Expression of a single inhibitory member of the Ly49 receptor family is sufficient to license NK cells for effector functions
Figures
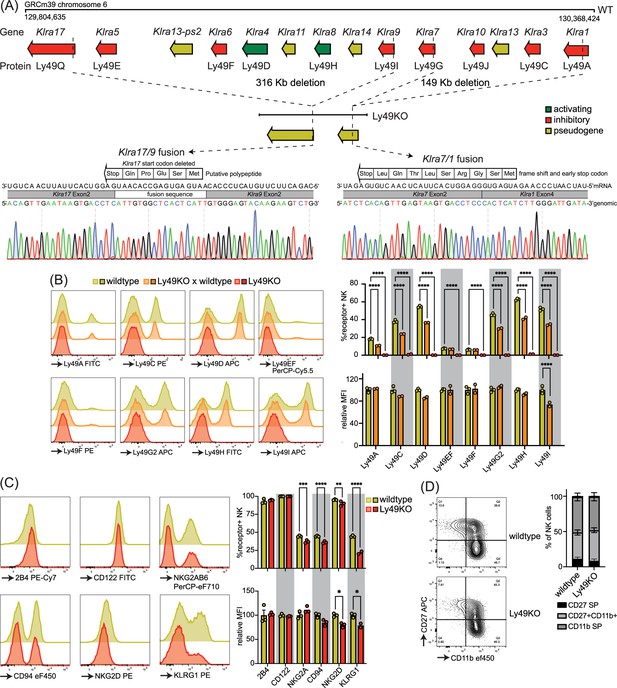
Mice generated to lack all natural killer (NK)-related Ly49 molecules using CRISPR have NK cells that display alterations in select surface molecules.
(A) Genetic map of the Ly49 family encoded by the Klra gene locus of wildtype C57BL/6 and Ly49KO mice with Sanger sequencing of the fusion sequences in the Ly49KO mice. (B) Ly49 receptor expression on splenic NK cells of the indicated genotype with 2-3 mice per group. (C) Surface receptor expression on splenic NK cells from indicated genotype with 3 mice per group. (D) Expression of the maturation markers CD27 and CD11b on splenic NK cells from indicated genotype with 3 mice per group. MFI, median fluorescent intensity. Statistics were calculated using two-way ANOVA with corrections for multiple testing. Error bars indicate SEM; ns, not significant; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, and ****p<0.0001.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Ly49KO Sanger sequencing files.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/100218/elife-100218-fig1-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 1—source data 2
Receptor expression profile raw data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/100218/elife-100218-fig1-data2-v1.xlsx
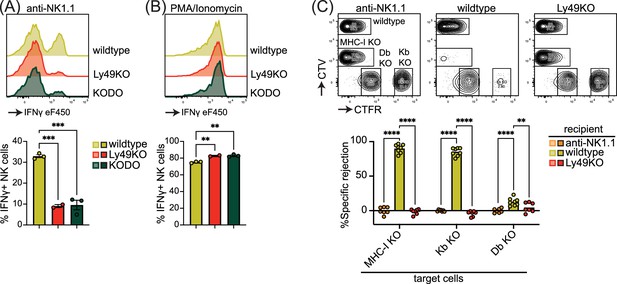
Natural killer (NK) cell licensing and rejection of MHC-I-deficient target cells are defective in Ly49KO mice.
Splenocytes from the indicated mice were stimulated with plate-bound anti-NK1.1 (A) or phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)/ionomycin (B) and IFNγ production by NKG2A- NK cells and analyzed by flow cytometry with 2-3 mice per group. (C) In vivo cytotoxicity assay against H-2Kb, H-2Db, and full MHC-I -deficient targets. Splenocytes from WT, H-2Kb, H-2Db, and MHC-I-deficient mice were differentially labeled with CellTrace Violet (CTV) and CellTrace Far Red (CTFR) as indicated. Mixture of labeled target cells was injected i.v. into wildtype, Ly49KO, and anti-NK1.1-depleted mice with 6-8 mice per group. Target cells were analyzed in the spleens by flow cytometry 2 days after challenge. KODO, H-2Kb × H-2Db knock out; MHC-I KO, KODO × B2m knockout; MFI, median fluorescent intensity. Statistics were calculated using one-way (A and B) and two-way (C) ANOVA with corrections for multiple testing. Error bars indicate SEM; ns, not significant; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, and ****p<0.0001.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
IFNγ production and in vivo killing assay raw data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/100218/elife-100218-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
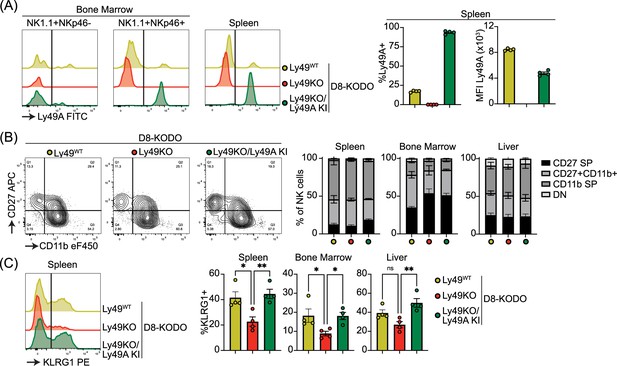
Ly49A is efficiently expressed in Ncr1-Ly49A knock-in mice and rescues KLRG1 expression in natural killer (NK) cells.
Flow cytometric analysis of NK cells in D8-KODO, Ly49KO D8-KODO, and Ly49KO/Ly49A KI D8-KODO mice (A) Ly49A expression in NKp46+ and NKp46- NK1.1+ NK cells in bone marrow and spleen of the indicated mice. (B) Expression of the maturation markers CD27 and CD11b on NK cells in the spleen, bone marrow, and liver of indicated mice. (C) KLRG1 expression by NK cells in the spleen, bone marrow, and liver of indicated mice. MFI, median fluorescent intensity. All data is from 4 mice per group. Statistics were calculated using one-way ANOVA with corrections for multiple testing. Error bars indicate SEM; ns, not significant; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, and ****p<0.0001.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Receptor expression profile raw data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/100218/elife-100218-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
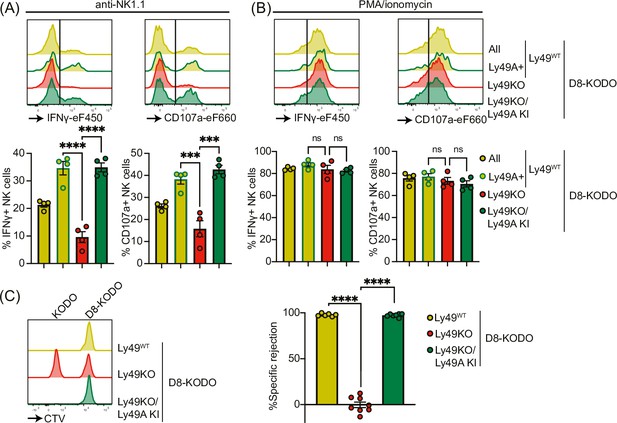
Expression of Ly49A in isolation is sufficient for natural killer (NK) cell licensing and missing-self rejection.
Splenocytes from the indicated mice were stimulated with plate-bound anti-NK1.1 (A) or phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)/ionomycin (B) with 4 mice per group. IFNγ production and degranulation (CD107a) by NKG2A- NK cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. (C) Splenocytes from D8-KODO and KODO mice were differentially labeled with CTV as indicated. A mixture of labeled target cells was injected i.v. into D8-KODO, Ly49KO D8-KODO, and Ly49KO/Ly49A KI D8-KODO mice with 6-8 mice per group. Specific rejection of target cells was analyzed in spleens by flow cytometry 2 days after challenge. Statistics were calculated using one-way ANOVA with corrections for multiple testing. Error bars indicate SEM; ns, not significant; ***p<0.001 and ****p<0.0001.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
IFNγ production, degranulation, and in vivo killing assay raw data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/100218/elife-100218-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus) | C57BL/6, wildtype | Charles River | Stock# 556 | |
| Strain, strain background (M. musculus) | H-2Kb x H-2Db double-deficient | Taconic Farms | Stock# 4215 | |
| Strain, strain background (M. musculus) | H-2Dd transgenic mouse | Marguiles | Bieberich et al., 1986 | |
| Strain, strain background (M. musculus) | ΔLy49-1 | Previously generated by authors | Parikh et al., 2020 | |
| Strain, strain background (M. musculus) | Ly49A KI | Previously generated by authors | Parikh et al., 2020 | |
| Strain, strain background (M. musculus) | Ly49 KO | This paper | Figure 1A | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Klra17 gRNA | This paper | gRNA | 5′-ACCCATGATGAGTGAGCAGG-3′ |
| Sequence-based reagent | Klra9 gRNA | This paper | gRNA | 5′-TGAGACTTCATAAGTCTTCAAGG-3′ |
| Sequence-based reagent | Klra17-Rv | This paper | Sequencing primer | 5′-GCCCATCTGGCTTCCTTTCT-3′ |
| Sequence-based reagent | Klra9-Rv | This paper | Sequencing primer | 5′-CAAGCCCCGATGAGATGGAT-3′ |
| Sequence-based reagent | Klra17-Fw | This paper | Sequencing primer | 5′-GGATCAGTCCATGTCAGGGTT-3′ |
| Sequence-based reagent | Klra7-Rv | This paper | Sequencing primer | 5′-AACCAAGCCCCAATGAGATC-3′ |
| Sequence-based reagent | Klra1-Fw | This paper | Sequencing primer | 5′-TGGGTCAGTCCATGTCAGTG-3′ |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-human/mouse CD107a eF660 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 50-1071-82 | 1:1000 dilution |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse/pig CD117 APC | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 17-1171-81 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse CD11b eF450 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 48-0112-82 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse CD122 FITC | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 11-1222-82 | 1:50 dilution |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse CD19 APC-eF780 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 47-0193-82 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse CD244.2 (2B4) PE-Cy7 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 25-2441-80 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Armenian hamster monoclonal anti-human/mouse/rat CD27 APC | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 17-0271-82 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse CD4 APC-eF780 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 47-0042-82 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse CD49b PE | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 12-5971-82 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse CD8 APC-eF780 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 47-0081-82 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse CD94 eF450 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 48-0941-82 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse IFN-gamma eF450 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 48-7311-82 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Syrian hamster monoclonal anti-mouse/human KLRG1 biotin | BioLegend | Catalog# 138406 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Syrian hamster monoclonal anti-mouse/human KLRG1 PE-Cy7 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 25-5893-82 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse Ly49A FITC | BioLegend | Catalog# 116805 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-mouse Ly49C PE | Leinco | Catalog# L312 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse Ly49D APC | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 17-5782-82 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse Ly49E/F PerCP | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 46-5848-82 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-mouse Ly49F PE | BD Biosciences | Catalog# 550987 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse Ly49G2 FITC | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 11-5781-85 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-mouse Ly49H APC | BioLegend | Catalog# 144710 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-mouse Ly49I Biotin | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# MA5-28667 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-mouse NK1.1 BV650 | BioLegend | Catalog# 108736 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse NKG2A/C/E FITC | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 11-5896-85 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse NKG2A PerCP | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 46-5897-82 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse NKG2D PE | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 12-5882-82 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse NKp46 PE-Cy7 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 25-3351-82 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse NKp46 PerCP | ThermoFisher Scientific | Catalog# 46-3351-82 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Armenian hamster monoclonal anti-mouse TCRB APC-eF780 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 47-5961-82 | 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody | Fc-Block | 2.4g2 hybridoma | In-house produced hybridoma supernatant | Undiluted |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-mouse NK1.1 for in vivo use | Leinco | N268 | 100 ug/mouse; 1–4 ug/ml for in vitro stimulation |
| Commercial assay or kit | CellTrace CFSE Cell Proliferation Kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# C34554 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | CellTrace Far Red Cell Proliferation Kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# C34564 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | CellTrace Violet Cell Proliferation Kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# C34557 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Cytofix/Cytoperm Fixation/Permeabilization Kit | BD Biosciences | Catalog# 554714 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Ionomycin calcium salt | MilliporeSigma | Catalog# IO634-5MG | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Monensin | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 00-4505-51 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | PMA (phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate) | MilliporeSigma | Catalog# P1585-1MG | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Sterptavidin-APC | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 17-4317-82 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Sterptavidin-PE | BioLegend | Catalog# 405204 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | eBioscience Fixable Viability Dye eFluor 506 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog# 65-0866 | |
| Software, algorithm | PRISM 10 | GraphPad | RRID:SCR_002798 | https://www.graphpad.com |
| Software, algorithm | FlowJo 10 | Treestar | RRID:SCR_008520 | https://www.flowjo.com/ |





