Enhanced neural speech tracking through noise indicates stochastic resonance in humans
Figures
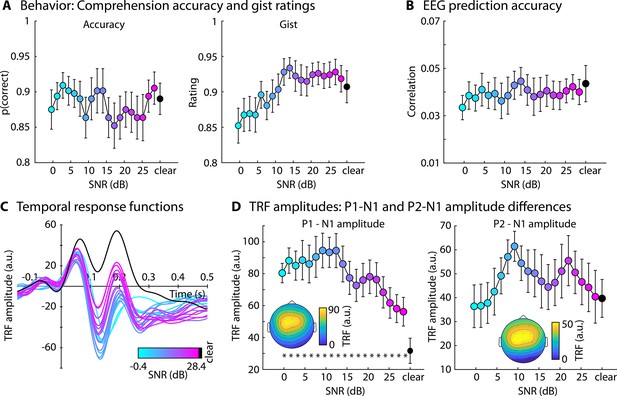
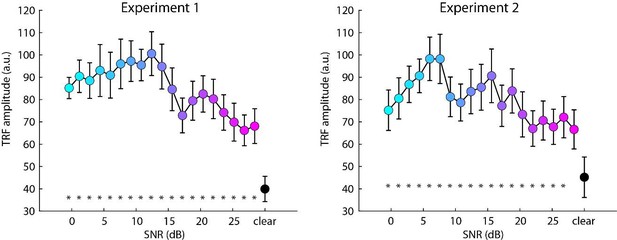
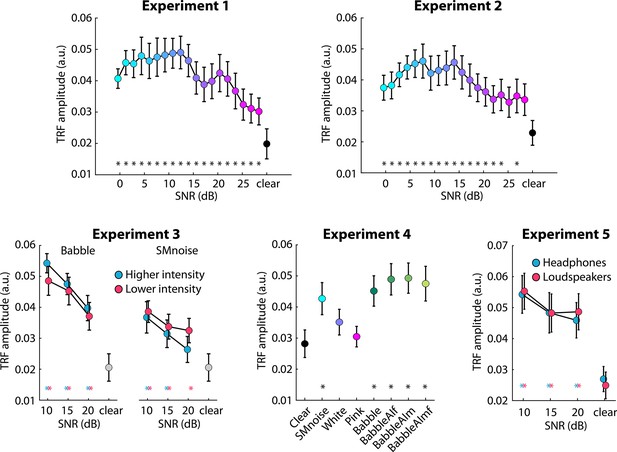
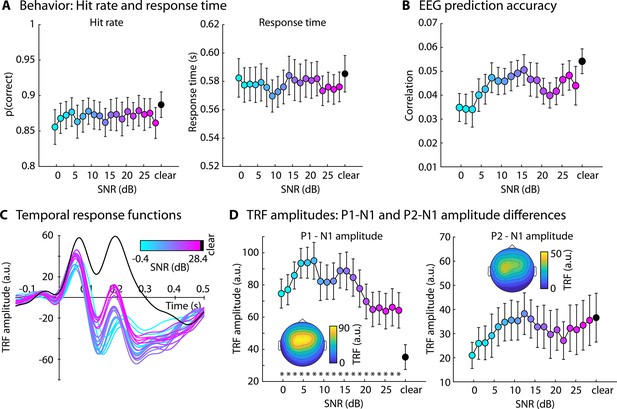
Results for Experiment 1 (N=22).
(A) Accuracy of story comprehension (left) and gist ratings (right). (B) Electroencephalography (EEG) prediction accuracy. (C) Temporal response functions (TRFs). (D) P1-N1 and P2-N1 amplitude difference for different speech-clarity conditions. Topographical distributions reflect the average across all speech-clarity conditions. The black asterisk close to the x-axis indicates a significant difference from a paired t-test relative to the clear condition (pFDR < 0.05; false discovery rate [FDR]-thresholded). The absence of an asterisk indicates that there was no significant difference. Error bars reflect the standard error of the mean.
P1-N1 amplitude from temporal response function (TRF) analyses using the amplitude envelope of speech.
An asterisk close to the x-axis indicates a significant difference from a paired t-test relative to the clear condition (pFDR < 0.05; false discovery rate [FDR]-thresholded). The absence of an asterisk indicates that there was no significant difference. Error bars reflect the standard error of the mean. For additional details, see the respective figure captions in the main article.
P1-N1 amplitude from cross-correlations analyses.
An asterisk close to the x-axis indicates a significant difference from a paired t-test relative to the clear condition (pFDR < 0.05; false discovery rate [FDR]-thresholded). The absence of an asterisk indicates that there was no significant difference. Error bars reflect the standard error of the mean. For additional details, see the respective figure captions in the main article.
Results for Experiment 2 (N=22).
(A) Hit rate (left) and response times (right) for the visual 1-back task. (B) Electroencephalography (EEG) prediction accuracy. (C) Temporal response functions (TRFs). (D) P1-N1 and P2-N1 amplitude difference for different speech-clarity conditions. Topographical distributions reflect the average across all speech-clarity conditions. The black asterisk close to the x-axis indicates a significant difference from a paired t-test relative to the clear condition (pFDR < 0.05; false discovery rate [FDR]-thresholded). The absence of an asterisk indicates that there was no significant difference. Error bars reflect the standard error of the mean.
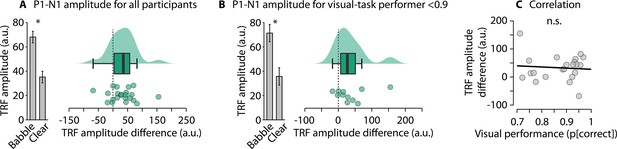
Relationship between visual performance and the noise-related enhancement of the P1-N1 amplitude in Experiment 2.
(A) Shows the P1-N1 amplitude for speech in babble (averaged across all signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) above 15 dB, for which speech was highly intelligible) and clear speech (paired t-test for statistical comparison; *p < 0.05). (B) Same as in Panel A for individuals performing below 0.9 in the visual task (to controls for potential influences of high performers, who could have attended the speech). (C) Correlation between visual-task performance and the difference in the P1-N1 amplitude between speech in babble and clear speech. The relationship was not significant. n.s. – not significant.
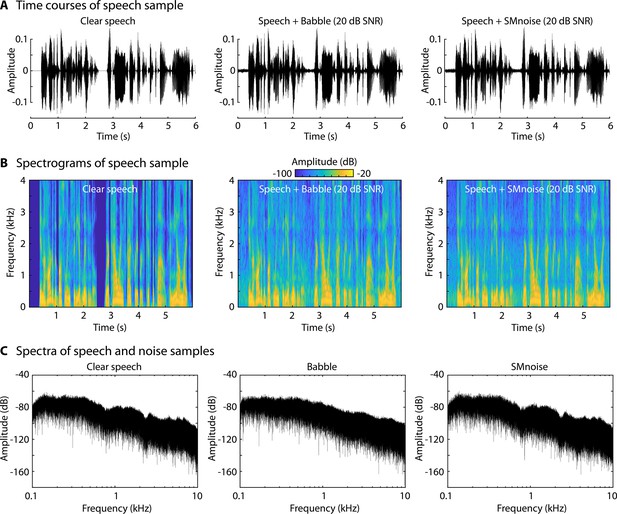
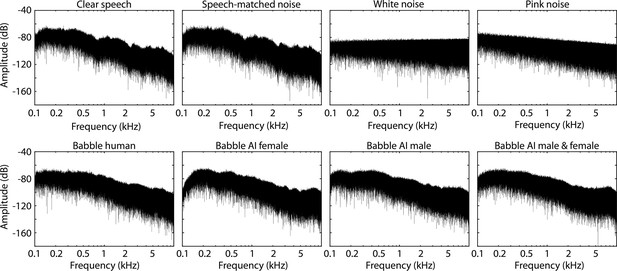
Depiction of stimulus samples.
(A) Time courses for clear speech and speech to which background babble or speech-matched noise was added at 20 dB signal-to-noise ratio (SNR; all sound mixtures were normalized to the same root-mean-square amplitude). The first 6 s of a story are shown. (B) Spectrograms of the samples in Panel A. (C) Power spectra for clear speech, babble, and speech-matched noise. In C, only background babble/noise is displayed, without added speech.
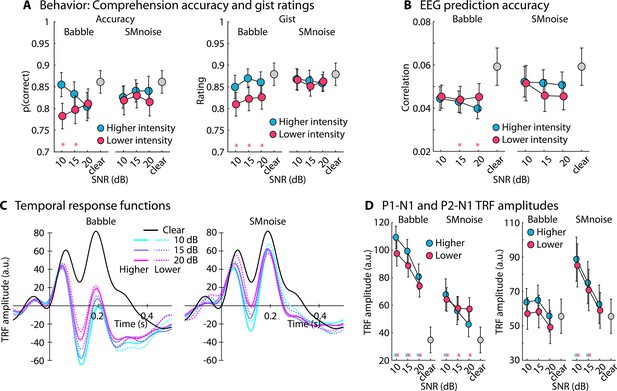
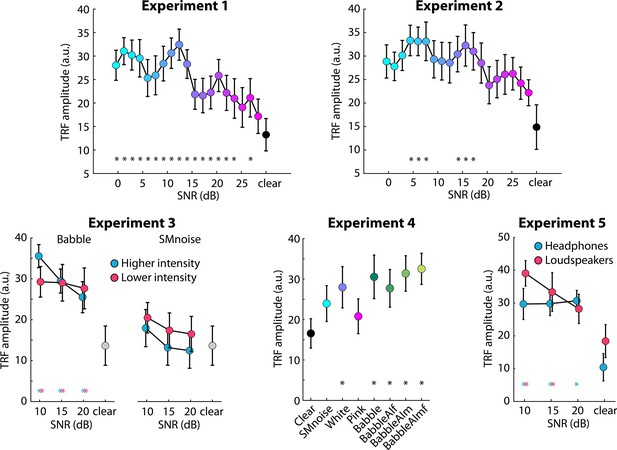
Results for Experiment 3 (N=23).
(A) Accuracy of story comprehension (left) and gist ratings (right). Higher versus lower intensity refers to the two sound-level normalization types, one resulting in a slightly lower intensity of the speech signal in the sound mixture than the other. (B) Electroencephalography (EEG) prediction accuracy. (C) Temporal response functions (TRFs). (D) P1-N1 (left) and P2-N1 (right) amplitude difference for clear speech and different speech-masking and sound normalization conditions. In panels A, B, and D, a colored asterisk close to the x-axis indicates a significant difference from a paired t-test relative to the clear condition (pFDR < 0.05; false discovery rate [FDR]-thresholded). The specific color of the asterisk – blue versus red – indicates the normalization type (higher vs. lower speech level, respectively). The absence of an asterisk indicates that there was no significant difference relative to clear speech. Error bars reflect the standard error of the mean.
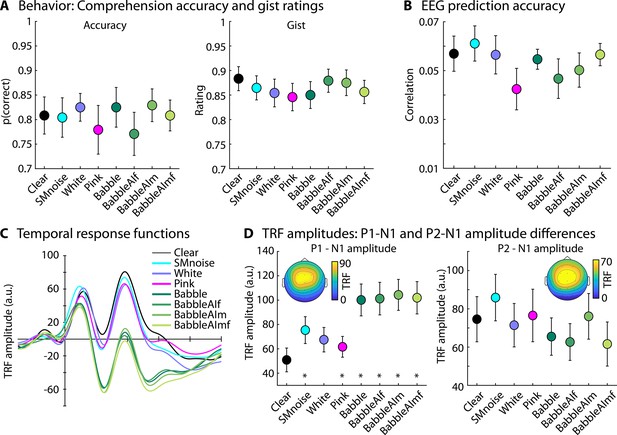
Results for Experiment 4 (N=20).
(A) Accuracy of story comprehension (left) and gist ratings (right). (B) Electroencephalography (EEG) prediction accuracy. (C) Temporal response functions (TRFs). (D) P1-N1 and P2-N1 amplitude difference for clear speech and different speech-masking conditions. Topographical distributions reflect the average across all conditions. In panels A, B, and D, the black asterisk close to the x-axis indicates a significant difference from a paired t-test relative to the clear condition (pFDR < 0.05; false discovery rate [FDR]-thresholded). The absence of an asterisk indicates that there was no significant difference relative to clear speech. Error bars reflect the standard error of the mean.
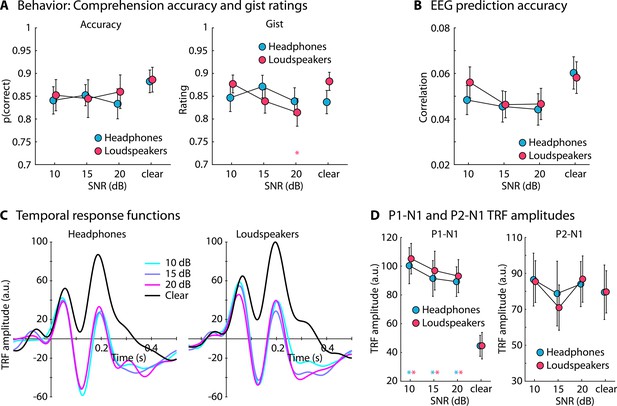
Results for Experiment 5 (N=22).
(A) Accuracy of story comprehension (left) and gist ratings (right). (B) Electroencephalography (EEG) prediction accuracy. (C) Temporal response functions (TRFs). (D) P1-N1 and P2-N1 amplitude difference for clear speech and different speech-masking and sound-delivery conditions. In panels A, B, and D, a colored asterisk close to the x-axis indicates a significant difference from a paired t-test relative to the clear condition (pFDR < 0.05; false discovery rate [FDR]-thresholded). The specific color of the asterisk – blue versus red – indicates the sound-delivery type. The absence of an asterisk indicates that there was no significant difference relative to clear speech. Error bars reflect the standard error of the mean.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Software, algorithm | MATLAB | MATLAB | RRID:SCR_001622 | |
| Software, algorithm | JASP | JASP | RRID:SCR_015823 | |
| Software, algorithm | PsychToolbox | PsychToolbox | RRID:SCR_002881 | |
| Software, algorithm | OpenAI | ChatGPT | RRID:SCR_023775 | |
| Software, algorithm | FieldTrip | FieldTrip | RRID:SCR_004849 |