Mixed representations of choice direction and outcome by GABA/glutamate cotransmitting neurons in the entopeduncular nucleus
Figures
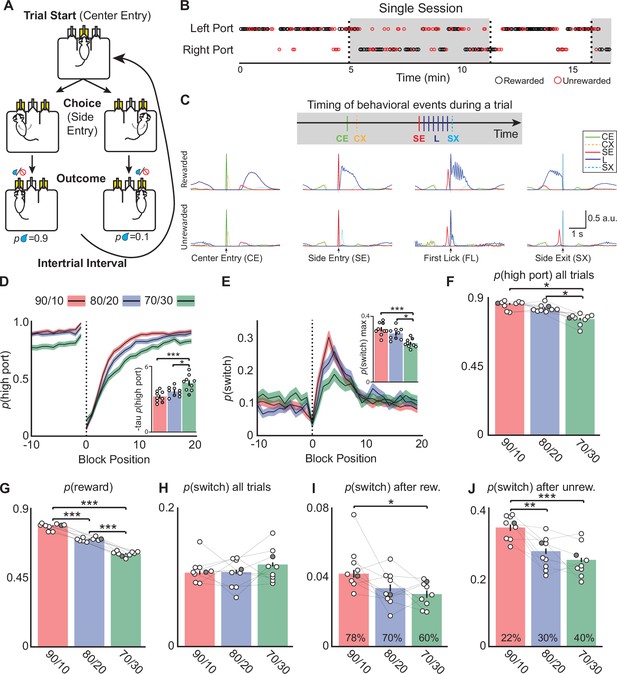
Mice alter choices to changing reward probabilities in a probabilistic switching task.
(A) Illustration of the animal movements and epochs (Trial Start, Choice, and Evaluation) of a single trial in the probabilistic two-port choice task. Yellow color of port(s) indicates when LED is active during a trial. (B) A sample of a behavioral session showing periods when the highly rewarded port is on the left (white) and when it switches to the right (gray). The reward probabilities switch (dotted vertical lines, ‘block transition’) once 50 rewards are gained by the animal. Rewarded trials are represented by black circles and unrewarded trials are red circles, reward probabilities are 70/30. (C) Probability distributions of different behavioral events during rewarded (top) and unrewarded (bottom) trials to illustrate the timing of different events within a trial (one session ~500 trials, 90/10 rew. prob). CE = Center Entry, CX = Center Exit, SE = Side Entry, FL = First Lick, SX = Side Exit. (D) The probability of choosing the highly rewarded port (phigh port) around a block transition (dotted vertical line) for different reward probabilities (black line = mean, shaded area = SEM). (Inset) Bar plot showing taup(high port) (time constant) calculated from an exponential fit to the first 20 trials following a block transition for each animal (circles) (bar = mean, error bar = SEM) in the different reward probabilities. The darkened circle represents the same animal across reward probabilities (see D-J) (one-way ANOVA df = 24, p-values: 90/10 vs 80/20=0.22, 90/10 vs 70/30=0.001, 80/20 vs 70/30=0.02). (E) The probability of choosing different side ports on consecutive trials (p switch) around a block transition (dotted vertical line) for different reward probabilities (black line = mean, shaded area = SEM). (Inset) Bar plot showing the maximum p(switch) in the 20 trials that follow a block transition for each animal (circles) (bar = mean, error bar = SEM) in the different reward probabilities (one-way ANOVA df = 24, p-values: 90/10 vs 80/20=0.23, 90/10 vs 70/30<0.001, 80/20 vs 70/30=0.003). (F) The probability of choosing the highly rewarded port on all trials across reward probabilities (bar = mean, error bar = SEM) (one-way ANOVA df = 24, p-values: 90/10 vs 80/20=0.25, 90/10 vs 70/30<0.001, 80/20 vs 70/30<0.001). (G) The probability that a trial results in a reward across reward probabilities (bar = mean, error bar = SEM) (one-way ANOVA df = 24, p-values: 90/10 vs 80/20<0.001, 90/10 vs 70/30<0.001, 80/20 vs 70/30<0.001). (H) p(switch) across all trials for different reward probabilities (bar = mean, error bar = SEM). (I) p(switch) for trials following a rewarded trial for different reward probabilities, percentages in bars represent the proportion of rewarded trials for each condition, also shown in (G) (bar = mean, error bar = SEM) (one-way ANOVA df = 24, p-values: 90/10 vs 80/20=0.06, 90/10 vs 70/30=0.01, 80/20 vs 70/30=0.74). (J) p(switch) for trials following an unrewarded trial for different reward probabilities, percentages in bars represent the proportion of unrewarded trials for each condition (bar = mean, error bar = SEM) (one-way ANOVA df = 24, p-values: 90/10 vs 80/20=0.002, 90/10 vs 70/30<0.001, 80/20 vs 70/30=0.55). For (D–J) n=9 male mice, 8–10 sessions/mouse/rew. prob, ~550 trials/session, total # of trials per condition are: 90/10: 44,512, 80/20: 42,302, 70/30: 43,796.
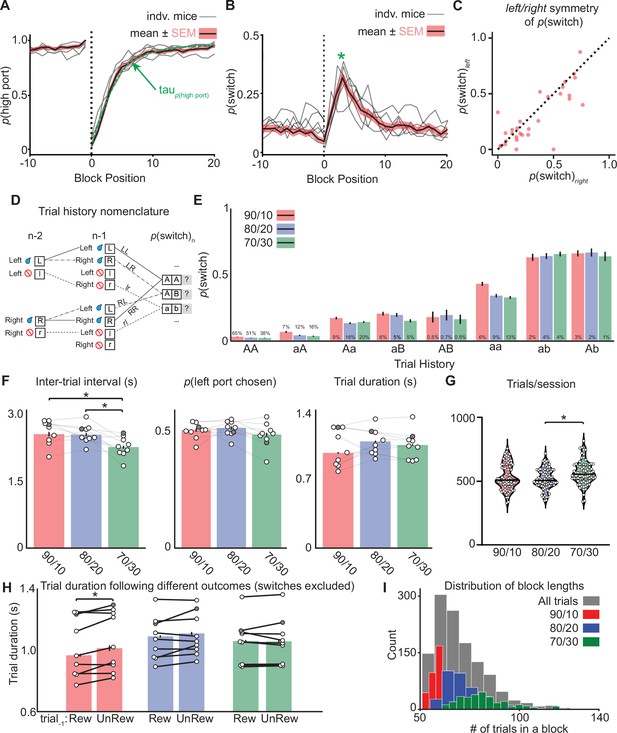
Behavioral data showing individual animals.
p(switch) across different trial histories, and additional behavioral metrics. (A) The probability of choosing the highly rewarded port p(high port, 90/10 rew. prob.) around a block transition (dotted vertical line) for individual mice (gray lines) and mean (black line = mean, shaded area = SEM). (B) The probability of choosing different side ports on consecutive trials (pswitch) around a block transition (dotted vertical line) for individual mice (gray lines) and mean (black line = mean, shaded area = SEM). (C) P(switch) for left and right choices for an individual animal. Each dot represents a trial type (n=30 trial types) with a different history of choices and rewards for three trials prior. (D) Nomenclature for describing trial types with different reward histories (capital vs lowercase) and choice directions (right vs left). As animals show roughly symmetric p(switch) for left and right choices See (C) those trial types have been collapsed. (E) p(switch) for trial types segregated by reward history and choice direction across different reward probabilities, percentages above bars refer to the percentage of trials in each category for the different reward probabilities (bar = mean, error bar = 95% CI). (F) (left to right) Inter-trial interval, choice bias, and trial duration across different reward probabilities (bar = mean, error bar = 95% CI). The darkened circle represents the same animal across reward probabilities (see F-H) (one-way ANOVA df = 24, p-values: 90/10 vs 80/20=0.94, 90/10 vs 70/30=0.02, 80/20 vs 70/30=0.04). (G) Violin plot showing the distribution of the number of trials completed in a ~40 min session for different reward probabilities (dots = individual session, horizontal bar = median). (H) Trial duration following previously rewarded or unrewarded trials across different reward probabilities for ‘repeat’ choices only (bar = mean, error bar = 95% CI) (paired t-test df = 8, 90/10 p=0.013). (I) Histogram showing the distribution of block lengths (number of trials prior to a block transition) for different reward probabilities.
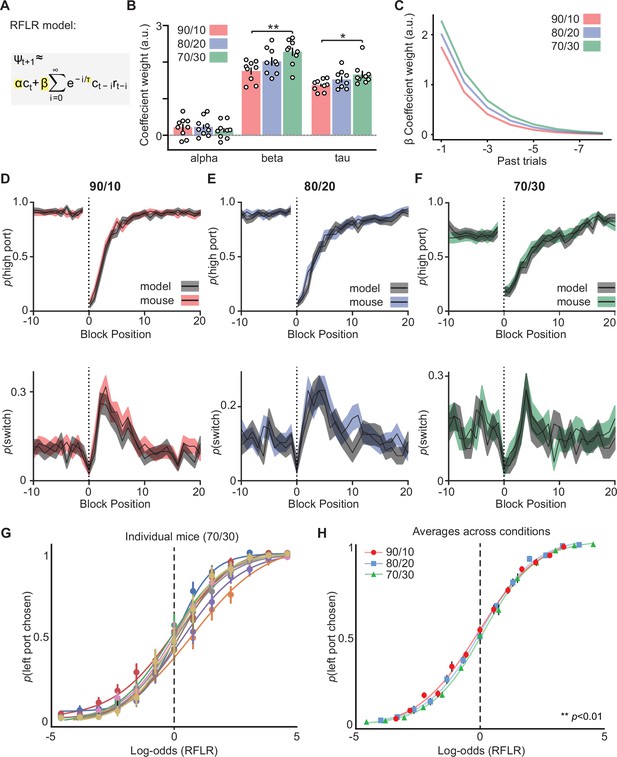
Behavioral modeling using a recursively formulated logistic regression (RFLR).
(A) The RFLR model, which calculates the log odds of the mouse’s next choice (Ψt+1) given its most recent choice (ct) and a series of prior choices and rewards. ct represents choice, rt represents reward outcome on trial (t), relative to current trial i=0. α (alpha) is the weight of the most recent choice, β (beta) is the weight on the choice and reward outcome which decays exponentially across trials at a rate of τ (tau). (B) Summary of RFLR model coefficients across reward probabilities coefficients highlighted in yellow in (A), each dot represents an individual mouse (bar = mean, error bar = SEM, negative log-likelihood of fits were equivalent across reward probabilities; 90/10 = –0.25 SD = 0.03; 80/20 = –0.24 SD = 0.03; 70/30 = −0.25 SD = 0.02) (one-way ANOVA df = 24, alpha p-values: 90/10 vs 80/20=0.99, 90/10 vs 70/30=0.76, 80/20 vs 70/30=0.69, beta p-values: 90/10 vs 80/20=0.22, 90/10 vs 70/30=0.006, 80/20 vs 70/30=0.23, tau p-values: 90/10 vs 80/20=0.36, 90/10 vs 70/30=0.04, 80/20 vs 70/30=0.47). (C) Exponential decay of choice and reward evidence (beta) for 8 trials in the past. Exponential fits made from beta and tau coefficients observed for different reward probabilities and shown in (B). (D) (top) The probability of choosing the highly rewarded port p(high port, 90/10 rew. prob.) around a block transition (dotted vertical line). RFLR model predictions (gray) trained on 70% of the 90/10 trials and compared to the remaining 30% of trials (red), (black line = mean, shaded area = SEM). (Bottom) The probability of choosing different side ports on consecutive trials (p switch) around a block transition (dotted vertical line). RFLR model predictions (graey) trained on 70% of the 90/10 trials and compared to the remaining 30% of trials (red), (black line = mean, shaded area = SEM). (E) (top) The probability of choosing the highly rewarded port (p high port, 80/20 rew. prob.) around a block transition (dotted vertical line). RFLR model predictions (gray) trained on 70% of the 80/20 trials and compared to the remaining 30% of trials (blue), (black line = mean, shaded area = SEM). (Bottom) The probability of choosing different side ports on consecutive trials (p switch) around a block transition (dotted vertical line). RFLR model predictions (gray) trained on 70% of the 80/20 trials and compared to the remaining 30% of trials (blue), (black line = mean, shaded area = SEM). (F) (top) The probability of choosing the highly rewarded port (p high port, 70/30 rew. prob.) around a block transition (dotted vertical line). RFLR model predictions (gray) trained on 70% of the 70/30 trials and compared to the remaining 30% of trials (green), (black line = mean, shaded area = SEM). (Bottom) The probability of choosing different side ports on consecutive trials (p switch) around a block transition (dotted vertical line). RFLR model predictions (gray) trained on 70% of the 70/30 trials and compared to the remaining 30% of trials (green), (black line = mean, shaded area = SEM). (G) The probability that an animal chooses the left port (p left port chosen) compared to log-odds (Ψt+1) of the animal’s next choice calculated using the RFLR model trained on data from the 70/30 reward probability (n=9 mice). Psychometric curves for individual animals were then fit with a logistic function, each color represents a different animal. (H) The probability that an animal chooses the left port (p left port chosen) compared to log-odds (Ψt+1) of the animal’s next choice calculated from the RFLR model for different reward probabilities. Psychometric curves for different reward probabilities were then fit with a logistic function (dots = mean, error bars = SEM, n=9 mice for each group, F-test; DF = 8, p=0.0095).
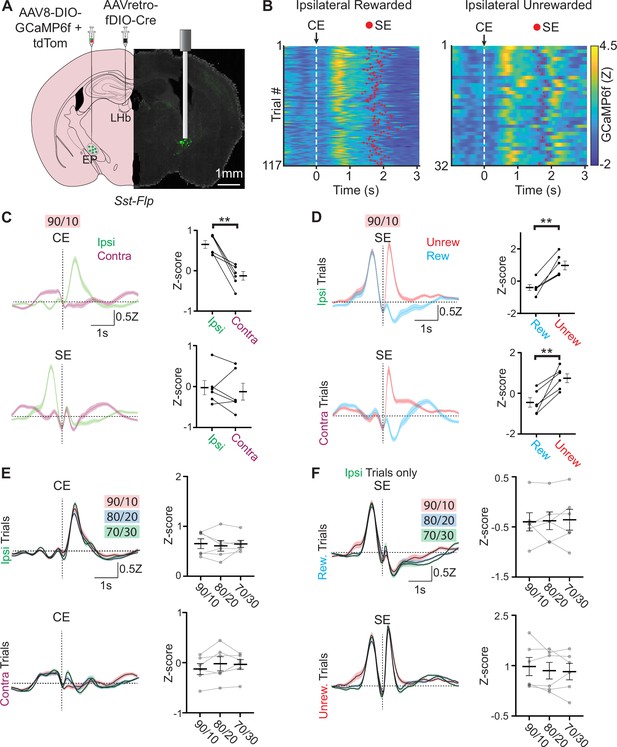
Neural activity in EPSst+ neurons encodes both choice and value.
(A) Viral injection location for specific infection of EPSst+ neurons with GCaMP6f in a Sst-Flp mouse line and fiber implant location for photometry recording. (B) Fiber photometry recording of EPSst+ neurons for individual trials during a behavioral session. Trials are aligned to center port entry (CE) and red dots indicated side port entry (SE). Only trials to the ipsilateral side (relative to the photometry recording) are shown and are divided by rewarded (left) and unrewarded (right) trials. (C) Averaged (± SEM) photometry signals across all mice aligned to center-port entry (CE, top) or side-port entry (SE, bottom) grouped by ipsilateral (green) and contralateral (magenta) choice, dotted horizontal line represents z-score equal to zero (all sessions are at 90/10 reward probability, n=6 male mice, 49 sessions, 20,355 trials). (right) Points represent the mean z-scored fluorescence per animal for the 500ms period immediately following the behavioral event, bars represent mean across animals ± SEM (all sessions are at 90/10 reward probability, n=6 male mice, 49 sessions, 20,355 trials) (top; paired t-test DF = 5, p=0.003). (D) Averaged photometry (± SEM) signals across all mice aligned to side port entry (SE) grouped by rewarded (blue) or unrewarded (red) outcomes and divided by ipsilateral choice (top) or contralateral choice (bottom). (right) Points represent the mean z-scored fluorescence per animal for the 500ms period immediately following the behavioral event, bars represent mean across animals ± SEM (all sessions are at 90/10 reward probability, n=6 male mice, 49 sessions, 20,355 trials) (top; paired t-test DF = 5, p=0.003, bottom paired t-test DF = 5, p=0.006). (E) Averaged (± SEM) photometry signals across different reward probabilities aligned to center port entry (CE) and divided by ipsilateral (top) and contralateral (bottom) choice. (right) Points represent the mean z-scored fluorescence per animal for the 500 ms period immediately following the behavioral event, bars represent mean across animals ± SEM (90/10: n=6 male mice, 49 sessions, 20,355 trials, 80/20: n=6 male mice, 54 sessions, 27,433 trials, 70/30: n=6 male mice, 49 sessions, 27,174 trials). (F) Averaged (± SEM) photometry signals across different reward probabilities aligned to side port entry (SE) and divided by rewarded (top) and unrewarded (bottom) outcomes. (right) Points represent the mean z-scored fluorescence per animal for the 500 ms period immediately following the behavioral event, bars represent mean across animals ± SEM (90/10: n=6 male mice, 49 sessions, 20,355 trials, 80/20: n=6 male mice, 54 sessions, 27,433 trials, 70/30: n=6 male mice, 49 sessions, 27,174 trials).
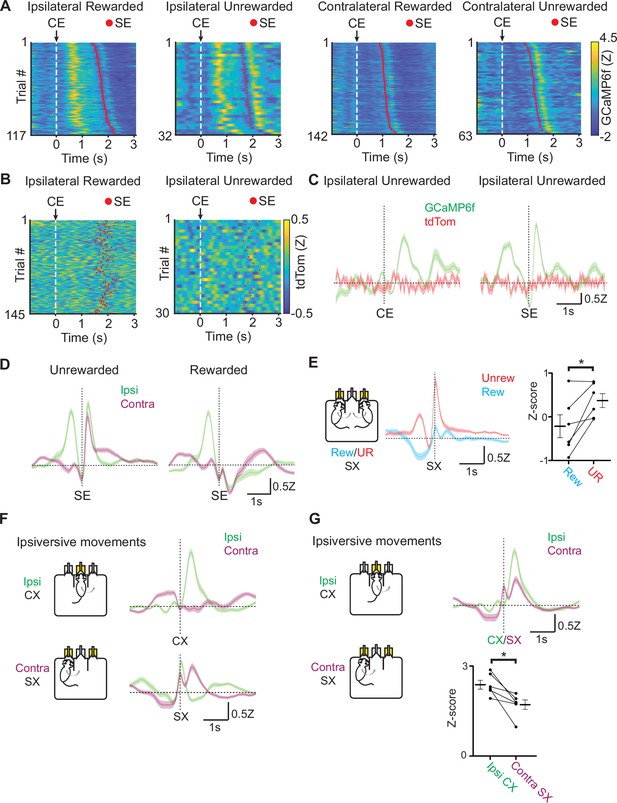
Alignment and sorting of photometry signals from EPSst+ neurons to different behavioral events.
(A) Fiber photometry recording of EPSst+ neurons for individual trials during a behavioral session. Trials are aligned to center port entry (CE) and red dots indicated side port entry (SE). Trials are sorted by the time elapsed between CE and SE. Trials to the ipsilateral and contralateral side (relative to the photometry recording) are shown and are divided by rewarded and unrewarded trials. (B) Control fiber photometry recording of EPSst+ neurons expressing static fluorophore tdTomato for individual trials during a behavioral session. Trials are aligned to center port entry (CE) and red dots indicate side port entry (SE). Only trials to the ipsilateral side (relative to the photometry recording) are shown and are divided by rewarded (left) and unrewarded (right) trials. (C) Averaged (± SEM) photometry signals across one mouse aligned to center port entry (CE, left) or side port entry (SE, right) for ipsilateral unrewarded trials. Traces show mean z-scored fluorescence intensity changes of simultaneously recorded from GCamp6f (green) and control fluorophore tdTomato (red). (D) Averaged (± SEM) photometry signals across all mice aligned to side port entry (SE), divided by unrewarded (left) or rewarded (right) outcome and grouped by ipsilateral (green) and contralateral (magenta) choice (90/10 reward probability, n=6 mice, 49 sessions, 20,355 trials). (E) Averaged (± SEM) photometry signals across all mice aligned to side port exit (SX) grouped by rewarded (blue) or unrewarded (red) outcomes. (right) Points represent the mean z-scored fluorescence per animal for the 500 ms period immediately prior to the behavioral event, bars represent mean across animals ± SEM (all sessions are at 90/10 reward probability, n=6 mice, 49 sessions, 20,355 trials) (paired t-test DF = 5, p=0.02). (F) Averaged (± SEM) photometry signals across all mice aligned to center port exit (CX, top) or side port exit (SX, bottom) grouped by ipsilateral (green) and contralateral (magenta) choice show increased activity during ipsiversive movements (90/10 reward probability, n=6 mice, 49 sessions, 20,355 trials). (G) Averaged (± SEM) photometry signals across all mice aligned to center port exit (CX) or side port exit (SX) grouped by ipsilateral (green) and contralateral (magenta) choice show differential peak responses during ipsiversive movements (top). (bottom) Points represent the maximum peak z-scored fluorescence per animal for the 1 s period immediately following to the behavioral event, bars represent mean across animals ± SEM (all sessions are at 90/10 reward probability, n=6 mice, 49 sessions, 20,355 trials) (paired t-test DF = 5, p=0.016).
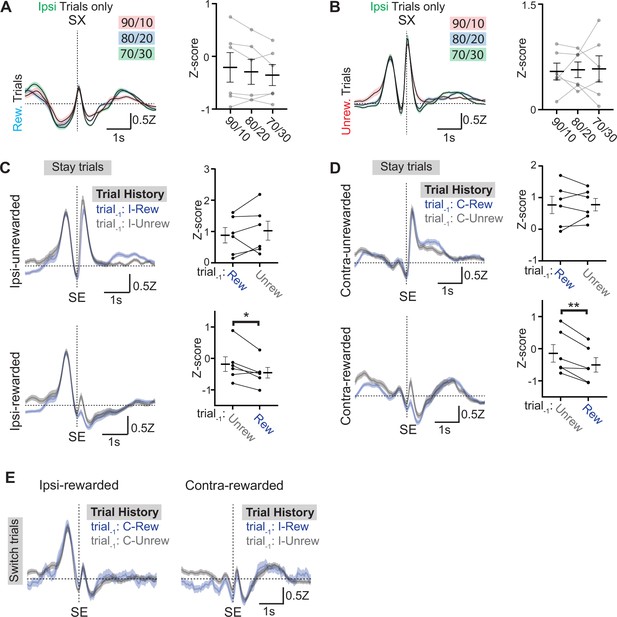
Examining the influence of reward history on photometry signals from EPSst+ neurons.
(A) (left) Ipsilateral rewarded trial-averaged (± SEM) photometry signals across reward probabilities aligned to side exit (SX) plotted to examine if reward expectation impacts photometry signals. (right) Points represent the mean z-scored fluorescence per animal for the 500 ms period immediately prior to the behavioral event, bars represent mean across animals ± SEM (n=6 mice/condition). (B) (left) Ipsilateral unrewarded trial-averaged (± SEM) photometry signals across reward probabilities aligned to side exit (SX) plotted to examine if reward expectation impacts photometry signals. (right) Points represent the mean z-scored fluorescence per animal for the 500ms period immediately prior to the behavioral event, bars represent mean across animals ± SEM (n=6 mice/condition) (C) Ipsilateral trial-averaged (± SEM) photometry signals across all mice aligned to side entry (SE) divided by unrewarded (top) and rewarded (bottom) outcome, grouped by whether the previous trial (also ipsilateral) was rewarded (blue) or unrewarded (gray) plotted to examine if reward history impacts photometry signals. (right) Points represent the mean z-scored fluorescence per animal for the 500 ms period immediately following the behavioral event, bars represent mean across animals ± SEM (all sessions are at 90/10 reward probability, n=6 mice, 49 sessions) (bottom; paired t-test DF = 5, p = 0.03). (D) Contralateral trial averaged (± SEM) photometry signals across all mice aligned to side entry (SE) divided by unrewarded (top) and rewarded (bottom) outcome, grouped by whether the previous trial (also contralateral) was rewarded (blue) or unrewarded (gray) plotted to examine if reward history impacts photometry signals. (right) Points represent the mean z-scored fluorescence per animal for the 500 ms period immediately following the behavioral event, bars represent mean across animals ± SEM (all sessions are at 90/10 reward probability, n=6 mice, 49 sessions) (bottom; paired t-test DF = 5, p=0.006). (E) Averaged (± SEM) photometry signals across all mice aligned to side entry (SE) divided by ipsi-rewarded (left) and contra-rewarded (right) trial types, grouped by whether the previous trial (opposite choice from current trial, i.e. ‘switch trials’) was rewarded (blue) or unrewarded (gray) plotted to examine if reward and choice history impacts photometry signals (all sessions are at 90/10 reward probability, n=6 mice, 49 sessions).
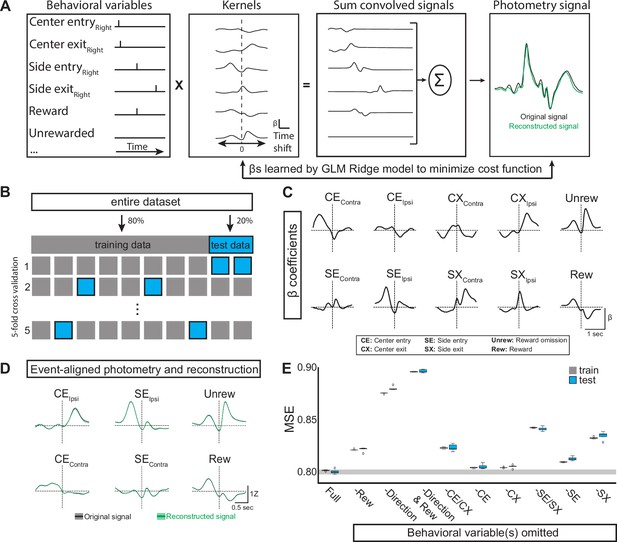
Generalized linear model of EPSst neural activity during behavior.
(A) GLM workflow: behavioral variables are convolved with their kernels. Each time shift in the kernel consists of an independent β coefficient fit jointly by minimizing a cost function. The convolved signals are then summed to generate a reconstructed signal (green) which can be directly compared to the original photometry recording (black). (B) The original dataset is divided into training and test datasets. The GLM is fit on the training data and evaluated on the test data using mean squared error (MSE). Following a grid search that compared multiple regularization types (ridge, elastic net, ordinary least squared) in combination with a large hyperparameter space, ridge regression (α=1) was found to give the smallest error following cross-validation. (C) Kernels for the ten behavioral variables included as features in the GLM (full model). Behavioral predictors gave information regarding choice (Ipsi/Contra), reward, and port entry and exit. (D) Average original (black) and reconstructed (green, using full model) photometry signals across trials aligned to behavioral events (solid line = mean, shaded area = SEM, R2=0.19 SD = 0.001, n=male 6 mice). (E) Box plots showing MSE for the full model (leftmost plot labeled ‘Full’) and models in which selected behavioral predictor(s) were omitted (See materials and methods). MSE for both the train (gray) and test (blue) datasets for each model are shown (Boxes represent the three quartiles (25%, 50%, and 75%) of the data and whiskers are 1.5*IQR, outliers are shown as dots, each model-run uses a different combination of data used for train/test split as illustrated in B).
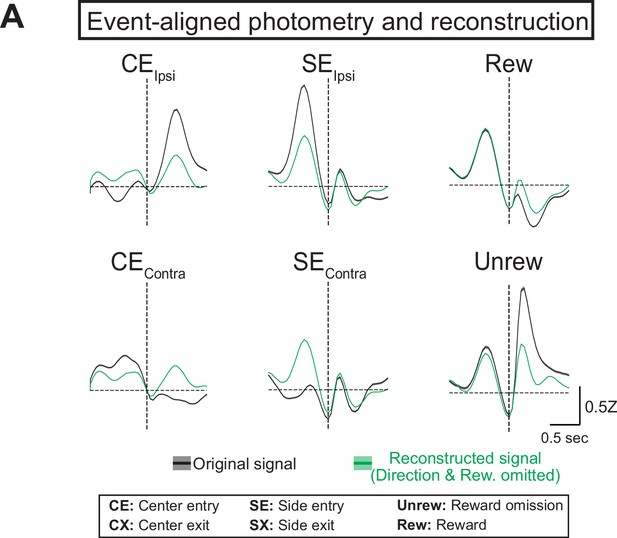
Generalized linear model (GLM) reconstructions of photometry signal with a partial model.
(A) Average original (black) and reconstructed (green, using model where direction and reward were omitted) photometry signals across trials aligned to behavioral events used in the full model (solid line = mean, shaded area = SEM, n=6 mice).
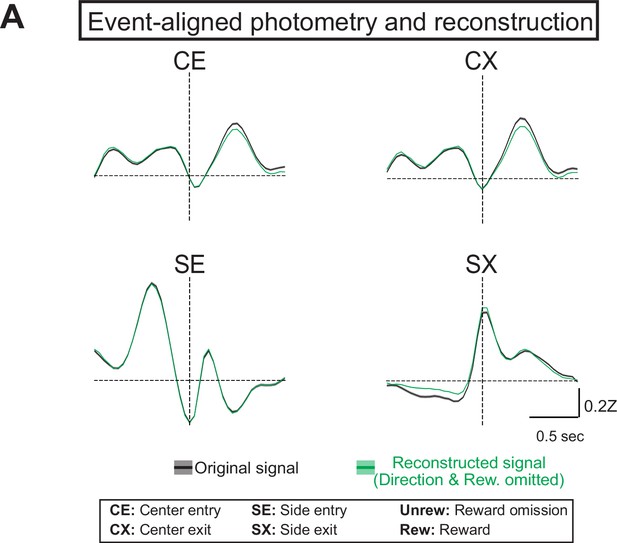
Generalized linear model (GLM) reconstructions of photometry signal with choice and reward variables omitted.
(A) Average original (black) and reconstructed (green, using model where direction and reward were omitted) photometry signals across trials aligned to behavioral events used in the partial model were choice and reward were omitted (solid line = mean, shaded area = SEM, n=6 mice).
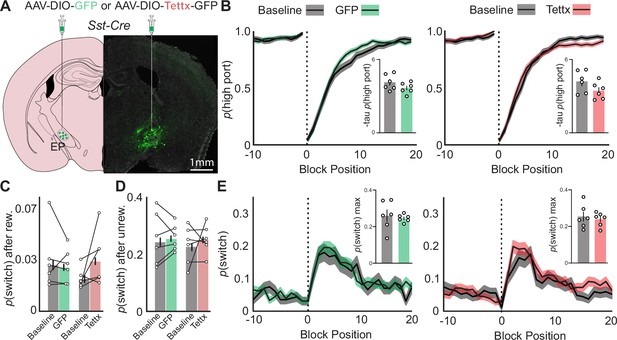
Effects of permanent genetic silencing of synaptic release from EPSst+ neurons on continued performance of a two-port choice probabilistic switching task.
(A) Viral injection location resulting in Cre-dependent expression of GFP (control) or tetanus toxin in EPSst+ neurons (green = Tettx GFP, gray = DAPI). (B) The probability of choosing the highly rewarded port (p high port) around a block transition (dotted vertical line) for GFP (control, left) or Tettx (right) injected mice (gray = 5 d prior to adeno-associated virus (AAV) injection, green/red = days 21–30 post-injection; black line = mean, shaded area = SEM). (Insets) Bar plot showing taup(high port) (time constant) calculated from an exponential fit to the first 20 trials following a block transition for each animal (circles) (bar = mean, error bar = SEM) before and after AAV injection. (C) p(switch) for trials following a rewarded trial for GFP (green) and Tettx (red) injected animals (bar = mean, error bar = 95% CI). (D) p(switch) for trials following an unrewarded trial for GFP (green) and Tettx (red) injected animals (bar = mean, error bar = 95% CI). (E) The probability of choosing different side ports on consecutive trials (p switch) around a block transition (dotted vertical line) for GFP (control, left) or Tettx (right) injected mice (gray = 5 d prior to AAV injection, green/red = days 21–30 post-injection; black line = mean, shaded area = SEM). (Insets) Bar plot showing the maximum p(switch) in the 20 trials that follow a block transition for each animal (circles) (bar = mean, error bar = SEM) before and after AAV injection. For (B–E) n=6 male GFP control and n=6 male Tettx mice, five sessions/mouse before AAV inj. and 10 sessions/mouse after AAV injection, GFP control = 15,120 trials before, 34,523 trials after; Tettx = 17,528 trials before, 32,761 trials after.
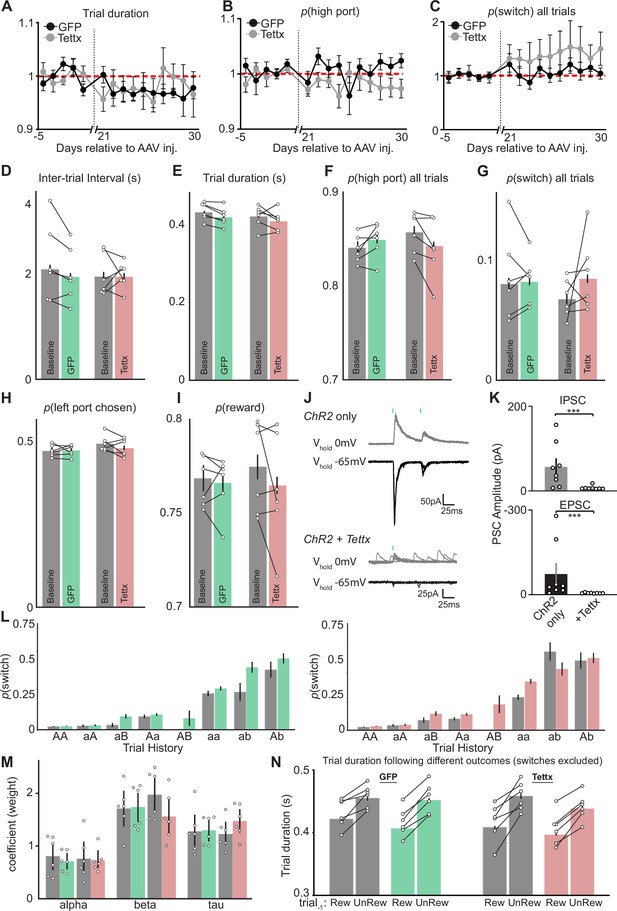
Additional behavioral performance metrics before and after viral injection and electrophysiological validation of Tettx effects on GABA/glutamate cotransmission from EPSst+ neurons.
(A) Trial duration (normalized to mean before adeno-associated virus (AAV) injection day- 5 - day-1, red dashed line) across behavioral sessions (days) before and after AAV injection of GFP (black) or Tettx (gray) (n=6 GFP, n=6 Tettx animals, dots = mean, error bar = SEM). (B) p(high port) (normalized to mean before AAV injection day-5- day-1), red dashed line across behavioral sessions (days) before and after AAV injection of GFP (black) or Tettx (gray) (n=6 GFP, n=6 Tettx animals, dots = mean, error bar = SEM). (C) p(switch) normalized to mean before AAV injection (day-5- day-1), red dashed line across behavioral sessions (days) before and after AAV injection of GFP (black) or Tettx (gray) (n=6 GFP, n=6 Tettx animals, dots = mean, error bar = SEM). (D–I) Behavioral metrics for GFP (green) and Tettx (red) injected animals before (gray) and after (color) injection of AAV (dots = individual mice, bar = mean, error bars = 95% CI). (J) Sample whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings from lateral habenula (LHb) neurons clamped at either 0 mV (gray) or –65 mV (black) to isolate optogenetically evoked IPSCs or EPSCs, respectively, from oChief + EPSst axons. Sample traces on top are from a Sst-Cre+ animal expressing oChief only in entopeduncular nucleus (EP) and bottom traces are from a Sst-Cre+ animal expressing both oChief and Tettx, blue dashes represent the timing of the blue light pulse (1 ms duration). (K) Quantification of peak amplitude from optogenetically evoked IPSCs (top) and EPSCs (bottom) from oChief only (control, left) and oChief/Tettx (right) groups (n=8 cells control, 8 cells Tettx; bar = mean, error bar = SEM) (top; Mann W. DF = 2, p=0.0006, bottom; Mann W. DF = 1.5, p=0.0005). (L) p(switch) for trial types divided by reward history and choice direction segregated into before injection (gray) and after injection (green = GFP, left; red = Tettx, right) (bar = mean, error bar = 95% CI). (M) Summary of recursively formulated logistic regression (RFLR) model coefficients segregated into before injection (gray) and after injection (green = GFP; red = Tettx), each dot represents an individual mouse (bar = mean, error bar = SEM, negative log-likelihood of fits were equivalent across conditions; control = – 0.22 SD = 0.04; Tettx = –0.20 SD = 0.05). (N) Trial duration following previously rewarded or unrewarded trials segregated into before injection (gray) and after injection (green = GFP; red = Tettx) (bar = mean, error bar = 95% CI). (A–I) and (L–N) n=6 GFP control and n=6 Tettx mice, five sessions/mouse before AAV inj. and 10 sessions/mouse after AAV injection, GFP control = 15,120 trials before, 34,523 trials after; Tettx = 17,528 trials before, 32,761 trials after.
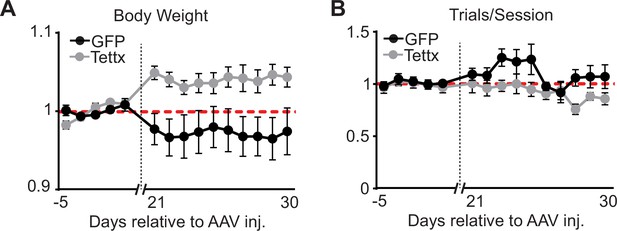
Body weight and total number of trials per session before and after viral injection.
(A) Body weight (normalized to mean before adeno-associated virus, AAV injection) across behavioral sessions (days) before and after AAV injection of GFP (black) or Tettx (gray) (n=6 GFP, n=6 Tettx animals, dots = mean, error bar = SEM). (B) Total number of trials per session (normalized to mean before AAV injection) across behavioral sessions (days) before and after AAV injection of GFP (black) or Tettx (gray) (n=6 GFP, n=6 Tettx animals, dots = mean, error bar = SEM).
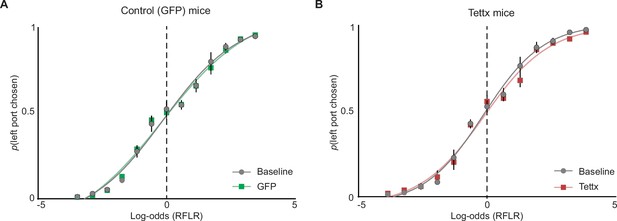
Psychometric curves of port choice before and after adeno-associated virus (AAV) injection.
(A) The probability that an animal chooses the left port (p(left port chosen)) compared to log-odds (Ψt+1) of the animal’s next choice calculated by the recursively formulated logistic regression (RFLR) model trained on ‘Baseline’ data. Psychometric curves were then fit with a logistic function on grouped data before (Baseline, gray) and after (GFP, green) AAV injection (dots = mean, error bars = SEM, n=6 mice). (B) Same as in (A) but for mice injected with AAV expressing Tettx (red, dots = mean, error bars = SEM, n=6 mice).
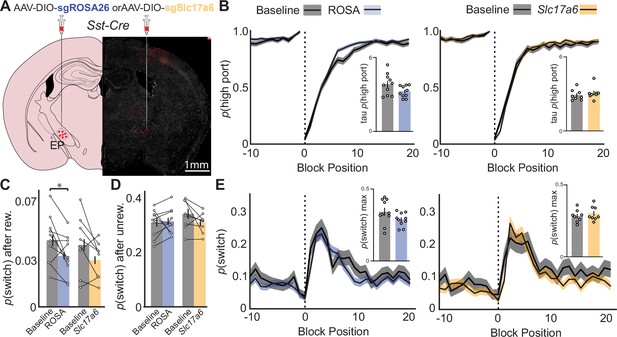
Effects of CRISPR Cas9 deletion of synaptic glutamate release from EPSst+ neurons on continued performance of a two-port choice probabilistic switching task.
(A) Viral injection location resulting in Cre-dependent expression of oChief-tdTom +SaCas9-sgRNA for ROSA26 (control) or Slc17a6 (vGluT2) in EPSst+ neurons (red = tdTomato, gray = DAPI). (B) The probability of choosing the highly rewarded port (p high port) around a block transition (dotted vertical line) for sgROSA (control, left) or sgSlc17a6 (right) injected mice (gray = 5 d prior to adeno-associated virus (AAV) injection, blue/orange = days 21–30 post-injection; black line = mean, shaded area = SEM). (Insets) Bar plot showing taup(high port) (time constant) calculated from an exponential fit to the first 20 trials following a block transition for each animal (circles) (bar = mean, error bar = SEM) before and after AAV injection. (C) p(switch) for trials following a rewarded trial for sgROSA26 (blue) and sgSlc17a6 (orange) injected animals (bar = mean, error bar = 95% CI) (paired t-test DF = 9, p-value = 0.02). (D) p(switch) for trials following an unrewarded trial for sgROSA26 (blue) and sgSlc17a6 (orange) injected animals (bar = mean, error bar = 95% CI). (E) The probability of choosing different side ports on consecutive trials (p switch) around a block transition (dotted vertical line) for sgROSA26 (control, left) or sgSlc17a6 (right) injected mice (gray = 5 d prior to AAV injection, green/red = days 21–30 post-injection; black line = mean, shaded area = SEM). (Insets) Bar plot showing the maximum p(switch) in the 20 trials that follow a block transition for each animal (circles) (bar = mean, error bar = SEM) before and after AAV injection. For (B–E) n=10 (five males, five females) sgROSA26 control and n=8 (two males, six females) sgSlc17a6 mice, five sessions/mouse before AAV inj. and 10 sessions/mouse after AAV injection, sgROSA26 control = 17,318 trials before, 39,710 trials after; sgSlc17a6=13,520 trials before, 29,256 trials after.
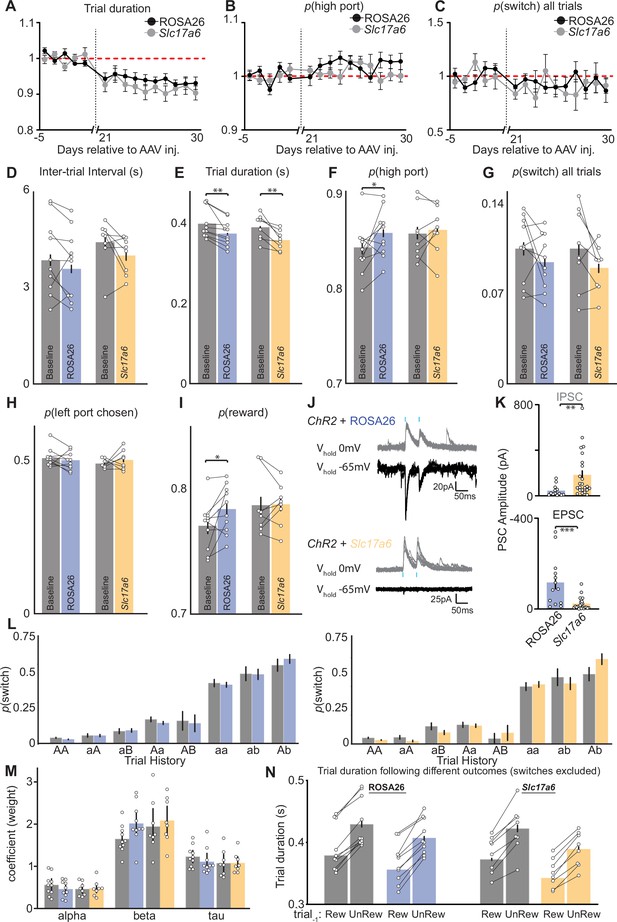
Additional behavioral performance metrics before and after viral injection and electrophysiological validation of CRISPR-SaCas9 mediated deletion of Slc17a6 (vGluT2) on GABA/glutamate cotransmission from EPSst+ neurons.
(A) Trial duration normalized to mean before adeno-associated virus (AAV) injection (day-5- day-1), red dashed line across behavioral sessions (days) before and after AAV injection of sgROSA26 (black) or sgSlc17a6 (gray) (n=10 sgROSA26, n=8 sgSlc17a6 animals, dots = mean, error bar = SEM). (B) p(high port) (normalized to mean before AAV injection day-5- day-1, red dashed line) across behavioral sessions (days) before and after AAV injection of sgROSA26 (black) or sgSlc17a6 (gray) (n=10 sgROSA26, n=8 sgSlc17a6 animals, dots = mean, error bar = SEM). (C) p(switch) (normalized to mean before AAV injection day-5- day-1, red dashed line) across behavioral sessions (days) before and after AAV injection of sgROSA26 (black) or sgSlc17a6 (gray) (n=10 sgROSA26, 8 sgSlc17a6 animals, dots = mean, error bar = SEM). (D–I) Behavioral metrics for sgROSA26 (blue) and sgSlc17a6 (orange) injected animals before (gray) and after (color) injection of AAV (dots = individual mice, bar = mean, error bars = 95% CI) (E); ROSA26 paired t-test, DF = 9, p-value = 0.002, Slc17a6 paired t-test, DF = 7, p-value = 0.004, (F); ROSA26 paired t-test, DF = 9, p-value = 0.05, (I); ROSA26 paired t-test, DF = 9, p-value = 0.03. (J) Sample whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings from lateral habenula (LHb) neurons clamped at either 0 mV (gray) or – 65 mV (black) to isolate optogenetically evoked IPSCs or EPSCs, respectively, from oChief + EPSst axons. Sample traces on top are from a Sst-Cre+ animal expressing both oChief and sgROSA26 in entopeduncular nucleus (EP) and bottom traces are from a Sst-Cre+ animal expressing both oChief and sgSlc17a6 blue dashes represent the timing of the blue light pulse (1 ms duration). (K) Quantification of peak amplitude from optogenetically evoked IPSCs (top) and EPSCs (bottom) from sgROSA26 (control, left) and sgSlc17a6 (right) groups (n=13 cells control, n=23 cells Tettx; bar = mean, error bar = SEM) (top; Mann W. DF = 60, p=0.0025, bottom; Mann W. DF = 46, p=0.0004). (L) p(switch) for trial types divided by reward history and choice direction segregated into before injection (gray) and after injection (blue = sgROSA26, left; orange = sgSlc17 a6, right) (bar = mean, error bar = 95% CI). (M) Summary of RFLR model coefficients segregated into before injection (gray) and after injection (blue = sgROSA26; orange = sgSlc17 a6), each dot represents an individual mouse (bar = mean, error bar = SEM), negative log-likelihood of fits were equivalent across conditions; (ROSA26 = –0.25 SD = 0.05; Slc17a6 = –0.24 SD = 0.05). (N) Trial duration following previously rewarded or unrewarded trials segregated into before injection (gray) and after injection (blue = sgROSA26; orange = sgSlc17 a6) (bar = mean, error bar = 95% CI). (A–I) and (L–N) n=10 sgROSA26 control and n=8 sgSlc17a6 mice, five sessions/mouse before AAV inj. and 10 sessions/mouse after AAV injection, sgROSA26 control = 17,318 trials before, 39,710 trials after; sgSlc17a6=13,520 trials before, 29,256 trials after.
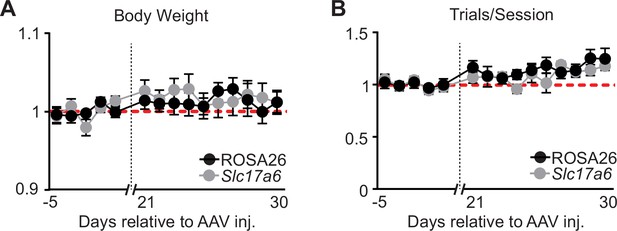
Total number of trials per session and animal body weight changes before and after viral injection.
(A) Body weight (normalized to mean before adeno-associated virus, AAV injection) across behavioral sessions (days) before and after AAV injection of sgROSA26 (black) or sgSlc17a6 (gray) (n=10 sgROSA26, n=8 sgSlc17a6 animals, dots = mean, error bar = SEM) (B) Total number of trials per session (normalized to mean before AAV injection) across behavioral sessions (days) before and after AAV injection of sgROSA26 (black) or sgSlc17a6 (gray) (n=10 sgROSA26, n=8 sgSlc17a6 animals, dots = mean, error bar = SEM).
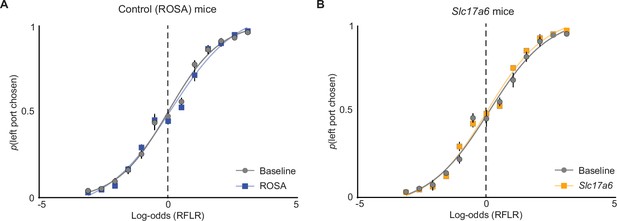
Psychometric curves of port choice before and after adeno-associated virus (AAV) injection.
(A) The probability that an animal chooses the left port (p(left port chosen)) compared to log-odds (Ψt+1) of the animal’s next choice calculated by the recursively formulated logistic regression (RFLR) model for trained on ‘Baseline’ data. Psychometric curves were then fit with a logistic function on grouped data before (Baseline, gray) and after (ROSA, blue) AAV injection (dots = mean, error bars = SEM, n = 10 mice). (B) Same as in (A) but for mice injected with AAV expressing SaCas9-sgSlc17a6 (orange, dots = mean, error bars = SEM, n=8 mice).
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain (Mus musculus) | C57Bl/6 J | The Jackson Laboratory | Cat# JAX:000664 RRID:IMSR_JAX:000664 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Sst-IRES-Cre | The Jackson Laboratory | Cat# JAX: 013044 RRID:IMSR_JAX:013044 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Sst-IRES-Flpo | The Jackson Laboratory | Cat# JAX: 031629 RRID:IMSR_JAX:031629 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Pvalb-2A-Flp | The Jackson Laboratory | Cat# JAX: 022730 RRID:IMSR_JAX:022730 | |
| Genetic reagent (AAV) | AAV1-Syn-FLEX-GCaMP6f | Addgene | Addgene# 100833 RRID:Addgene_100833 | |
| Genetic reagent (AAV) | AAV8-CAG-FLEX-tdTomato | Addgene | Addgene# 51503 RRID:Addgene_51503 | |
| Genetic reagent (AAV) | AAVrg-Ef1a-fDIO-Cre | Addgene | Addgene# 121675 RRID:Addgene_121675 | |
| Genetic reagent (AAV) | AAV8-Syn-FLEX-TeLC-P2A-GFP | Addgene | Addgene# 135391 RRID:Addgene_135391 | |
| Genetic reagent (AAV) | AAV8-Syn-DIO-EGFP | Addgene | Addgene# 50457 RRID:Addgene_50457 | |
| Genetic reagent (AAV) | AAV1-CMV-FLEX-SaCas9-sgSlc17a6 | Addgene | Addgene# 124847 RRID:Addgene_124847 | |
| Genetic reagent (AAV) | AAV1- CMV-FLEX-SaCas9-sgROSA26 | Addgene | Addgene# 159914 RRID:Addgene_159914 | |
| Genetic reagent (AAV) | AAV8-Ef1a-DIO-oChief-tdTomato | Addgene | Addgene# 51094 RRID:Addgene_51094 | |
| Antibody | anti-GFP (chicken polyclonal) | Invitrogen | Cat# A10262 RRID:AB_2534023 | IF(1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-mcherry (rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat# Ab167453 RRID:AB_2571870 | IF(1:500) |
| Software, algorithm | MATLAB (R2015a) | MathWorks | RRID:SCR_001622 | |
| Software, algorithm | Fiji | PMID:22743772 | RRID:SCR_002285 | https://imagej.net/Fiji |
| Software, algorithm | Python | https://www.python.org/ | RRID:SCR_008394 | https://www.python.org/ |





