Quantification of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium population dynamics in murine infection using a highly diverse barcoded library
Figures
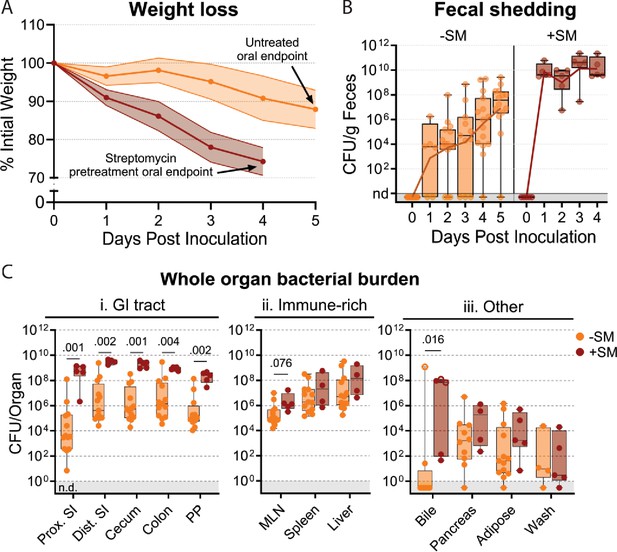
S. Typhimurium burden following orogastric inoculation of untreated or streptomycin-treated mice.
(A) Percentage of initial weight over time; means and standard deviations are shown. (B) Bacterial fecal burden. Box and whisker plots represent max-to-min and interquartile ranges. (C) Bacterial burden in organs and fluids. Open circles indicate when the whole gallbladder was used instead of bile. Box and whisker plots represent max-to-min and interquartile ranges. Untreated n=16 (8 males and 8 females), streptomycin (SM) pretreated n=5 (female) unless otherwise noted. Sex-disaggregated data in Figure 3—figure supplement 2. Mann-Whitney tests were used for statistical analyses. Values with p<0.1 shown. Abbreviations: Adipose, left perigonadal adipose tissue; MLN, mesenteric lymph node; PP, Peyer’s patches; SI, small intestine; wash, peritoneal wash.
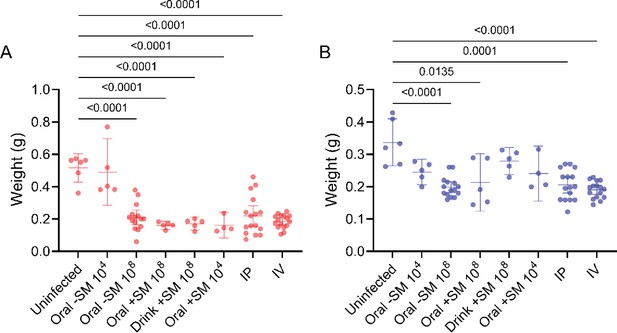
Weight of cecum (A) and colon (B) after different infection schemes.
Mann-Whitney tests were used for statistical analyses.
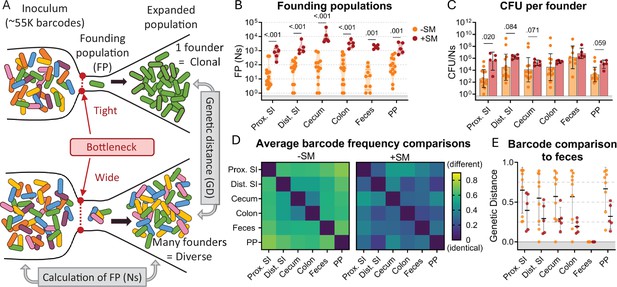
The bottleneck to S. Typhimurium intestinal colonization in orogastrically inoculated mice is widened after streptomycin treatment.
(A) Schematic depicting the effect of a tight versus wide bottleneck on a diverse inoculum and the STAMPR analytical methods used to calculate the founding population (FP) and compare populations at separate sites of infection using genetic distance (GD) analysis. (B) Founding populations (Ns) of intestinal samples. Truncated violin plot with all points shown. (C) CFU per founder (CFU/Ns) in intestinal tissues. Bars are geometric means and geometric standard deviations. (D) Heatmaps of average genetic distance comparisons throughout the GI tract in untreated (left) and streptomycin-treated (right) mice. (E) Comparison of genetic distance of GI tract to fecal samples. Mann-Whitney tests were used for statistical analyses. Values with p<0.1 shown. Abbreviations: PP, Peyer’s patches; SI, small intestine; SM, streptomycin.
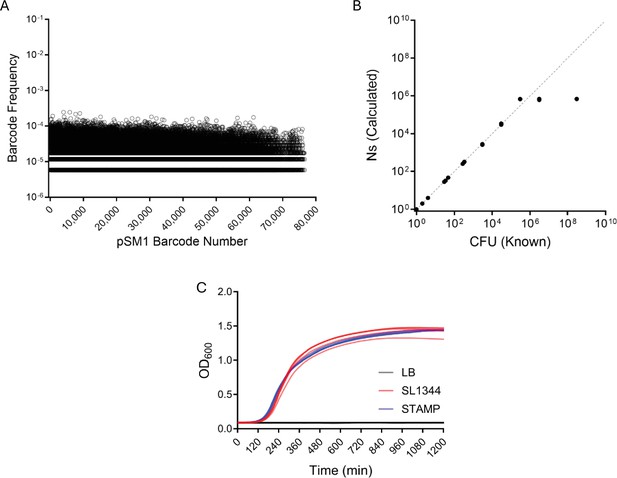
S. Typhimurium barcoded library diversity and standard curve.
(A) Barcodes in S Typhimurium library were mapped to the barcodes in the donor library (pSM1) and the frequency of barcodes in the S. Typhimurium library were distributed relatively evenly. (B) Calibration curve indicating the library has an Ns resolution limit of ~7 × 105. (C) Growth of barcoded STAMP library in LB supplemented with SM is not different than the parent strain (SL1344). Significance was tested with Mann-Whitney test and growth curves were performed 5 times. Curves displayed with 50% opacity.
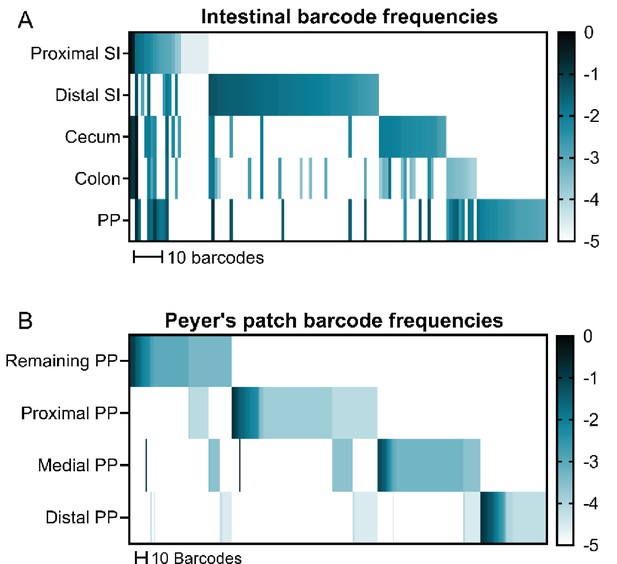
Barcodes from different regions of the intestine and Peyer’s patches from a single animal are largely distinct.
(A) Barcode frequencies of different regions of the intestine and (B) individual Peyer’s patches (PP) of an untreated mouse after orogastric gavage of S. Typhimurium. “Remaining PP” sample contains the PP from the animal not taken for individual analysis. Frequencies of barcodes are displayed as heatmaps (each box represents a barcode and darker colors represent increased frequency within the sample) and sorted by abundance in each sample sequentially.
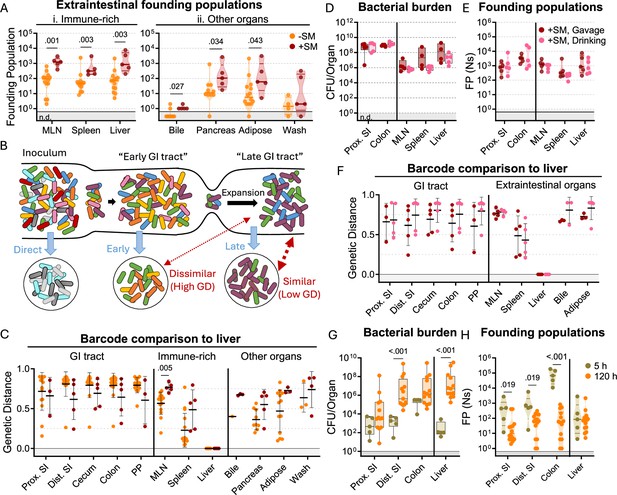
S. Typhimurium disseminates from the intestine before substantial replication.
(A) Founding populations and (C) genetic distance from the liver after orogastric inoculation (Gavage) of S. Typhimurium with (+SM) or without (-SM) streptomycin pretreatment. (B) Scheme depicting proposed dissemination patterns during infection. (D–F) Organ CFUs (D), founding populations (E), and genetic distance from the liver (F) after inoculation via drinking (+SM, Drinking) are not statistically different from orogastric gavage (+SM, Gavage). Data for +SM, gavage mice repeated from Figures 1—3. (G–H) Organ CFUs (G) and founding populations (H) in untreated mice at 5 or 120 hr after inoculation. 120 hr data repeated from Figures 1—3. +SM, Drinking n=5, untreated 5 hr n=5. Mann-Whitney tests were used for statistical analyses. Values with p<0.1 shown. Abbreviations: GD, genetic distance; GI, gastrointestinal; MLN, mesenteric lymph node; PP, Peyer’s patches; SI, small intestine.
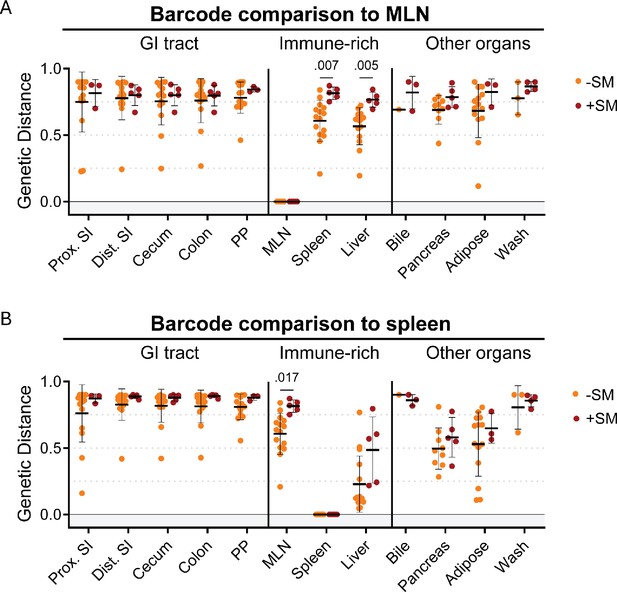
S. Typhimurium disseminates to the MLN and spleen prior to substantial replication in the intestine.
Genetic distance from the MLN (A) and spleen (B) after orogastric inoculation of S. Typhimurium with (+SM) or without (-SM) streptomycin pretreatment. -SM n=16 (8 males and 8 females),+SM n=5 (female). Mann-Whitney tests were used for statistical analyses. Values with p<0.1 shown. Abbreviations: GI, gastrointestinal; MLN, mesenteric lymph node; PP, Peyer’s patches; SI, small intestine.
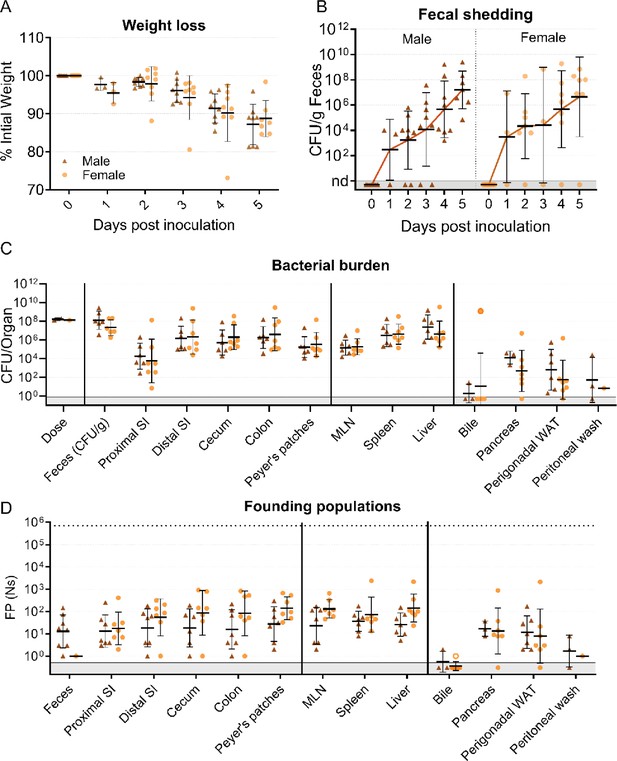
Sex-disaggregated data in mice inoculated through orogastric gavage.
(A) Percentage of initial weight over time; means and standard deviations shown. (B) Bacterial burden in feces. (C) Bacterial burden in organs and fluids, open circles indicate when the whole gallbladder was taken instead of bile. (D) Founding populations (Ns) in organs and fluids. Geometric means and geometric standard deviations are used unless otherwise noted. -SM female n=8, -SM male n=8.
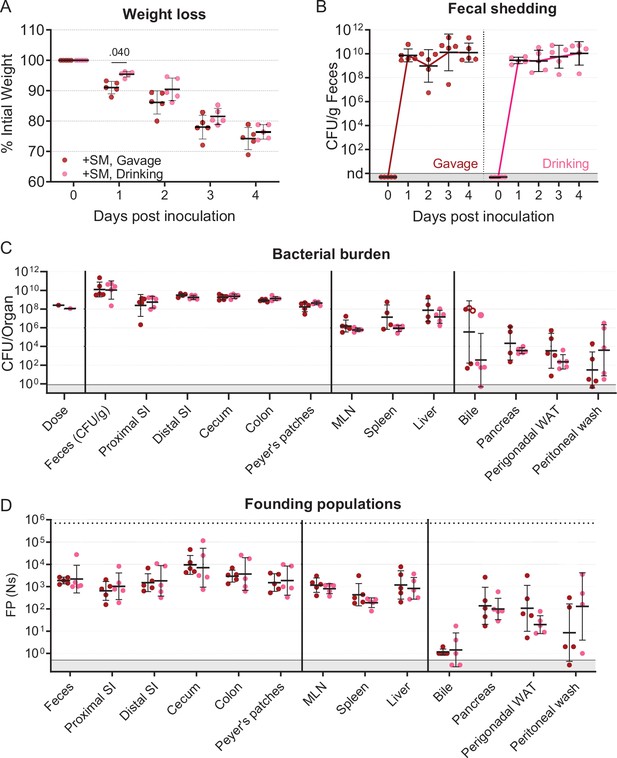
Extended data for streptomycin pretreated mice inoculated through orogastric gavage and drinking.
(A) Percentage of initial weight over time; means and standard deviations shown. (B) Bacterial burden in feces. (C) Bacterial burden in organs and fluids, open circles indicate when the whole gallbladder was taken instead of bile. (D) Founding populations (Ns) in organs and fluids. Geometric means and geometric standard deviations are used unless otherwise noted. +SM, Gavage female n=5, and +SM, Drinking female n=5. Mann-Whitney tests were used for statistical analyses. Values with p<0.1 shown.
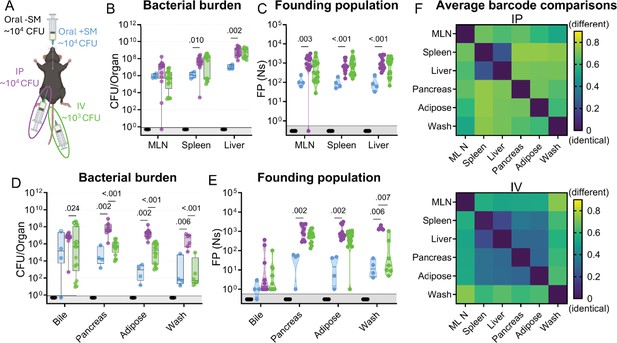
S. Typhimurium population dynamics following different routes of inoculation.
(A) Infections were performed via 3 routes: orogastric gavage with (Oral +SM) or without (Oral -SM) streptomycin pretreatment, intraperitoneal injection (IP), and intravenous injection (IV). (B–C) Bacterial burden (B) and founding populations (C) in immune-rich extraintestinal organs. (D–E) Bacterial burden (D) and founding population (E) in extraintestinal samples. (F) Heatmaps of average genetic distance between extraintestinal organs after IP (top) and IV (bottom) inoculation. Box and whisker plots represent max-to-min and interquartile ranges. Truncated violin plots with all points displayed. Oral -SM n=5, Oral +SM n=4, IP n=16 (8 male, 8 female), IV n=16 (8 male, 8 female). Sex-disaggregated data in Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Mann-Whitney tests were used for statistical analyses. Values with p<0.1 shown. Abbreviations: MLN, mesenteric lymph node.
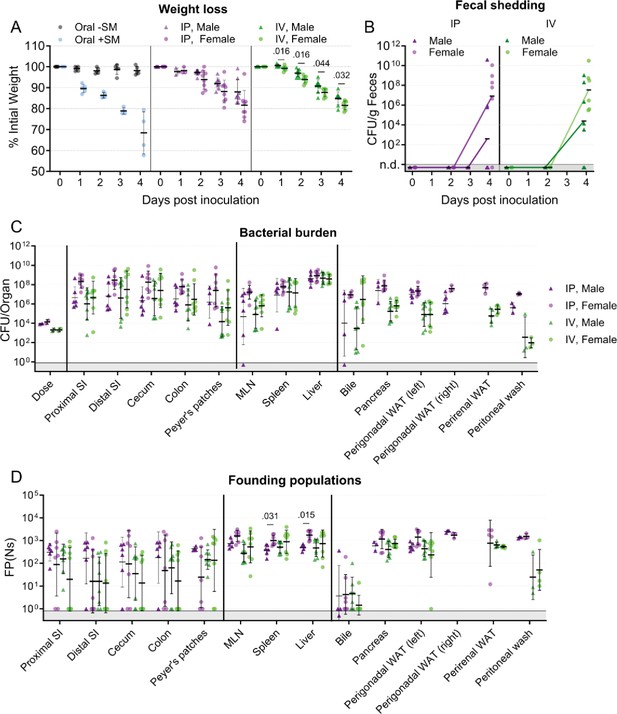
Sex-disaggregated data in mice after inoculation with 103–104 CFU S.Typhimurium through different routes.
(A) Percentage of initial weight over time; means and standard deviations shown. (B) Sex-disaggregated bacterial burden in feces. (C) Bacterial burden in organs and fluids. (D) Founding populations (Ns) in organs and fluids. Geometric means and geometric standard deviations are used unless otherwise noted. Oral -SM female n=5, Oral +SM n=5, IP male n=8, IP female n=8, IV male n=8, and IV female n=8. Statistical analysis is a Mann-Whitney test. Values with p<0.1 are shown.
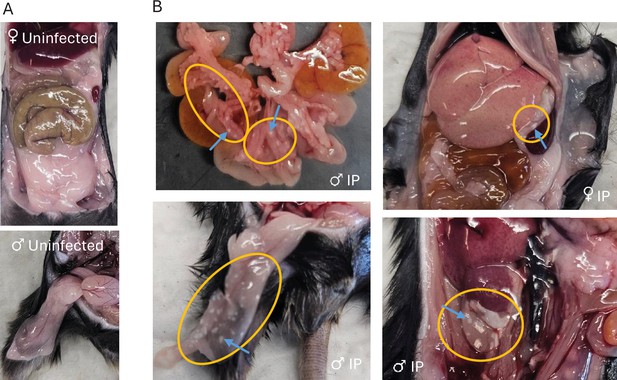
Pathology observed in mouse adipose tissue.
(A) Images of uninfected adipose. (B) Images of white spots on mesenteric (top left), upper mesenteric (top right), perigonadal (bottom left) and perirenal (bottom right) adipose in mice. Yellow circles outline areas with pathology. Blue arrows point to focal lesions. Abbreviations: IV, intravenous; IP, intraperitoneal.
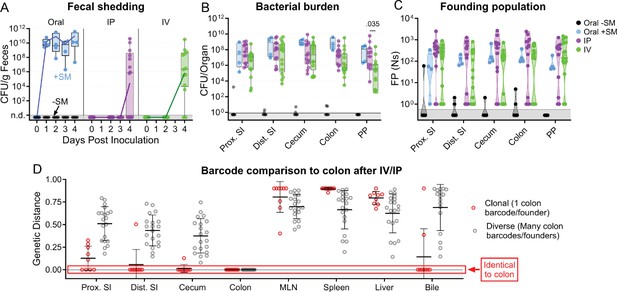
S. Typhimurium population dynamics after IV and IP inoculation differ compared to those after oral gavage.
(A) Fecal shedding after orogastric gavage with (Oral +SM) or without (Oral -SM) streptomycin pretreatment, intraperitoneal injection (IP), and intravenous injection (IV) with S. Typhimurium. (B) Bacterial burdens in the intestine. Box and whisker plots represent max-to-min and interquartile ranges. (C) Founding population of GI organs. (D) Genetic distance comparison of colon samples of IV and IP animals to other sites disaggregated by number of colon founders. Means and standard deviations displayed. Mann-Whitney tests were used for statistical analyses. Values with p<0.1 shown. Abbreviations: MLN, mesenteric lymph node; PP, Peyer’s patches; SI, small intestine.
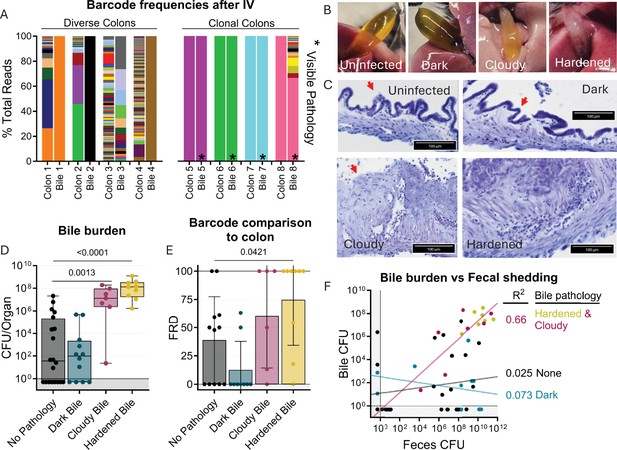
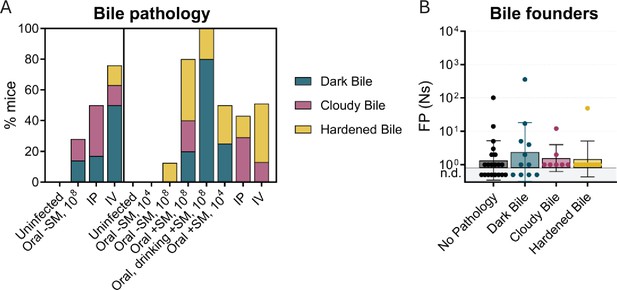
Bile re-seeding the intestine is correlated with gallbladder pathology.
(A) Barcode frequency of clonal and diverse colons and bile in mice after IV inoculation. Asterisks indicate visible pathology in the bile. (B) Gross anatomy and (C) H&E-stained sections of normal, dark, cloudy, and hardened bile after S. Typhimurium infection. Red arrows indicate the luminal side of the gallbladder. (D) CFU in bile after all infection routes disaggregated by bile phenotype. Box and whisker plots represent max-to-min and interquartile ranges. (E) FRD of bile barcodes also found in colon samples. Bars are means with standard deviations. (F) Fecal shedding correlates with bile burden when hardened or cloudy bile is present. Line of best fit displayed. Mann-Whitney tests were used for statistical analyses. Values with p<0.1 shown.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus) | C57BL/6 J | Jackson laboratory | Strain #:000664 RRID:IMSR_JAX:000664 | Mice |
| Strain, strain background (Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium) | SL1344 | Hoiseth and Stocker, 1981 | NCBI:txid216597 | Bacterial strains |
| Software, algorithm | STAMPR scripts | Hullahalli et al., 2021; Hullahalli, 2024 | https://github.com/hullahalli/stampr_rtisan | STAMP sample processing |
Primer sequences for PCR.
| Name | Sequence |
|---|---|
| Forward Primers | |
| var21 | AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTAATGATGGGTTAAAAAGGATCGATCC |
| var22 | AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTATGCGATGGGTTAAAAAGGATCGATCC |
| var23 | AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTTGCACGATGGGTTAAAAAGGATCGATCC |
| var24 | AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTTCATTCGATGGGTTAAAAAGGATCGATCC |
| var25 | AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTGAATCGAGATGGGTTAAAAAGGATCGATCC |
| var26 | AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTGTCAACTTGATGGGTTAAAAAGGATCGATCC |
| var27 | AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTCGGCGTGGCGATGGGTTAAAAAGGATCGATCC |
| var28 | AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTCC TGTACCTTGATGGGTTAAAAAGGATCGATCC |
| Reverse Primers | |
| AD001 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCGT GATGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD002 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATACATCGGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD003 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATGCCTAAGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD004 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATTGGTCAGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD005 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCACTGTGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD006 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATATTGGCGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD007 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATGATCTGGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD008 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATTCAAGTGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD009 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCTGATCGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD010 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATAAGCTAGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD011 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATGTAGCCGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD012 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATTACAAGGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD013 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATTTGACTGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD014 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATGGAACTGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD015 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATTGACATGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD016 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATGGACGGGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD018 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATGCGGACGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD019 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATTTTCACGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD020 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATGGCCACGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD021 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCGAAACGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD022 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCGTACGGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD023 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCCACTCGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD025 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATATCAGTGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
| AD027 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATAGGAATGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCAGATCCTTGGCGGCAAGAAA |
Additional files
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/101388/elife-101388-mdarchecklist1-v1.pdf
-
Source data 1
Barcode counts for all samples in the manuscript (separate file).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/101388/elife-101388-data1-v1.csv