Valence and salience encoding in the central amygdala
Figures
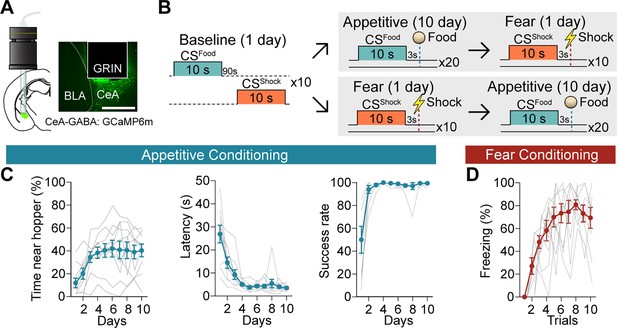
Acquisition of calcium signals during Pavlovian appetitive and fear conditioning.
(A) CeA-GABAergic neurons were labelled with GCaMP6m, and their activity was recorded using a miniature microscope (Inscopix) via an implanted GRIN lens (left). A representative image of GCaMP6m expression and lens placement is shown on the right. Scale bar, 0.5 mm. (B) Behavioral paradigm of the baseline, appetitive, and fear conditioning. To counterbalance the order of the two valence conditioning paradigms, there were two groups: appetitive → fear (5 mice) and fear → appetitive (5 mice) after the baseline session. (C) Time spent near the food hopper during CSFood (left, day: F=7.422, P=0.0005), latency to procure a pellet (middle, day: F=20.41, P<0.0001), and success rate (right, day: F=14.69, P=0. 0017) over 10 days of appetitive learning (mean ± s.e.m., grey lines represent individual data, n=10). (D) Freezing behavior during CSShock (trial: F=13.49, P<0.0001) throughout 10 trials of fear conditioning (mean ± s.e.m., grey lines represent individual data, n=10). Detailed information about statistical results is provided in Supplementary file 1.

GRN lens placements.
Histological reconstructions of GRIN lens locations.
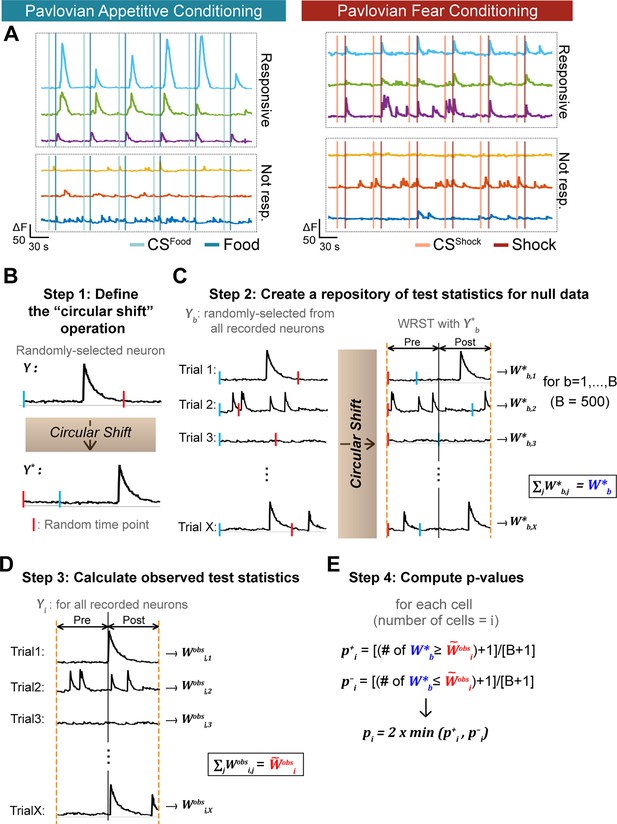
Determination of CeA responses to appetitive and fearful stimuli.
(A) Left: Example traces of CeA neurons that were responsive (upper three traces) and not responsive to food reward (bottom three traces). Right: Example traces of CeA neurons that were responsive (upper three traces) and not responsive to foot shock (bottom three traces). (B) Step 1: Defining the “circular shift” operation. A neuron is randomly selected from the recorded neuron pool in our current study (denoted as ). The calcium trace of the selected neuron is subjected to a circular shift operation, wherein it is moved from a randomly chosen time point (red bar). This operation results in a new calcium trace, as shown by the movement of the blue bar in (B); the traces that initially start with blue bars become red bar starting traces. (C) Step 2: Creating a repository of test statistics for null data. A neuron is selected at random; then, the activity in each of its trials (20 trials for appetitive or 10 trials for fear conditioning, X=the number of trials) undergoes ‘circular shifting’, where a random point (red bar) is chosen within the circular shifting range. Then, on each trial, the Wilcoxon rank sum test between pre-stimulus vs. post-stimulus periods is computed. The final test statistic representing a summary of all trials is obtained by summing the individual Wilcoxon rank sum test statistics over the trials with Step 2 is repeated times (we used B=500), generating a null distribution of summed statistics . (D) Step 3: calculating observed test statistics. Each observed neuron receives a summary test statistic obtained by summing the Wilcoxon rank sum test statistics from the individual trials. (E) Step 4: Computing p-values. A p-value for the ith neuron comes from a comparison of with . For the ith neuron, (the number of ≥ +1 divided by B+1) and (the number of ≤ +1 divided by B+1) are calculated. The final p-value for the ith neuron (denoted as ) is 2 times the lesser of and . A detailed description of this statistical analysis is provided in Methods.
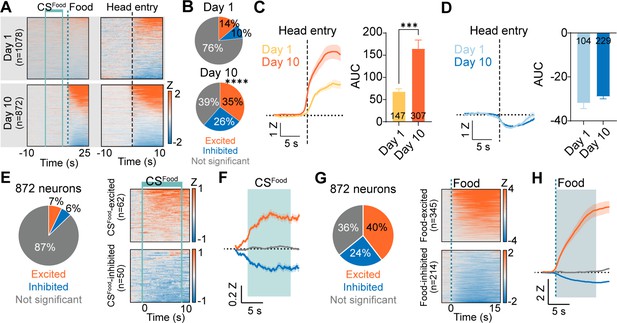
Responses of CeA neurons during Pavlovian appetitive conditioning.
(A) Top: Heat maps of CeA neurons aligned to CSFood onset (top left, 1078 neurons) and head entry (top right) from day 1 of Pavlovian appetitive conditioning. Bottom: Heat maps of CeA neurons aligned to CSFood onset (bottom left, 872 neurons) and head entry (bottom right) from day 10 of Pavlovian appetitive conditioning. Solid mint lines indicate CSFood, and a dotted darker mint line represents food delivery. Black dotted line represents the first head entry after food delivery. (B) Proportion of head entry responsive neurons between day 1 (top) and day 10 (bottom). (C) Left: The average Z-scored activity of head entry-excited neurons on day 1 (147 neurons) and day 10 (307 neurons) of appetitive conditioning during –10 s to 10 s after the first head entry of each reward delivery. The dark lines and shaded areas indicate the mean and standard error of the mean (s.e.m.). Right: Average area under the curve (AUC) for the Z-scored activity after head entry on day 1 compared to day 10 of appetitive conditioning (0–5 s after head entry, mean ± s.e.m.). (D) Left: The average Z-scored activity of head entry-inhibited neurons on day 1 (104 neurons) and day 10 (229 neurons) of appetitive conditioning during –10 s to 10 s after the first head entry of each reward delivery. Right: Average AUC for the Z-scored activity after head entry on day 1 compared to day 10 of appetitive conditioning (0–5 s after head entry). (E) Left: Proportion of CSFood -excited (orange), CSFood -inhibited (blue), and not significant neurons (grey) on day 10 of appetitive learning (total 872 neurons). Right: Heat maps of CSFood-excited neurons (top, n=62) and CSFood-inhibited neurons (bottom, n=50) from all trials (20 trials). Solid mint lines indicate CSFood onset and offset. (F) The average Z-scored activity of each response type (orange, CSFood-excited; blue, CSFood-inhibited; grey, not significant). The dark lines and shaded areas represent the mean and s.e.m. The mint area represents 10 s of CSFood. (G) Left: Proportion of food-excited (orange), food-inhibited (blue), and not significant neurons (grey) on day 10 of appetitive learning (total 872 neurons). Right: Heat maps of food-excited neurons (top, n=345) and food-inhibited neurons (bottom, n=241) from all trials (20 trials). The dotted line indicates a food delivery (H) The average Z-scored activity of each response type (orange, food-excited; blue, food-inhibited; grey, not significant). The dark lines and shaded areas represent the mean and s.e.m. ***P< 0.001, ****P< 0.0001. Detailed information about statistical results is provided in Supplementary file 1.

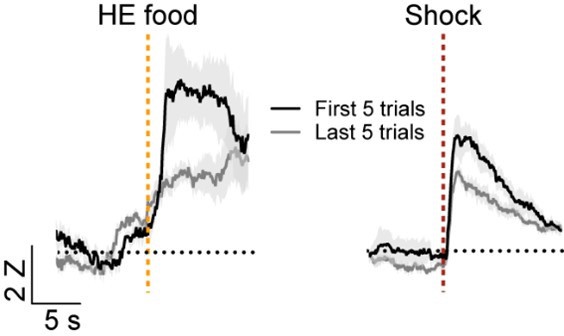
CSFood and food response in the CeA neurons.
(A) Proportion of CSFood-only, Food-only, CSFood+ Food, and not significant neurons during appetitive learning. Blue and orange in the outer pie chart indicate the number of excited and inhibited responses from CSFood-only and Food-only responsive neurons. (B) The average Z-scored activity of CSFood excited +Food excited (first), CSFood excited+ Food inhibited (second), CSFood inhibited+ Food excited (third) and CSFood inhibited+ Food inhibited (fourth) neurons. (C) Left: Average Z-scored activity of CSFood-excited neurons during the first five trials (early; grey) vs. the last five trials (late; black) of appetitive learning. Right: Average AUC for the Z-scored activity during CSFood (0–10 s, mean ± s.e.m.). (D) Left: Average Z-scored activity of CSFood-inhibited neurons during the first five trials (early; grey) vs. the last five trials (late; black) of appetitive learning. Right: Average AUC for the Z-scored activity during CSFood (0–10 s). (E) Left: Average Z-scored activity of food-inhibited neurons during the first five trials vs. the last five trials. A dotted darker mint line indicates food delivery. Right: Average AUC for the Z-scored activity after food delivery (t=3.787, P=0.0002). (F) Left: Average Z-scored activity of shock-excited neurons during the first five trials vs. the last five trials. Right: Average AUC for the Z-scored activity after shock delivery (0–10 s; t=5.246, P<0.0001). The dark lines and shaded areas represent the mean and s.e.m. **P< 0.01, ***P< 0.001. Detailed information about statistical results is provided in Supplementary file 1.
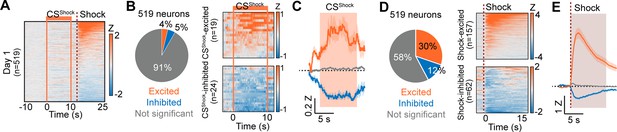
Responses of CeA neurons during Pavlovian fear conditioning.
(A) Heat maps of CeA neurons aligned to CSShock onset (519 neurons) from day 1 of Pavlovian fear conditioning. Solid orange lines indicate CSShock, and a dotted red line represents shock delivery. (B) Left: Proportion of CSShock-excited (orange), CSShock-inhibited (blue), and not significant neurons (grey) on day 1 of fear conditioning (total 519 neurons). Right: Heat maps of CSShock-excited neurons (top, n=19) and CSShock-inhibited neurons (bottom, n=24) from all trials (10 trials). Solid orange lines indicate CSShock onset and offset. (C) The average Z-scored activity of each response type (orange, CSShock-excited; blue, CSShock-inhibited; grey, not significant). The dark lines and shaded areas represent the mean and s.e.m. The orange area represents 10 s of CSShock. (D) Left: Proportion of shock-excited (orange), shock-inhibited (blue), and not significant neurons (grey) on day 1 of fear conditioning (total 519 neurons). Right: Averaged heat maps of shock-excited neurons (top, n=157) and shock-inhibited neurons (bottom, n=62) from all trials (10 trials). A dotted red line represents shock delivery. (E) The average Z-scored activity of each response type (orange, shock-excited; blue, shock-inhibited; grey, not significant). The dark lines and shaded areas represent the mean and s.e.m.

CSShock and shock response in the CeA neurons.
(A) Proportion of CSShock-only, Shock-only, CSShock +Shock, and not significant neurons during fear conditioning. Blue and orange in the outer pie chart indicate the number of excited and inhibited responses from CSShock-only and Shock-only responsive neurons. (B) The average Z-scored activity of CSShock excited +Shock excited (first), CSShock excited +Shock inhibited (second), CSShock inhibited +Shock excited (third) and CSShock inhibited +Shock inhibited (fourth) neurons. (C) Left: Average Z-scored activity of CSShock-excited neurons during the first vs. last five trials of fear conditioning. Right: Average AUC for the Z-scored activity during CSShock (0–10 s, mean ± s.e.m.). (D) Left: Average Z-scored activity of CSShock-inhibited neurons during the first vs. last five trials. Right: Average AUC for the Z-scored activity during CSShock. The orange area represents 10 s of CSShock. (E) Left: Average Z-scored activity of shock-excited neurons during the first five trials vs. the last five trials. Right: Average AUC for the Z-scored activity after shock delivery (0–10 s; t=5.246, P<0.0001). (F) Left: Average Z-scored activity of shock-inhibited neurons during the first five trials vs. the last five trials. A dotted darker red line indicates shock delivery. Right: Average AUC for the Z-scored activity after food delivery. The dark lines and shaded areas represent the mean and s.e.m. ****P< 0.0001. Detailed information about statistical results is provided in Supplementary file 1.
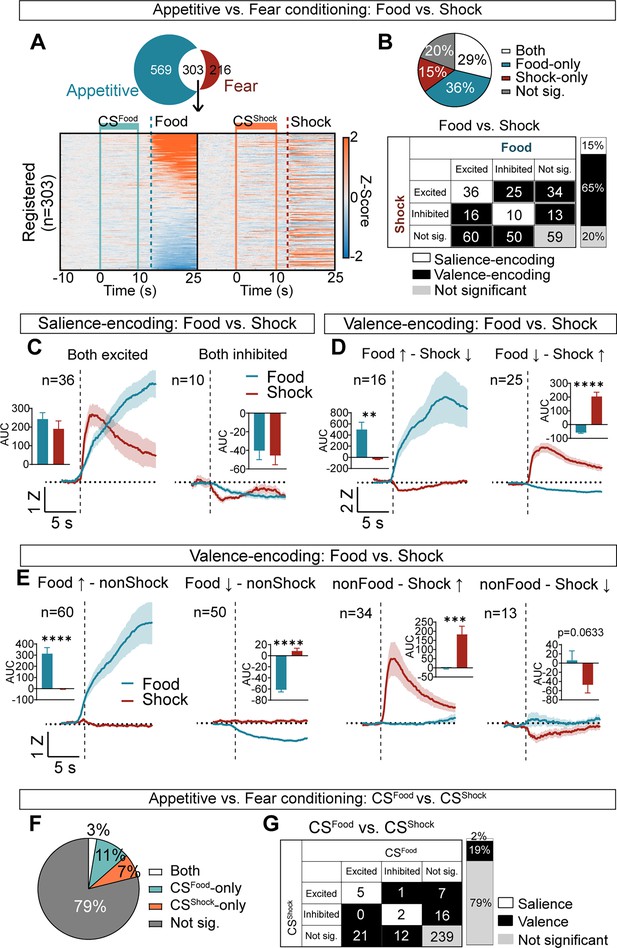
Salience and valence encoding in the CeA.
(A) Among 872 neurons from appetitive conditioning and 519 neurons from fear conditioning, 303 neurons were registered during both learning. Heat maps of these 303 neurons during –10 s to 25 s after CSFood onset from appetitive (left) and during –10 s to 25 s after CSShock onset from fear conditioning (right). All neurons are aligned to their activity to food. The same neuron is represented in the same row. Solid mint lines indicate CSFood, and a dotted darker mint line represents food delivery, solid orange lines indicate CSShock, and a dotted red line represents shock delivery. (B) Top: the proportion of significant neurons to food and shock (both; white), food-only (blue), shock-only (red), and not significant to both (grey). Bottom: detailed response types of all possible categories (excited, inhibited, not significant) for food vs. shock. White represents salience-encoding neurons showing the same response types to food and shock (n=46, 15%), and black represents valence-encoding neurons showing different response types to food and shock (n=198, 65%). Grey represents not significant neurons (n=59, 20%). (C) Salience-encoding neurons: the average Z-scored activity of neurons that were excited to both food and shock (n=36, left) and inhibited to both food and shock (n=10, right). Inserted bar graphs indicate average AUC of the Z-scored activity after food and shock delivery (0–10 s, mean ± s.e.m.). (D) Valence-encoding neurons: the average Z-scored activity of neurons that were excited to food but inhibited to shock (n=16, left) and inhibited to food but excited to shock (n=25, right). Average AUC of the Z-scored activity after food and shock delivery are shown in inserted bar graphs (0–10 s, mean ± s.e.m.). (E) The average Z-scored activity of neurons that were excited to food but not responsive to shock (n=60, first), neurons that were inhibited to food but not responsive to shock (n=50, second), neurons that were not responsive to food but excited to shock (n=34, third), and neurons that were not responsive to food but inhibited to shock (n=13, fourth). Inserted bar graphs indicate average AUC of the Z-scored activity after food and shock delivery (0–10 s, mean ± s.e.m.). The dark lines and shaded areas represent the mean and s.e.m. (F) Proportion of significant neurons to CSFood and CSShock (both; white), CSFood-only (mint), CSShock-only (orange), and not significant to both (grey). (G) Detailed response type of all possible categories (excited, inhibited, not significant) for CSFood vs. CSShock. White represents salience-encoding neurons showing the same response types to CSFood and CSShock (n=7, 2%), and black represents valence-encoding neurons showing different response types to CSFood and CSShock (n=57, 19%). Grey represents not significant neurons (n=239, 79%). *P< 0.05, ****P< 0.0001. Detailed information about statistical results is provided in Supplementary file 1.

Characteristics of CS and US responses in the CeA.
(A) Peak time comparisons of food-excited (blue) vs. shock-excited (red) neurons from food/shock delivery (t=21.76, P<0.0001). (B) Maximum Z-score comparisons of food-excited vs. shock-excited neurons (t=3.210, P=0.0014). Black bars represent the median. Circles indicate individual data. (C) Salience-encoding neurons: the average Z-scored activity of neurons that were excited to both CSFood (mint) and CSShock (orange, n=5, left) and inhibited to both CSFood and CSShock (n=2, right). (D) Valence-encoding neurons: the average Z-scored activity of neurons that were excited to CSFood but not significant to shock (n=21, first), inhibited to CSFood but not significant to shock (n=12, second), not significant to CSFood but excited to shock (n=7, third), and not significant to CSFood but inhibited to shock (n=716, fourth). Black bars indicate 10 s of CS. The dark lines and shaded areas represent the mean and s.e.m. (E) The averaged Z-scored activity of CeA neurons (n=925) during –10 s to 20 s after CSFood (left) and CSShock onset (right) from the baseline. Solid mint lines indicate CSFood and solid orange lines indicate CSShock. (F) Proportion of CSFood-responsive (left) and CSShock-responsive neurons (right). (G) The averaged freezing behavior during CSFood (mint) and CSShock (orange) during the baseline (mean ± s.e.m., n=10). (H–J) The same analyses as in A-C but with neurons from the post-test (n=788). **P< 0.01, ****P< 0.0001. Detailed information about statistical results is provided in Supplementary file 1.

Determining responsive neurons using the “theoretical” distribution of the Wilcoxon rank sum test, which assumes independence between timepoints.
(A) Each trial’s pre vs. post-stimulus activity was compared using Wilcoxon rank sum test. Neurons showing significant activity to the stimulus in more than 7 trials (appetitive; food or CSFood) or 3 trials (fear; shock or CSShock) were considered responsive neurons. (B) Histograms of the number of significant cells by their number of significant trials to food (left) and shock (right). (C) Histograms of the number of significant cells by their number of significant trials to CSFood (left) and CSShock (right). (D) The proportion of food-excited (orange), food-inhibited (blue), and not significant neurons (grey) from day 10 of appetitive learning (total 872 neurons) tested by Wilcoxon rank sum test. (E) Left: all trials (20 trials) averaged heat maps of food-excited neurons (top, n=273) and food-inhibited neurons (bottom, n=207). The dotted line indicates a food delivery. Middle: the average Z-scored activity of each response type (orange, food-excited; blue, food-inhibited; grey, not significant). The dark lines and shaded areas represent the mean and s.e.m. Right: average AUC for the Z-scored activity after food delivery (10 s, mean ± s.e.m.). (F, G) The same analyses as in D,E but with shock-responsive neurons from day 1 of aversive learning (total 519 neurons, shock-excited=165, shock-inhibited=105). (H) The proportion of significant neurons to food and shock (both; white), food-only (blue), shock-only (red), and not significant to both (grey) tested with Wilcoxon rank sum test. (I) Detailed response type of all possible categories (excited, inhibited, not significant) for food vs. shock. White represents salience-encoding neurons showing the same response types for food and shock (16%), and black represents valence-encoding neurons showing different response types for food and shock (62%). (J, K) The same analyses as in D,E with CSFood-responsive neurons from day 10 of appetitive learning (total 872 neurons, CSFood-excited=63, CSFood-inhibited=56). (L, M) The same analyses as in D,E with CSShock-responsive neurons from day 1 of aversive learning (total 519 neurons, CSShock-excited=53, CSShock-inhibited=65). (N, O) The same analyses as in H,I with CS-responsive neurons registered from day 10 of appetitive and day 1 of aversive learning (total 303 neurons). *P< 0.05, ****P< 0.0001. Detailed information about statistical results is provided in Supplementary file 1.

The order of valence conditioning did not affect the encoding of food, shock, and CSs in the CeA.
(A–D) Data of 165 neurons from appetitive → fear learning order. (A) The averaged Z-scored activity during –10 s to 25 s after CSFood onset from appetitive learning (left) and during –10 s to 25 s after CSShock onset from aversive learning (right). All neurons are aligned to their activity to food. The same neuron is represented in the same row. Solid mint lines indicate CSFood, a dotted darker mint line represents food delivery, solid orange lines indicate CSShock, and a dotted red line represents shock delivery. (B) Left: Proportion of salience-encoding, valence-encoding, and not significant neurons for food vs. shock. Right: Proportion of Food + Shock, Food-only, and Shock-only responsive neurons. (C) Left: Proportion of salience-encoding, valence-encoding, and not significant neurons for CSFood and CSShock. Right: Proportion of CSFood + CSShock, CSFood-only, and CSShock-only responsive neurons. (D) Top: Location of each neuron that was Food + Shock, Food-only, Shock-only, or not significantly responsive (Mouse1-5). Bottom: Location of each neuron that was CSFood + CSShock, CSFood-only, CSShock-only, or not significantly responsive. (E–H) The same analyses as in A-D but with 138 neurons from fear → appetitive learning order (Mouse6-10). (E) The averaged Z-scored activity during –10 s to 25 s after CSShock onset from fear learning (left) and during –10 s to 25 s after CSFood onset from appetitive (right). All neurons are aligned to their activity to shock. (I) Left: Average Z-scored activity of food-excited neurons from appetitive → fear vs. fear → appetitive. Right: Average AUC for the Z-scored activity after food delivery (0–10 s, mean ± s.e.m.). The number in the bar graph represents the number of neurons for each group. (J–L) The same analyses as in L with shock-excited/inhibited neurons (J), CSFood-excited/inhibited neurons (K), and CSShock-excited/inhibited neurons (L). A dotted darker mint line represents food delivery, a dotted red line represents shock delivery, a mint bar indicates CSFood, and an orange bar indicates CSShock. The dark lines and shaded areas represent the mean and s.e.m. Detailed information about statistical results is provided in Supplementary file 1.
Videos
CeA activity during the appetitive conditioning day 10.
CeA activity during the fear conditioning.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody | Anti-GFP (chicken polyclonal) | abcam | RRID:AB_300798 | (1:6000) |
| Antibody | Anti-chicken- AlexaFluor 488 (donkey polyclonal) | Jackson ImmunoResearch | RRID:AB_2340375 | (1:250) |
| Strain, strain background | AAV1-FLEX-GCaMP6m | University of Washington | N/A | |
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus) | B6J.129S6(FVB)-Slc32a1tm2(cre)Lowl/M warJ | Jackson laboratory | RRID:IMSR_JAX:028862 | 4 males and 6 females |
| Software, algorithms | MATLAB | The MathWorks, Inc | RRID:SCR_001622 | |
| Software, algorithms | R | The R Foundation | RRID:SCR_001905 | |
| Software, algorithms | Med-PC | Med Associates, Inc | RRID:SCR_012156 | |
| Software, algorithms | Graph Pad Software | GraphPad Software, Inc | RRID:SCR_002798 | |
| Software, algorithms | Inscopix data processing software | Inscopix | ||
| Software, algorithms | Inscopix data acquisition software | Inscopix | IDAS 1.5.4 | |
| Other | DAPI Fluoromount-G | SouthernBiotech | 0100–20 | DAPI staining |
| Other | Gradient-index (GRIN) lens | Inscopix | 1050–004413 | ProViewTM Integrated Lens 0.6mm x7.3mm |
| Other | Dental cement | Lang Dental | 1530BLK | Contemporary Ortho-Jet Powder BLACK Powder |
| Other | Dental cement | Lang Dental | 1504BLK | Contemporary Ortho-Jet Liquid |
| Other | Anchoring screws | Antrin Miniature Specialties, Inc | AMS 120/1 P-25 | Screws for anchoring a lens |
Additional files
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/101980/elife-101980-mdarchecklist1-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 1
Results of statistical analyses.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/101980/elife-101980-supp1-v1.docx