Synaptic cell adhesion molecule Cdh6 identifies a class of sensory neurons with novel functions in colonic motility
Figures
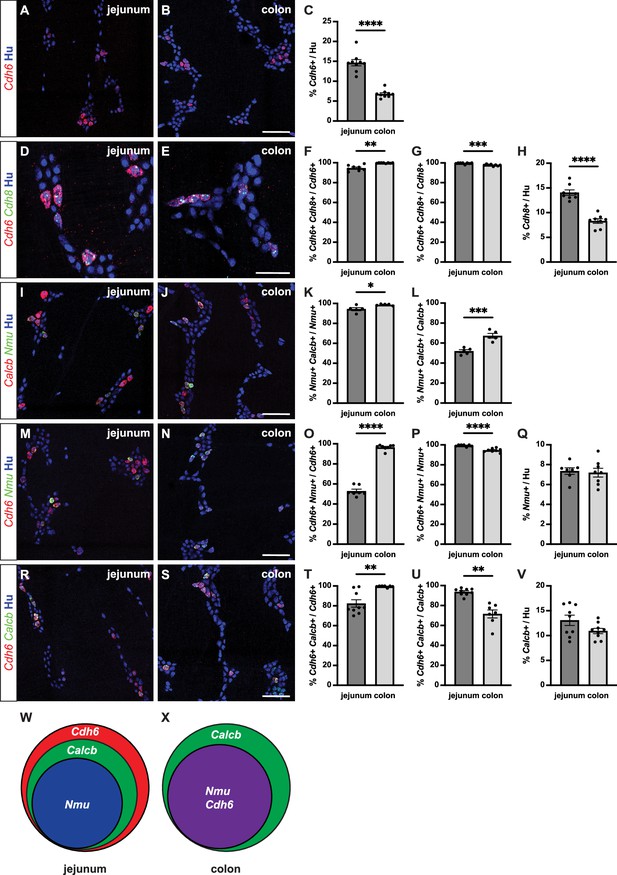
Cdh6 expression overlaps with intrinsic primary afferent neuron (IPAN) markers Calcb and Nmu.
(A, B) Representative images of jejunum (A) and distal colon (B) myenteric plexus labeled with HuC/D (IHC) (blue) and Cdh6 (RNA) (red). (C) Proportion of total HuC/D neurons positive for Cdh6 (jejunum, n=9; distal colon, n=9). (D, E) As in (A, B) for HuC/D (IHC) (blue), Cdh6 (RNA) (red), and Cdh8 (RNA) (green). (F) Proportion of Cdh6+ neurons positive for Cdh8 (jejunum, n=8; distal colon, n=8). (G) Proportion of Cdh8+ neurons positive for Cdh6 (jejunum, n=8; distal colon, n=8). (H) Proportion of total HuC/D neurons positive for Cdh8 (jejunum, n=8; distal colon, n=8). (I, J) As in (A, B) for HuC/D (IHC) (blue), Calcb (RNA) (red), and Nmu (RNA) (green). (K) Proportion of Nmu+ neurons positive for Calcb (jejunum, n=5; distal colon, n=5). (L) Proportion of Calcb+ neurons positive for Nmu (jejunum, n=5; distal colon, n=5). (M, N) As in (A, B) for HuC/D (IHC) (blue), Cdh6 (RNA) (red), and Nmu (RNA) (green). (O) Proportion of Cdh6+ neurons positive for Nmu (jejunum, n=7; distal colon, n=8). (P) Proportion of Nmu+ neurons positive for Cdh6 (jejunum, n=7; distal colon, n=8). (Q) Proportion of total HuC/D neurons positive for Nmu (jejunum, n=7; distal colon, n=8). (R, S) As in (A, B) for HuC/D (IHC) (blue), Cdh6 (RNA) (red), and Calcb (RNA) (green). (T) Proportion of Cdh6+ neurons positive for Calcb (jejunum, n=9; distal colon, n=7). (U) Proportion of Calcb+ neurons positive for Cdh6 (jejunum, n=9; distal colon, n=7). (V) Proportion of total HuC/D neurons positive for Calcb (jejunum, n=9; distal colon, n=9). (W, X) Schematic of marker overlap in jejunum (W) and distal colon (X). Scale bar represents 100 μm for (A, B, I, J, M, N, R, S), 50 μm for (D, E). All charts (mean ± SEM). *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001.
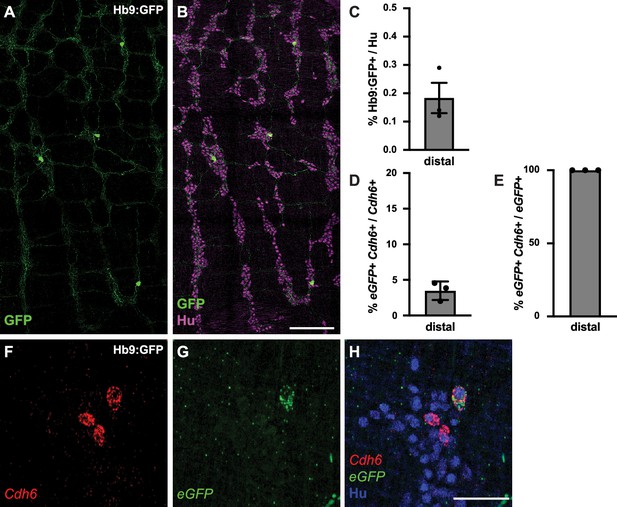
Hb9:GFP+ is expressed in a small proportion of Cdh6+ colon myenteric neurons.
(A, B) Representative images of Hb9:GFP+ distal colon myenteric plexus labeled with HuC/D (IHC) (magenta) and GFP (green). (C) Proportion of total distal colon HuC/D neurons positive for GFP (n=3). (D) Proportion of distal colon Cdh6+ neurons positive for eGFP (n=3). (E) Proportion of distal colon eGFP+ neurons positive for Cdh6 (n=3). (F–H) Representative images of Hb9:GFP+ distal colon myenteric plexus labeled with HuC/D (IHC) (blue), Cdh6 (RNA) (red), and eGFP (RNA) (green). Scale bar represents 200 μm for (A, B), 50 μm for (F-H). All charts (mean ± SEM).
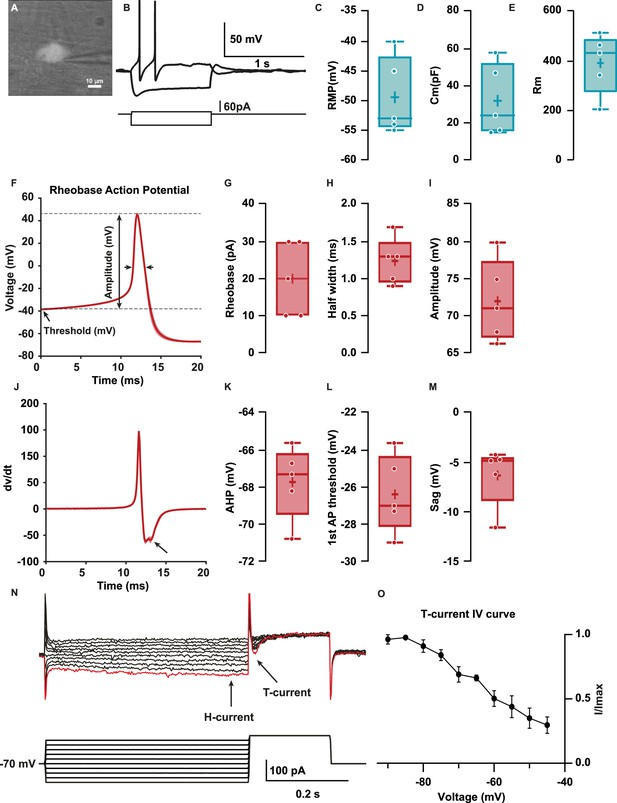
Hb9:GFP+ distal colon neurons have afterhyperpolarizing (AH) electrophysiological characteristics.
(A) IR videomicroscopy image of an Hb9:GFP distal colon neuron that presented a large soma located in a ganglion (scale bar, 10 μm). (B) Current-clamp recordings of the same neuron in (A) obtained in response to application of current pulse (bottom traces) of –50 pA and +10 pA. Note the presence of a sag and a post-hyperpolarization rebound depolarization. (C–E) Box-and-whisker plots of cellular properties of recorded neurons. (C) Resting membrane potential (RMP), (D) capacitance (Cm), and (E) membrane resistance (Rm) (N=5). (F) Averaged traces of the first spike (rheobase action potential) after a depolarization step of 1 s. (J) Averaged derivative traces of the first spike (rheobase action potential). An inflection on the repolarizing phase is observed in the first derivative (arrow). (G–I, K–N) Box-and-whisker plots of electrophysiological properties of recorded neurons; rheobase action potential (AP, G–I) (G) current threshold, (H) half-width, (I) amplitude, (K) afterhyperpolarization (AHP), and (L) threshold. (M, N) Non-AP properties sag (mV) and rebound (mV). (O) H and T currents in recorded neurons. Top: example of currents obtained from voltage protocol. Bottom: 500 ms hyperpolarizations ranging from –90 to –45 for 500 ms followed by depolarizing to –40 mV. Hyperpolarizations evoked slowly activating inward current (H-current, arrow), followed by a transient inward current upon post-conditioning step to –30 mV (T-current, arrow). Largest T and H currents were obtained with the most hyperpolarized potentials (red trace). (P) Normalized peak IT plotted versus holding potential to obtain the I/Imax curve (N=3/3). Scale bar represents 10 μm for (A).
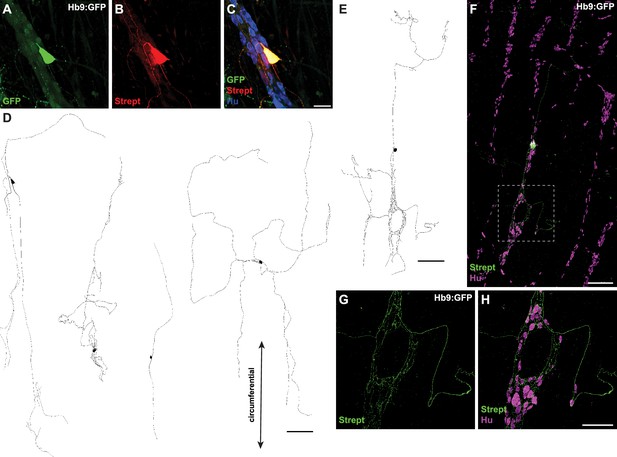
Hb9:GFP+ distal colon neurons have circumferential branching projections.
(A–C) Representative images of Hb9:GFP+ distal colon myenteric plexus labeled with HuC/D (blue), streptavidin (red), and GFP (green). (D, E) Tracings of Hb9:GFP+ distal colon neurons filled with biocytin during whole-cell patch-clamp recording. (F) Image of patched and filled Hb9:GFP+ distal colon neuron traced in (E). (G, H) Inset of (F). Scale bar represents 40 μm for (A–C), 200 μm for (D–F), 100 μm for (G, H).
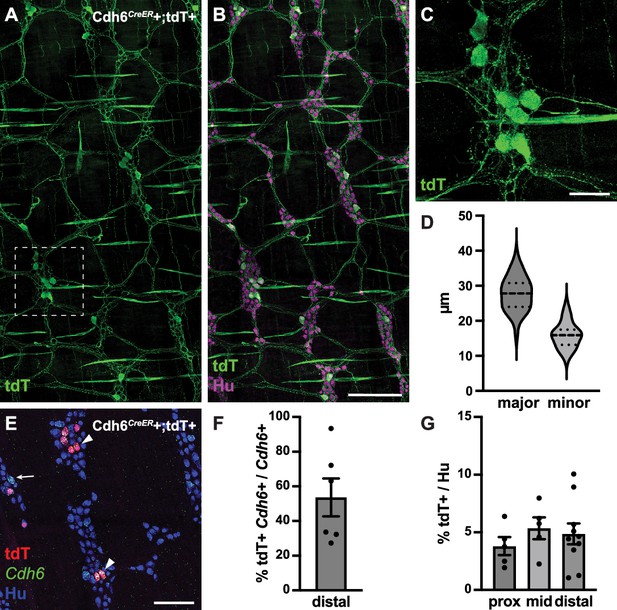
Cdh6CreER+/tdTomato+ neurons have Dogiel type II morphology.
(A, B) Representative images of Cdh6CreER+;tdTomato+ distal colon myenteric plexus labeled with HuC/D (IHC) (magenta) and tdTomato (IHC) (green). (C) Inset of (A). (D) Dimensions of tdTomato+ neurons (major and minor axes) (N=73; n=3). (E) Representative image of Cdh6CreER+;tdTomato+ distal colon myenteric plexus labeled with HuC/D (IHC) (blue), tdTomato (IHC) (red), and Cdh6 (RNA) (green). Arrowheads indicate Cdh6+/tdTomato+ cells; arrow, Cdh6+/tdTomato-negative cell. (F) Proportion of Cdh6+ distal colon neurons positive for tdTomato (n=6). (G) Proportion of total HuC/D neurons positive for tdTomato (proximal colon, n=5; mid colon, n=5; distal colon, n=10). Scale bar represents 100 μm for all images. All charts (mean ± SEM).
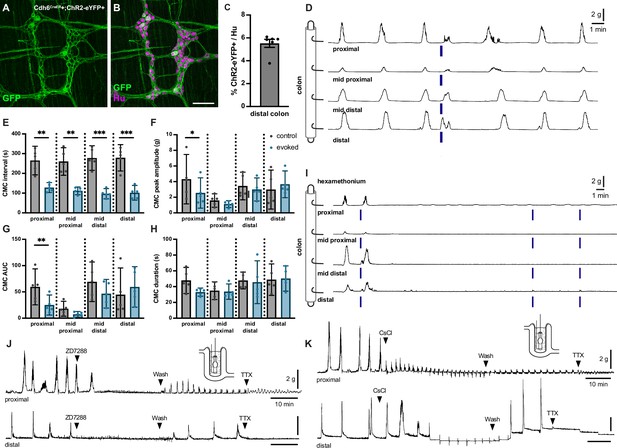
Optogenetic stimulation of distal colonic Cdh6+ neurons evokes colonic motor complexes (CMCs), while pharmacologic blockade of IH abolishes spontaneous CMCs.
(A, B) Representative images of Cdh6CreER+;ChR2-eYFP+ distal colon myenteric plexus labeled with HuC/D (magenta) and GFP (green). (C) Proportion of total distal colon HuC/D neurons positive for ChR2-eYFP (n=6). (D) Representative force traces. Blue bars indicate timing of light stimulation. LEDs placed distal to distal hook. (E) CMC intervals recorded from force traces. Evoked (blue) intervals represent the time from the prior spontaneous CMC before stimulation to the evoked CMC following stimulation. Control (gray) intervals represent the time between the spontaneous CMC prior to stimulation and the previous spontaneous CMC (n=5). Paired t test, one-tailed. (F) CMC peak amplitude recorded from force traces. Evoked (blue) indicates the evoked CMC following stimulation. Gray (control) indicates the spontaneous CMC prior to stimulation (n=5). Paired t test, two-tailed. (G) CMC AUC (area under the curve). Evoked (blue) and control (gray) as in (F) (n=5). Paired t test, two-tailed. (H) CMC duration. Evoked (blue) and control (gray) as in (F) (n=5). Paired t test, two-tailed. (I) Representative force traces. Hex indicates addition of 300 µM hexamethonium. Blue bars indicate timing of light stimulation. LEDs placed distal to distal hook (n=5/5). (J) Representative force traces on tethered pellets. First arrowhead indicates addition of 10 µM ZD7288. Second arrowhead indicates washout in Krebs. Third arrowhead indicates addition of 1 µM TTX. ZD7288 abolished CMCs in both proximal and distal colon (n=6/6, p=0.0022, Fisher’s exact test). Washout in Krebs restored CMCs in both proximal and distal colon (n=6/6, p=0.0022, Fisher’s exact test). (K) As in (J). First arrowhead indicates addition of 2 mM CsCl. Second arrowhead indicates washout in Krebs. Third arrowhead indicates addition of 1 µM TTX. Typical CMC production was impaired or altered by CsCl (proximal colon, n=5/6, p=0.0152; distal colon, n=6/6, p=0.0022, Fisher’s exact test): increased frequency (proximal colon, n=5/6, p=0.0152; distal colon, n=6/6, p=0.0022, Fisher’s exact test), decreased in amplitude (proximal colon, n=5/6, p=0.0152; distal colon, n=4/6, p=0.0606, Fisher’s exact test); retrograde force (proximal colon, n=2/6; distal colon, n=2/6). Scale bar represents 100 μm for (A, B). *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.
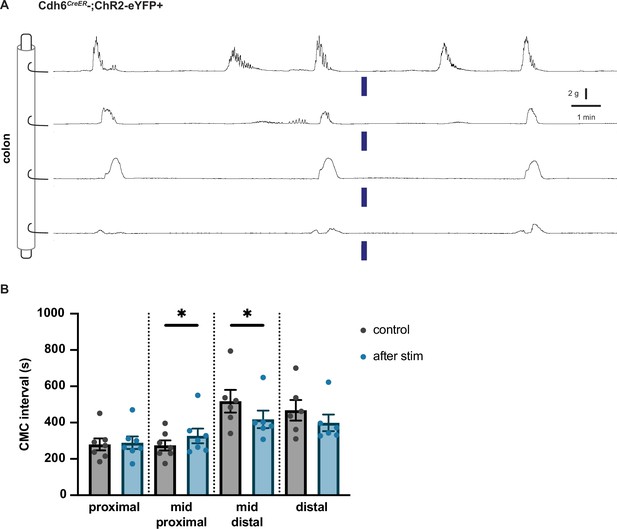
Optogenetic stimulation control.
(A) Representative force traces of control Cdh6CreER-;Chr2eYFP+ colon (n=5). Blue bars indicate timing of light stimulation. LEDs placed distal to distal hook. (B) The duration of CMC intervals recorded from force traces in control Cdh6CreER-;Chr2eYFP+ colon. CMC intervals containing optical stimulation are shown in blue in comparison to preceding spontaneous CMC intervals shown in black/grey (control). Each data point represents average data from a single animal. N=7 for the first two groups (proximal and mid-proximal) and N=6 for the last two groups (mid-distal and distal). Paired t test, one tailed.
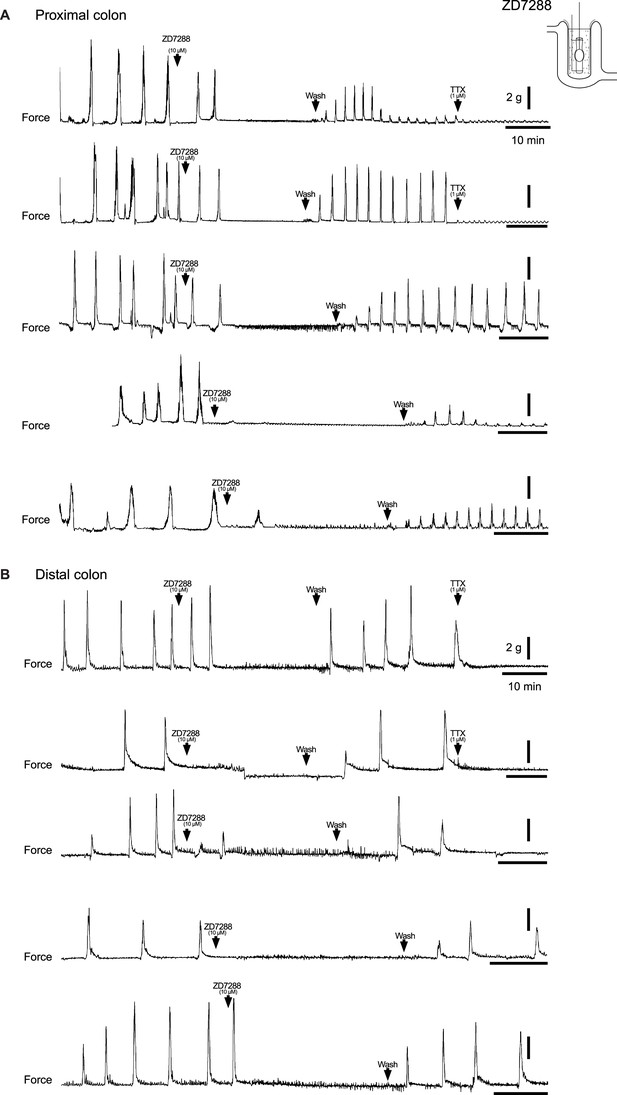
Pharmacologic blockade of IH with ZD7288 abolishes spontaneous colonic motor complexes (CMCs).
(A, B) Representative force traces from tethered pellet in proximal half (A) or distal half (B) of colon. Addition of 10 µM ZD7288 (first arrowhead), followed by washout in Krebs (second arrowhead), and addition of 1 µM TTX (third arrowhead). Scale bars represent 2 g force (vertical bars) and 10 min (horizontal bars) for all traces.
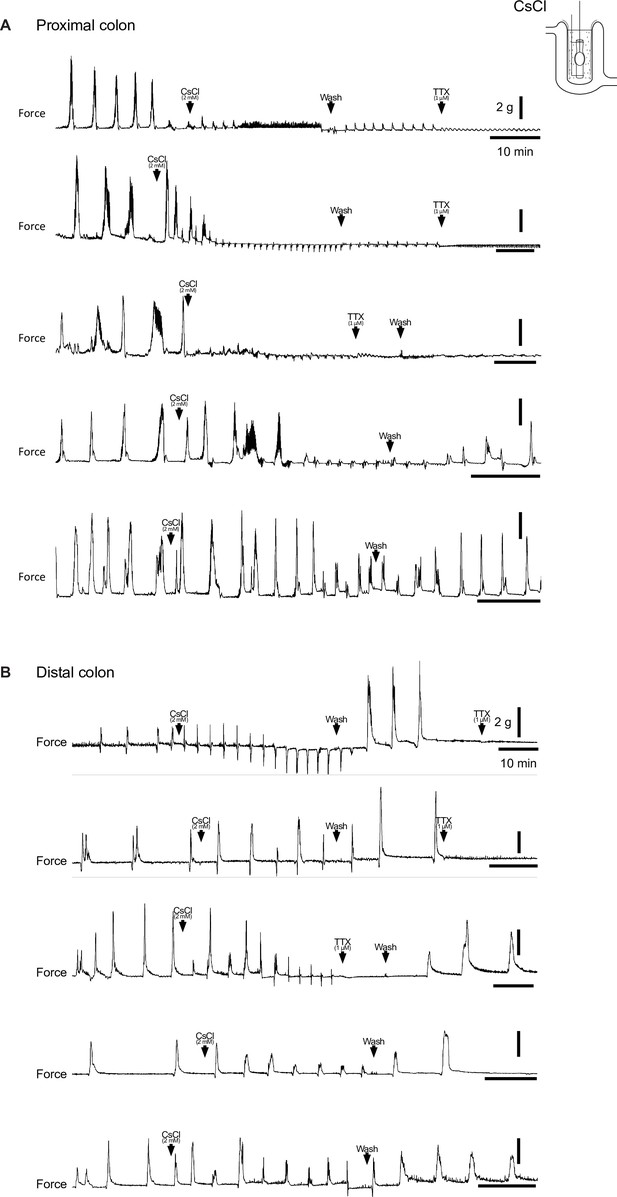
Pharmacologic blockade of IH with CsCl impairs generation of colonic motor complexes (CMCs).
(A, B) Representative force traces from tethered pellet in proximal half (A) or distal half (B) of colon. Addition of 2 mM CsCl (first arrowhead), followed by washout in Krebs (second arrowhead), and addition of 1 µM TTX (third arrowhead). Scale bars represent 2 g force (vertical bars) and 10 min (horizontal bars) for all traces.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus) | C57BL/6J | Jackson Laboratory | #000664 | |
| Strain, strain background (M. musculus) | Hb9:GFP | Jackson Laboratory | #005029 | |
| Strain, strain background (M. musculus) | Ai14 | Jackson Laboratory | #007908 | |
| Strain, strain background (M. musculus) | Ai32 (ChR2-eYFP) | Jackson Laboratory | #024109 | |
| Strain, strain background (M. musculus) | Cdh6CreER | Xin Duan, UCSF | ||
| Antibody | Human anti-HuC/D | Vanda Lennon, Mayo Clinic | IF(1:75,000) | |
| Antibody | Sheep anti-GFP (polyclonal) | Biogenesis | Cat# 4745-1051, RRID:AB_619712 | IF(1:1000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit anti-RFP (polyclonal) | Rockland | Cat# 600-401-379, RRID:AB_2209751 | IF(1:1000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit anti-PGP9.5 (polyclonal) | Abcam | #ab15503, RRID:AB_301912 | IF(1:4000) |
| Antibody | Donkey anti-human Alexa Fluor (AF)-647 (polyclonal) | Jackson ImmunoResearch | #709-605-098, RRID:AB_2340577 | IF(1:500) |
| Antibody | Donkey anti-sheep AF-488 (polyclonal) | Invitrogen | #A11015, RRID:AB_141362 | IF(1:1000) |
| Antibody | Donkey anti-rabbit AF-488 (polyclonal) | Invitrogen | #A21206, RRID:AB_2535792 | IF(1:1000) |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Streptavidin AF-546 | Invitrogen | #S11225 | IF(1:500) |
| Sequence-based reagent | RNAscope probe Mm-Cdh6 | Advanced Cell Diagnostics | Cat #519541 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | RNAscope probe Mm-Cdh8 | Advanced Cell Diagnostics | Cat #485461 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | RNAscope probe Mm-Nmu | Advanced Cell Diagnostics | Cat #446831 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | RNAscope probe Mm-Calcb | Advanced Cell Diagnostics | Cat #425511 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | RNAscope probe Mm-eGFP | Advanced Cell Diagnostics | Cat #400281 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | RNAscope Multiplex Fluorescent V2 Assay kit with RNA-Protein Co-detection Ancillary Kit | Advanced Cell Diagnostics | Cat #323100 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Protease XIV | Sigma | #P5417 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Collagenase | Worthington | #CLS-4 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dispase | Sigma | #D4693 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | ZD7288 | Sigma-Aldrich | #73777 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Cesium chloride | Sigma-Aldrich | #C4036 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tetrodotoxin citrate | Alomone Labs | #T-550 | |
| Software, algorithm | Imaris Filament Tracer | Bitplane, Oxford Instruments | ||
| Software, algorithm | LabChart 7, 8 | AD Instruments | ||
| Software, algorithm | Prism 9 | GraphPad |





