TRPML1 gating modulation by allosteric mutations and lipids
Figures
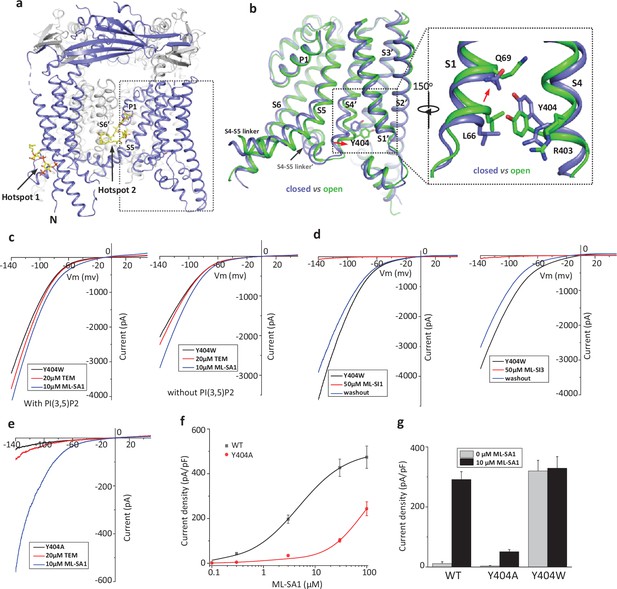
Design and characterization of allosteric mutations at Tyr404 that recapitulate TRPML1 gating.
(a) The structure of PI(3,5)P2/Temsirolimus-activated TRPML1 (PDB code:7SQ9) illustrating the two hot spots for ligand binding. Temsirolimus (Tem) is a rapamycin analog. (b) Ligand-induced conformational change and the zoomed-in view of the Y404 movement. Only the boxed region in (a) is shown in the structural comparison between the open (green) and closed (blue) structures. Red arrows mark the bending of S4 and upward movement of S1. (c) Sample traces of Y404W gain-of-function mutant recorded using patch clamp in whole-cell configuration with (left) or without (right) 100 µM PI(3,5)P2 in the pipette (cytosolic). Tem or agonist ML-SA1 was introduced in the bath solution (extracellular/luminal). (d) Sample traces of Y404W inhibition by antagonists ML-SI1 (left) and ML-SI3 (right) recorded using patch clamp in whole-cell configuration. The antagonists were introduced in the bath solution (extracellular/luminal). (e) Sample traces of Y404A loss-of-function mutant with 100 µM PI(3,5)P2 in the pipette (cytosolic). Tem or ML-SA1was introduced in the bath solution (extracellular/luminal). (f) ML-SA1 activation of TRPML1(WT) and Y404A mutant measured at –140 mV. Data for WT is least square fits to the Hill equation with EC50=4.8 ± 0.7 µM, n=0.93 ± 0.10. Data points are mean ± SEM (n=5 independent experiments). (g) Current density of wild-type and mutant TRPML1 at –140 mV with and without 10 µM ML-SA1. Data points are mean ± SEM (n=5 independent experiments).
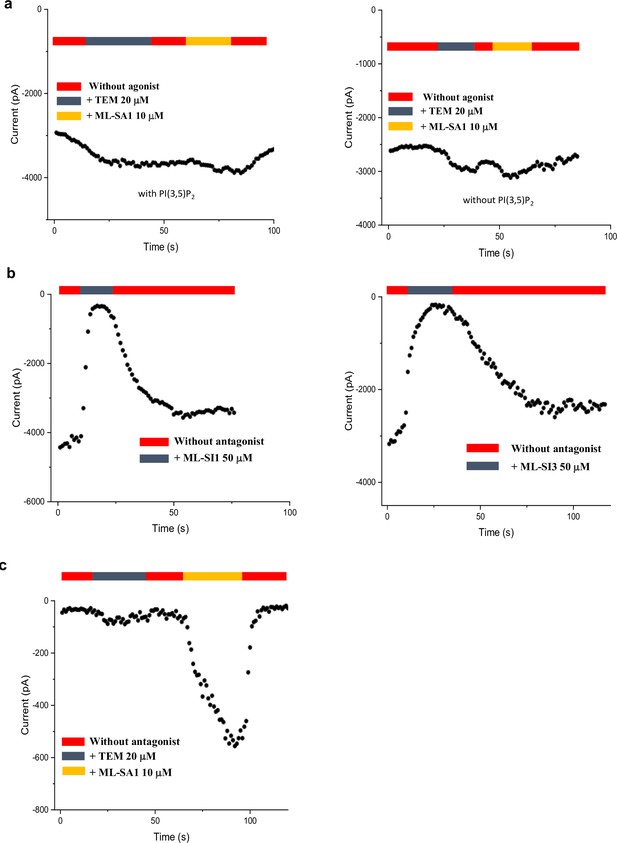
Time course plots of current amplitudes of Y404 mutations recorded at –140 mV with symmetrical pH of 7.4.
(a) Time course plots of Y404W recorded using patch clamp in whole-cell configuration with (left) or without (right) 100 µM PI(3,5)P2 in the pipette (cytosolic). Tem or agonist ML-SA1 was introduced in the bath solution (extracellular/luminal). (b) Time course plots of Y404W inhibition by antagonists ML-SI1 (left) and ML-SI3 (right) recorded using patch clamp in whole-cell configuration. The antagonists were introduced in the bath solution (extracellular/luminal). (c) Time course plots of Y404A with 100 µM PI(3,5)P2 in the pipette (cytosolic). Tem or ML-SA1was introduced in the bath solution (extracellular/luminal).
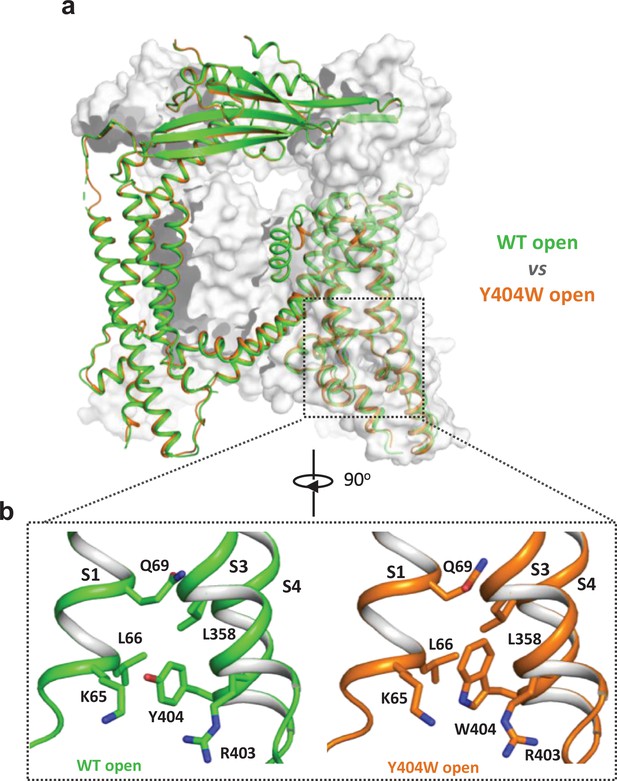
Y404W mutant adopts an open conformation in the absence of ligands.
(a) Structural comparison between PI(3,5)P2/Tem-bound open structure (green) and the Y404W mutant structure (orange). Only the front subunit and the neighboring S1-S4 regions are highlighted in color for clarity. (b) Zoomed-in views of the regions surrounding Y404 (WT, green) and W404 (mutant, orange).
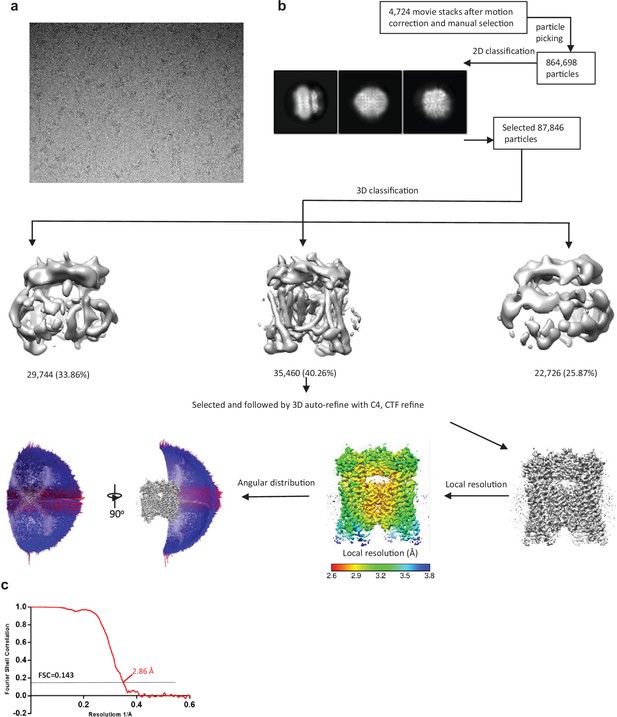
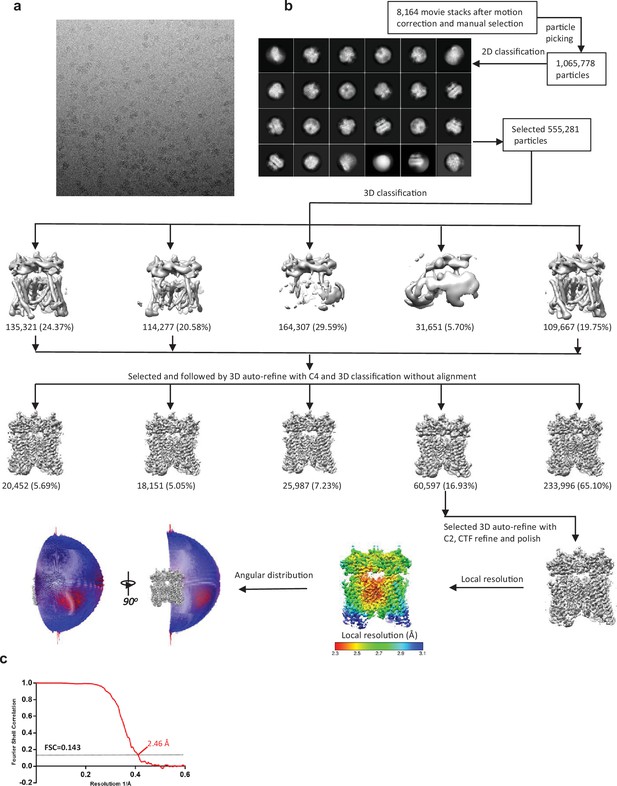
Cryo-EM data processing scheme of the TRPML1 Y404W.
(a) Representative micrograph. (b) Flow chart of the cryo-EM data processing procedure and the Euler angle distribution of particles used in the final three-dimensional reconstruction. Selected 2D class averages are shown. The final structure represents an open state. (c) Fourier Shell Correlation curves showing the overall resolution at FSC = 0.143.
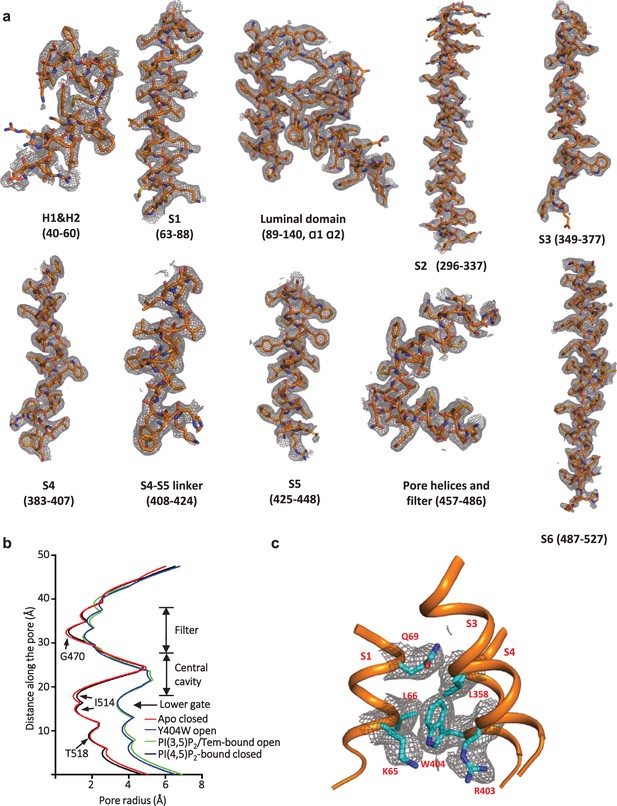
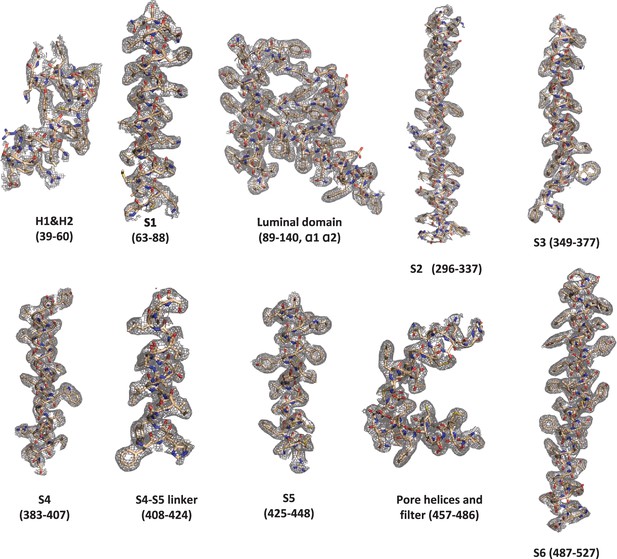
Sample density maps of Y404W and pore radius.
(a) Sample density maps of the Y404W open TRPML1 structure contoured at 4 σ. (b) Pore radius along the central axis in the open and closed states. PDB codes for apo closed and PI(3,5)P2/Tem-bound open are 7SQ8 and 7SQ9, respectively. (c) EM density map surrounding W404 region shown in grey mesh and contoured at 4σ, key W404-interacting residues are shown in cyan. The local resolution of this region is 3.2 Å.
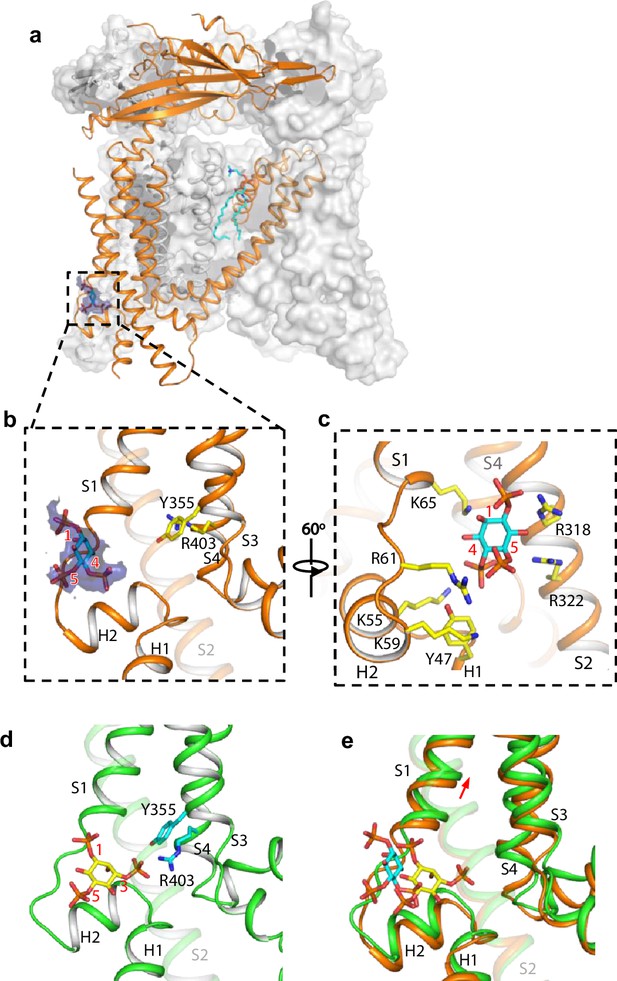
Structure of TRPML1 in complex with PI(4,5)P2.
(a) Overall structure of PI(4,5)P2-bound TRPML1 with the front subunit shown in orange cartoon and the rest shown as grey surface representation. Density for PI(4,5)P2 head group is shown in blue surface. (b) Zoomed-in view of the PI(4,5)P2-binding pocket with the density of its IP3 head group shown in blue surface. (c) Zoomed-in view of the PI(4,5)P2-binding pocket with side chains of IP3-interacting residues shown as yellow sticks. (d) Zoomed-in view of the IP3 position in the PI(3,5)P2-bound open TRPML1 structure. The C3 phosphate group directly interacts with Y355 and R403. (e) Comparison of the head group positions in PI(3,5)P2-bound open (green) and PI(4,5)P2-bound closed (orange) structures. The inositol rings PI(3,5)P2 and PI(4,5)P2 are colored yellow and cyan, respectively. The red arrow marks the upward movement of S1 from closed to open conformation.
Cryo-EM data processing scheme of the TRPML1 sample prepared in the presence of PI(4,5)P2.
(a) Representative micrograph. (b) Flow chart of the cryo-EM data processing procedure and the Euler angle distribution of particles used in the final three-dimensional reconstruction. Selected 2D class averages are shown. The final structure represents an open state. (c) Fourier Shell Correlation curves showing the overall resolution at FSC = 0.143.
Sample density maps of the PI(4,5)P2-bound closed TRPML1 structure contoured at 4 σ.
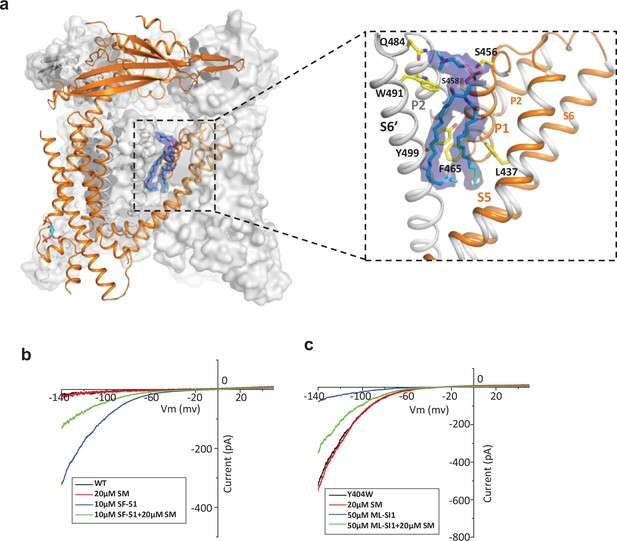
Sphingomyelin binding in TRPML1.
(a) Overall structure of PI(4,5)P2-bound TRPML1 and the zoomed-in view of the lipid-binding site. The lipid density is shown as blue surface and modeled as sphingomyelin (SM). The side chains of lipid-interacting residues are shown as yellow sticks. (b) SM inhibition effect on SF-51-activated wild-type TRPML1. (c) SM activation effect on ML-SI1-inhibited Y404W mutant. Currents shown in (b) and (c) were recorded using patch clamp in whole-cell configuration with pH 4.6 in the bath solution as the adverse effect of SM on agonist or antagonist is subtle and is measurable only at low luminal pH.
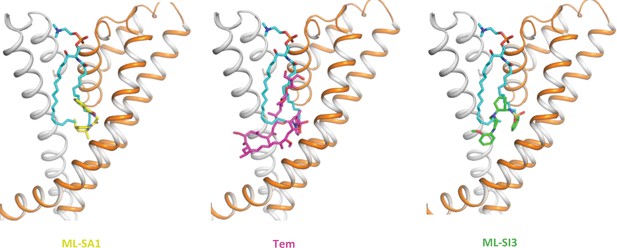
Sphingomyelin (cyan) binding overlaps with that of agonist ML-SA1 (yellow), rapamycin analog Tem (magenta), or antagonist ML-SI3 (green).
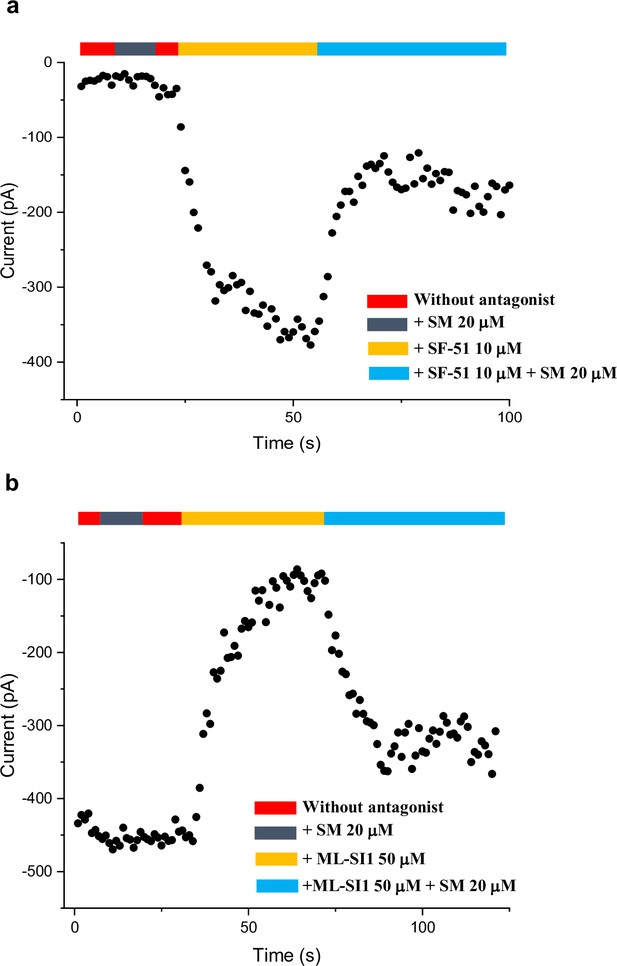
Time course plots of sphingomyelin affected TRPML1 current amplitudes.
(a) Sphingomyelin inhibition effect on SF-51-activated wild-type TRPML1. (b) SM activation effect on ML-SI1-inhibited Y404W mutant. Currents shown in (a) and (b) were recorded at –140 mV using patch clamp in whole-cell configuration with pH 4.6 in the bath solution as the adverse effect of SM on agonist or antagonist is subtle and is measurable only at low luminal pH.
Videos
Conformational changes between open and closed TRPML1.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | TOP10 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 18258012 | |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | DH10bac | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 10361012 | |
| Cell line (Spodoptera frugiperda) | Sf9 cells | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 11496015; RRID:CVCL_0549 | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | FreeStyle 293 F cells | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# R79007; RRID:CVCL_D603 | |
| Transfected construct (H. sapiens) | pEZT-BM-mTRPML1-CHis | This paper | N/A | Construct made to express the protein in HEK293F cells |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pEZT-BM | DOI:10.1016 /j.str.2016.03.004 | Addgene:74099 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mcoln1_F_primer: cgCTCGAG gccgccaccATGGCC ACCCCGGCGGGC | Integrated DNA Technologies | N/A | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mcoln1_R_primer: at gcggccgcTCAGTTC ACCAGCAGCGA | Integrated DNA Technologies | N/A | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mcoln1_Y404A_F_primer: cttgtggaaaaatgtcaggg cgcgaatgacaccgacccag | Integrated DNA Technologies | N/A | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mcoln1_Y404A_R_primer: ctgggtcggtgtcattcgcg ccctgacatttttccacaag | Integrated DNA Technologies | N/A | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mcoln1_Y404W_F_primer: cttgtggaaaaatgtcag ccagcgaatgacaccgaccc | Integrated DNA Technologies | N/A | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mcoln1_Y404W_R_primer: gggtcggtgtcattcgctg gctgacatttttccacaag | Integrated DNA Technologies | N/A | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Sodium Butyrate | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# 303410 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | n-dodecyl-β-D-maltopyranoside | Anatrace | Cat# D310 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | glyco-diosgenin | Anatrace | Cat# GDN101 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | ML-SA1 | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# SML0627 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | ML-SI1 | Medchemexpress | Cat# HY-134818 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | PI(4,5)P2 diC8 | Echelon | Cat# P-4508 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Sphingomyelin | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# 567706 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Temsirolimus | Fisher Scientific | Cat# 52-641-0 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | ML-SI3 | Selleckchem | Cat# E0026 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | SF-51 | Chemspace | Cat# CSSS00121681914 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Thrombin | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# T4648 | |
| Software, algorithm | MotionCor2 | Zheng et al., 2017 | https://emcore.ucsf.edu/ucsf-software | |
| Software, algorithm | GCTF | Zhang, 2016; JackZhang-Lab, 2021b | https://github.com/JackZhang-Lab/GCTF | |
| Software, algorithm | RELION | Scheres, 2012 | http://www2.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/relion | |
| Software, algorithm | Chimera | Pettersen et al., 2004 | RRID:SCR_004097 | https://www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera |
| Software, algorithm | PyMol | Schrödinger | RRID:SCR_000305 | https://pymol.org/2 |
| Software, algorithm | COOT | Emsley et al., 2010 | RRID:SCR_014222 | https://www2.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/personal/pemsley/coot |
| Software, algorithm | MolProbity | Chen et al., 2010 | http://molprobity.biochem.duke.edu/ | |
| Software, algorithm | PHENIX | Adams et al., 2010 | https://www.phenix-online.org | |
| Other | Superose 6 Increase10/300 GL | GE Healthcare | Cat# 29091596 | Used to perform gel filtration |
| Other | Ni-NTA Agarose | Qiagen | Cat# 30210 | Used to purify His-tagged protein |
| Other | Amicon Ultra-15 Centrifugal Filter Units | Milliporesigma | Cat# UFC9100 | Used to concentrate protein sample |
| Other | Quantifoil R 1.2/1.3 grid Au300 | Quantifoil | Cat# Q37572 | Used to prepare cryoEM samples |
| Commercial assay or kit | Cellfectin | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 10362100 | |
| Other | Sf-900 II SFM medium | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 10902088 | Used to culture SF9 cells |
| Other | FreeStyle 293 Expression Medium | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 12338018 | Used to culture HEK293F cells |
| Chemical compound, drug | Antibiotic Antimycotic Solution | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# A5955 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Proteinase K | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# EO0491 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Lipofectamine 2000 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 11668027 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Data collection and refinement statistics.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/100987/elife-100987-supp1-v1.docx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/100987/elife-100987-mdarchecklist1-v1.docx





