 | 14.026 | <10−15 |
-
The table rows report information associated with each term in our statistical model (see ‘Materials and methods’), which represent distinct sources for the variation we observed in embryonic lethality. All terms were highly significant, including the strain-by-gene interaction, which represents variation attributable to cryptic genetic modifiers that act gene-specifically. This term and the strain term, which represents variation attributable to informational modifiers affecting germline RNAi, explain similar amounts of variation, and together account for 31% of the total deviance.
Genome heritability estimates for CGV phenotypes associated with 29 targeted genes
| Targeted gene | Heritability estimate | p-value |
|---|---|---|
| aph-1 | 0.6747 | 0.16 |
| car-1 | 0.9149 | 0.02 |
| cdc-37 | 0.7308 | 0.11 |
| cdc-42 | 0.3639 | 0.29 |
| emb-30 | 0.0000 | 0.46 |
| fat-2 | 0.3548 | 0.32 |
| lag-1 | 0.9075 | 0.01 |
| lsy-22 | 0.1270 | 0.43 |
| mel-26 | 0.8245 | 0.05 |
| mel-28 | 0.8410 | 0.04 |
| mel-32 | 0.0000 | 0.47 |
| mex-3 | 0.0000 | 0.76 |
| mom-2 | 0.7485 | 0.09 |
| mom-5 | 0.0000 | 0.46 |
| nmy-2 | 0.4841 | 0.26 |
| par-1 | 0.7871 | 0.08 |
| par-2 | 0.9719 | 0.01 |
| par-3 | 0.0000 | 0.77 |
| par-4 | 0.9032 | 0.07 |
| par-5 | 0.6640 | 0.15 |
| par-6 | 0.9258 | 0.01 |
| pkc-3 | 0.8136 | 0.06 |
| pos-1 | 0.7307 | 0.10 |
| rfc-3 | 0.6958 | 0.13 |
| rpn-9 | 0.8715 | 0.02 |
| rpn-10 | 0.8397 | 0.05 |
| skn-1 | 0.8599 | 0.03 |
| skr-2 | 0.8961 | 0.02 |
| sur-6 | 0.0000 | 0.47 |
Factorial analysis of deviance of strain N2 lethality on targeted gene mom-2
| Df | Deviance | Resid. Df | Resid. Dev | F | Pr (>F) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NULL | – | – | 284 | 9191.7 | – | – |
| Date | 1 | 1060.26 | 283 | 8131.4 | 38.397 | 2.0 × 10—09 |
| Bacterial source | 2 | 172.47 | 281 | 7958.9 | 3.123 | 0.04556 |
Factorial analysis of deviance of strain N2 lethality phenotypes across 29 targeted genes
| Df | Deviance | Resid. Df | Resid. Dev | F | Pr (>F) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NULL | – | – | 2254 | 280,706 | – | – |
| Silenced gene | 28 | 221,081 | 2226 | 59,624 | 378.3275 | <2 × 10—16 |
| Date | 1 | 6090 | 2225 | 53,534 | 291.8186 | <2 × 10—16 |
| Adults per well | 1 | 249 | 2224 | 53,285 | 11.9248 | 0.00056 |
| Silenced gene × date | 28 | 5265 | 2196 | 48,020 | 9.0099 | <2 × 10−16 |
| Silenced gene × adults per well | 28 | 2423 | 2168 | 45,597 | 4.1467 | 2.7 × 10—12 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
This Excel file reports correlations for strain-by-gene interaction coefficients for each pairwise combination of targeted genes.
Above the diagonal are the estimated correlations; below the diagonal are the correlation p-values; in green are pairs of genes with interactions reported in the literature.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.09178.011
-
Supplementary file 2
This extended table reports genome-wide SNPs associated with hatching phenotypes with p-values <0.0001 and <1.64 × 10−5 (*).
The LD column indicates clusters of SNPs in strong disequilibrium with each other (R2 > 0.90) across our test strains. A source data file has been deposited at Dryad under doi:10.5061/dryad.d5j06.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.09178.012





